Rare UK Wildlife Facing Extinction Due To Increasing Wildfires
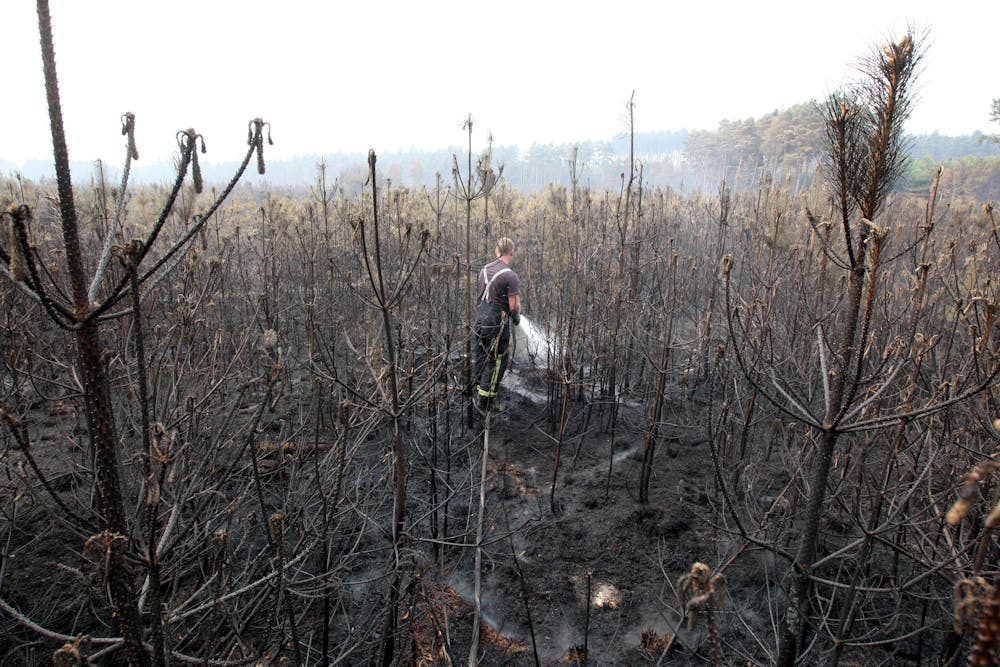

Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Habitats
Wildfires inflict catastrophic damage on the delicate ecosystems that support rare UK wildlife. The intense heat and flames obliterate vital habitats, leaving behind a scorched wasteland unsuitable for many species. The destruction extends across various habitats, including:
- Heathland: These fire-sensitive ecosystems, home to specialized plants and animals, are particularly vulnerable. Wildfires can decimate decades-old heather communities, destroying crucial nesting sites and food sources.
- Peat bogs: These unique wetlands store vast amounts of carbon and support a range of specialized flora and fauna. Wildfires release this stored carbon into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change, while simultaneously devastating the habitat itself.
- Woodland: While some woodlands are adapted to low-intensity fires, intense wildfires can completely destroy the tree canopy, understory, and ground vegetation, impacting everything from nesting birds to woodland invertebrates.
- Grasslands: While grasslands might seem resilient, intense wildfires can eradicate plant communities, leaving behind bare earth and severely impacting the insects, mammals, and birds that rely on them.
Beyond the immediate destruction, wildfires lead to:
- Loss of shelter and food sources: The destruction of vegetation leaves many animals without the protection and sustenance they need to survive.
- Fragmentation of habitats: Wildfires can create barriers between remaining habitat patches, isolating populations and hindering crucial breeding and genetic exchange. This isolation makes these populations more vulnerable to extinction.
For instance, the endangered Dartford warbler relies heavily on heathland for breeding. Wildfires destroy its nesting habitat, directly impacting its population numbers. [Insert citation linking to a relevant scientific study or conservation report here].
Species Most at Risk
Numerous rare UK wildlife species are disproportionately impacted by wildfires due to their specialized habitat requirements and often slow reproductive rates. Some of the most vulnerable include:
- Birds: The nightjar, with its ground-nesting habits, and the woodlark, reliant on specific grassland habitats, are highly susceptible. Loss of cover and food sources after a wildfire directly threatens their survival. (Include images of nightjar and woodlark here)
- Reptiles: The adder and slow worm are particularly vulnerable due to their reliance on specific microhabitats, such as sheltered areas within heathlands and grasslands. Wildfires eliminate these vital refuges. (Include images of adder and slow worm here)
- Invertebrates: Certain beetles and butterflies are specialized to specific plant communities within these habitats, making them exceptionally vulnerable to wildfire-induced habitat loss. The loss of their larval food plants can have cascading effects throughout the food web. (Include images of relevant invertebrates here)
Their vulnerability stems from various factors:
- Slow reproduction rates: Many of these species have low reproductive rates, making it difficult for their populations to recover after a significant wildfire event.
- Specific habitat needs: Their specialized habitat requirements mean they cannot easily adapt to the altered conditions left after a wildfire.
The Link Between Climate Change and Increasing Wildfires
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires in the UK are inextricably linked to climate change. Rising temperatures and prolonged periods of drought create ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. Drier vegetation acts as readily available fuel, accelerating the spread of blazes.
Climate change exacerbates the existing threats to rare UK wildlife by:
- Increasing the likelihood and severity of wildfires.
- Altering habitats, making them less suitable for many species.
- Creating more stressful conditions for already vulnerable populations.
Human activity also plays a significant role:
- Carelessly discarded cigarettes are a leading cause of wildfires.
- Arson accounts for a concerning percentage of wildfire incidents.
[Insert data and statistics here, e.g., "The number of wildfires in the UK has increased by X% over the past decade, according to [Source]."]
Conservation Efforts and Mitigation Strategies
Protecting rare UK wildlife from the devastating effects of wildfires requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing various conservation efforts and mitigation strategies:
- Controlled burns: In carefully managed situations, controlled burns can reduce fuel loads and prevent the spread of large, devastating wildfires.
- Improved fire detection and response systems: Early detection and rapid response are crucial in minimizing the impact of wildfires. Investing in improved technology and training is essential.
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about wildfire prevention, including responsible behaviour in fire-prone areas, is paramount.
- Habitat restoration projects: Restoring damaged habitats after wildfires is vital for the recovery of affected species.
- Community involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for long-term success.
Protecting our rare UK wildlife from the threat of wildfires requires a unified and proactive response. By supporting and strengthening these initiatives, we can work towards safeguarding our valuable natural heritage for future generations.
Conclusion
Wildfires pose a catastrophic threat to the survival of rare UK wildlife, decimating habitats and pushing vulnerable species towards extinction. The increasing frequency of these devastating events, largely driven by climate change and human activity, necessitates immediate and decisive action. We must work collectively to prevent wildfires, improve our response capabilities, and support habitat restoration efforts.
Protect our rare UK wildlife; learn how you can help prevent wildfires and support conservation initiatives today! [Include links to relevant organizations such as the RSPB, The Wildlife Trusts, etc.]

Featured Posts
-
 Elsbeth Season 2 Episode 18 Unexpected Death Stuns Viewers
May 13, 2025
Elsbeth Season 2 Episode 18 Unexpected Death Stuns Viewers
May 13, 2025 -
 Braunschweig Details Zum Amokalarm An Der Neuen Oberschule
May 13, 2025
Braunschweig Details Zum Amokalarm An Der Neuen Oberschule
May 13, 2025 -
 Close Contest Archbishop Bergan Edges Out Norfolk Catholic In District Final
May 13, 2025
Close Contest Archbishop Bergan Edges Out Norfolk Catholic In District Final
May 13, 2025 -
 Marvels Avengers Doomsday Using Ian Mc Kellen To Correct The Scarlet Witch And Quicksilver Origin Story
May 13, 2025
Marvels Avengers Doomsday Using Ian Mc Kellen To Correct The Scarlet Witch And Quicksilver Origin Story
May 13, 2025 -
 Liverpool Transfers Reds And Chelsea Vie For Lookman
May 13, 2025
Liverpool Transfers Reds And Chelsea Vie For Lookman
May 13, 2025
