Reactor Power Uprate: Understanding And Meeting NRC Regulations
Table of Contents
A reactor power uprate involves modifying a nuclear power plant's operational parameters to increase its electricity generation capacity beyond its original design limits. This requires a thorough review and approval process by the NRC, a process fraught with technical, regulatory, and logistical challenges. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of reactor power uprates and ensuring successful compliance with NRC regulations.
Understanding the NRC's Regulatory Framework for Reactor Power Uprates
The NRC is responsible for overseeing the safety and security of all civilian nuclear power plants in the United States. Its primary objective is to protect public health and safety, and the environment, from the hazards associated with nuclear power generation. Power uprates fall under the purview of the NRC's stringent regulatory framework, primarily outlined in 10 CFR Part 50, which details the licensing requirements for nuclear power plants. Demonstrating unwavering compliance with these regulations and all applicable safety standards is paramount for securing approval for a power uprate.
-
Licensing Process: The licensing process for a power uprate involves a meticulous review of the proposed modifications, detailed safety analyses, and extensive documentation. This includes submitting a detailed application and undergoing rigorous NRC scrutiny.
-
Safety Analysis Reports (SARs): Comprehensive SARs, documenting the technical basis for the proposed uprate and demonstrating compliance with safety standards, are central to the licensing process. These reports require extensive technical analysis and must clearly address all potential safety concerns.
-
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Meticulous documentation and record-keeping throughout the entire process are critical. This includes maintaining detailed records of all analyses, test results, and modifications. This is crucial for demonstrating compliance to the NRC during the review process.
The Technical Aspects of a Successful Reactor Power Uprate
A successful reactor power uprate demands a thorough understanding and execution of various technical aspects. These include detailed evaluations and analyses to ensure the plant's safety and operational integrity at the increased power level.
-
Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis: This crucial analysis assesses the plant's ability to effectively manage heat and coolant flow at higher power levels. It's critical for ensuring the safety of the reactor core and preventing potential accidents.
-
Comprehensive Testing and Validation: Thorough testing and validation of upgraded systems and components are vital to verify their performance and reliability at the increased power levels. This process verifies that the modifications meet the required safety standards.
-
Key Technical Considerations:
- Stress Analysis and Structural Integrity: Evaluations must confirm that all plant structures can withstand the increased stresses associated with higher power levels.
- Fuel Performance Assessment: The analysis must demonstrate that the nuclear fuel can safely operate at the increased power levels without compromising its integrity.
- Instrumentation and Control Systems Review: Upgrading and verifying the instrumentation and control systems are crucial for ensuring reliable monitoring and control of the plant at higher power levels.
- Accident Scenario Analysis: A comprehensive probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is needed to evaluate the potential for accidents and the effectiveness of safety systems at the increased power levels.
Navigating the NRC Application and Approval Process
The application process for a reactor power uprate is intricate and demanding. Proactive communication and collaboration with the NRC are crucial for a smooth and efficient process.
-
Pre-Application Consultations: Early engagement with the NRC through pre-application consultations can help clarify requirements and streamline the application process.
-
Application Submission: The application must include a detailed description of the proposed uprate, along with comprehensive safety analysis reports and technical specifications, all meticulously documented.
-
NRC Review and Challenges: The NRC's review process is thorough and may involve requests for additional information. Addressing these requests promptly and comprehensively is crucial for timely approval.
-
Public Hearings and Stakeholder Involvement: Depending on the specifics of the proposed uprate, public hearings and stakeholder involvement might be required.
Managing Cost and Timelines for Reactor Power Uprate Projects
Reactor power uprates involve significant financial investments, encompassing engineering, licensing, and construction costs. Effective project management is crucial for minimizing delays and cost overruns.
- Budgeting and Cost Estimation: Developing a detailed budget and cost estimation is crucial for managing the financial aspects of the project.
- Project Scheduling: Creating a realistic project schedule, incorporating potential delays and unforeseen issues, is vital for on-time completion.
- Risk Management: Implementing robust risk management and mitigation strategies is essential for addressing potential challenges and preventing delays.
- Stakeholder Communication: Effective communication and collaboration among all stakeholders are critical for successful project execution.
Conclusion: Ensuring a Smooth Reactor Power Uprate with Effective NRC Compliance
Successfully completing a reactor power uprate requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and strict adherence to NRC regulations. The process is demanding, involving complex technical analyses, extensive documentation, and rigorous regulatory review. However, the benefits of increased energy production and improved grid reliability make a successful reactor power uprate a worthwhile endeavor. By prioritizing safety, complying with all NRC requirements, and employing effective project management, nuclear power plant operators can significantly enhance their capacity and contribute to a more secure and sustainable energy future. Contact us today to learn more about navigating the complexities of reactor power uprates and ensuring seamless compliance with NRC regulations. Let our expertise guide your successful reactor power uprate project.

Featured Posts
-
 A List Celebrity Seeks Invitation To Melissa Gorgas Exclusive New Jersey Beach House
May 02, 2025
A List Celebrity Seeks Invitation To Melissa Gorgas Exclusive New Jersey Beach House
May 02, 2025 -
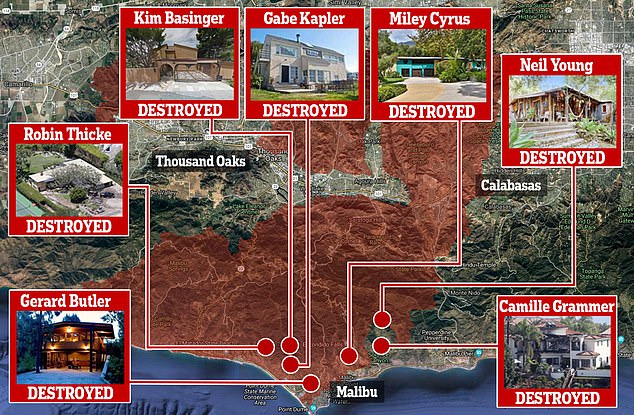 Homes Destroyed Celebrities Impacted By The Palisades Fire
May 02, 2025
Homes Destroyed Celebrities Impacted By The Palisades Fire
May 02, 2025 -
 Another Lawsuit Alleges Unfair Practices In Fortnites In Game Store
May 02, 2025
Another Lawsuit Alleges Unfair Practices In Fortnites In Game Store
May 02, 2025 -
 Open Ai Simplifies Voice Assistant Development
May 02, 2025
Open Ai Simplifies Voice Assistant Development
May 02, 2025 -
 Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias 2025 2028 Kritikes Kai Analysi
May 02, 2025
Stratigiki P Syxikis Ygeias 2025 2028 Kritikes Kai Analysi
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ukraine Receives Strong Backing From Switzerland Presidential Statement
May 02, 2025
Ukraine Receives Strong Backing From Switzerland Presidential Statement
May 02, 2025 -
 Laura Keller Biquini E Tantra Yoga Em Retiro Exclusivo
May 02, 2025
Laura Keller Biquini E Tantra Yoga Em Retiro Exclusivo
May 02, 2025 -
 Tantra Yoga E Biquini Laura Keller Em Retiro Espiritual
May 02, 2025
Tantra Yoga E Biquini Laura Keller Em Retiro Espiritual
May 02, 2025 -
 Laura Keller Aparicao De Biquini Em Retiro De Tantra Yoga
May 02, 2025
Laura Keller Aparicao De Biquini Em Retiro De Tantra Yoga
May 02, 2025 -
 Is That Christina Aguilera Fans Question Singers Altered Appearance
May 02, 2025
Is That Christina Aguilera Fans Question Singers Altered Appearance
May 02, 2025
