Rare Earth Minerals: Fueling A New Cold War?
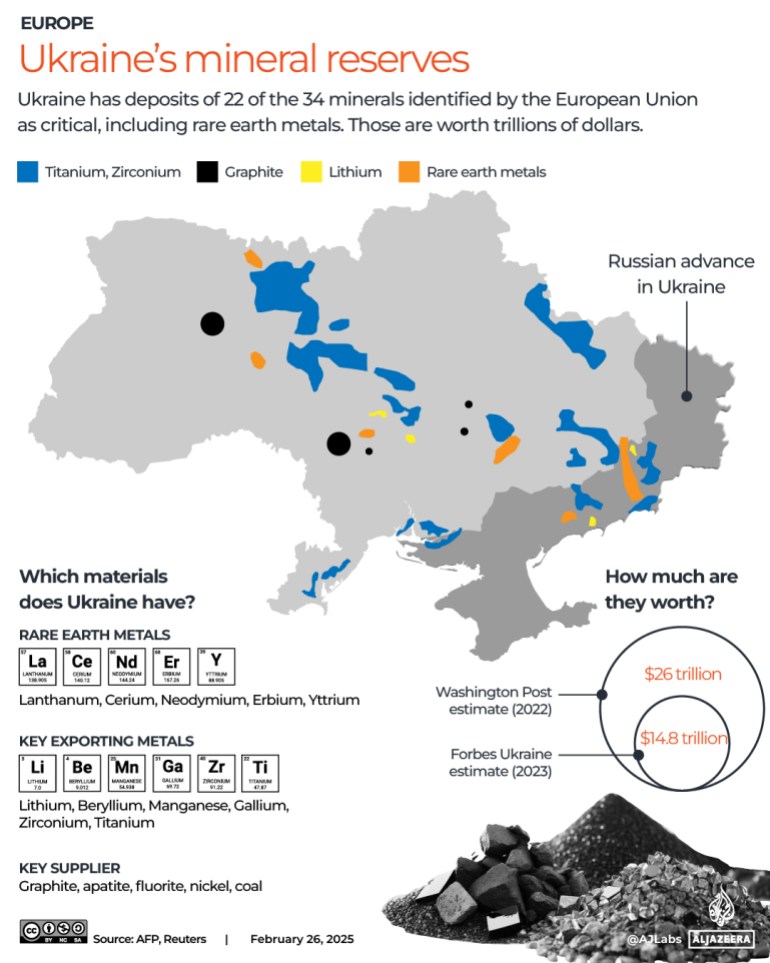
Table of Contents
2. The Critical Role of Rare Earth Minerals in Modern Technology
2.1 Electronics and Consumer Goods: Our dependence on rare earth minerals in everyday electronics is staggering. These minerals aren't just minor components; they are integral to the functionality of many devices.
- Neodymium: Used in powerful permanent magnets found in smartphones, headphones, and computer hard drives. Without neodymium magnets, many of our electronic devices would simply not function.
- Dysprosium: Another crucial element in powerful magnets, essential for electric motors and speakers. Its strength and resistance to demagnetization make it invaluable.
- Praseodymium: Contributes to the color and strength of glass used in smartphones and other screens. It's a vital ingredient in high-tech displays.
The sheer ubiquity of these minerals underscores our vulnerability to disruptions in the rare earth supply chain. Any scarcity directly impacts the production and price of countless consumer electronics.
2.2 Renewable Energy Technologies: The green energy revolution relies heavily on rare earth minerals. The transition to a sustainable future is inextricably linked to our ability to secure a stable supply.
- Wind Turbines: The powerful magnets in wind turbine generators rely heavily on neodymium and dysprosium, ensuring efficient energy conversion. A shortage of these minerals directly impacts wind power generation capacity.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): EV motors also depend heavily on rare earth magnets for their power and efficiency. As EV adoption accelerates, so does the demand for these crucial minerals.
- Solar Panels: While not as reliant as wind turbines and EVs, some specialized solar technologies still utilize rare earth minerals in their components.
Bottlenecks in rare earth mineral supply could severely hinder the global transition to renewable energy, delaying crucial progress in fighting climate change.
2.3 Military and Defense Applications: The strategic importance of rare earth minerals extends far beyond consumer electronics and green technologies. Their use in military and defense applications adds another layer of geopolitical complexity.
- Guided Missiles and Weapons Systems: Precision-guided munitions and other advanced weaponry rely on rare earth magnets for their accuracy and functionality.
- Radar and Sonar Systems: These systems depend on rare earth elements for their efficient operation and performance.
- Aerospace Technology: Rare earth minerals are vital in advanced aircraft and spacecraft components.
The military implications of rare earth mineral scarcity are profound, potentially impacting national security and strategic capabilities on a global scale. Control over these resources translates to significant military advantage.
3. Uneven Geographic Distribution and Geopolitical Implications
3.1 China's Dominance in Rare Earth Mining and Processing: China currently holds a near-monopoly in rare earth mineral production and processing, controlling a significant portion of the global supply chain.
- Market Share: China's dominance allows it to influence global prices and exert considerable economic leverage.
- Export Restrictions: The potential for China to restrict exports of rare earth minerals poses a significant threat to countries heavily reliant on these resources. This represents a significant geopolitical risk.
This situation creates a dangerous dependency, leaving many nations vulnerable to geopolitical pressures and potential trade conflicts.
3.2 Diversification Efforts and the Search for Alternatives: Recognizing the risks associated with China's dominance, many countries are actively pursuing diversification strategies.
- Investment in Mining and Processing: Several nations are investing heavily in exploring and developing their own rare earth mineral reserves.
- Recycling Initiatives: Increased focus is being placed on recycling rare earth elements from end-of-life products to reduce reliance on newly mined materials.
- Urban Mining: Exploring urban areas for recoverable rare earths from discarded electronics and other waste streams represents a significant potential source.
However, these efforts face significant challenges, including high extraction costs, environmental concerns, and the complexity of establishing new supply chains.
3.3 Trade Wars and Resource Nationalism: Competition for rare earth minerals could easily escalate into trade disputes and resource nationalism.
- Trade Restrictions: Countries may resort to imposing tariffs or other trade barriers to protect their access to rare earth resources.
- Resource Securitization: Nations may view control over rare earth minerals as a matter of national security, leading to heightened tensions and potential conflicts.
The potential for conflict underscores the urgent need for international cooperation and responsible resource management.
4. Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Practices
4.1 Environmental Impact of Rare Earth Mining: The extraction and processing of rare earth minerals can have significant environmental consequences.
- Water Pollution: Mining activities often result in water contamination with heavy metals and radioactive materials.
- Habitat Destruction: Mining operations can lead to deforestation and habitat loss, impacting biodiversity.
- Air Pollution: Processing rare earth minerals can release harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
Sustainable mining practices are crucial to mitigate these environmental impacts and ensure responsible resource management.
4.2 Recycling and Urban Mining: Recycling rare earth minerals from discarded electronics and other waste streams is essential for reducing environmental damage and ensuring resource security.
- Recycling Programs: Developing efficient and effective recycling programs is vital for recovering valuable rare earth elements.
- Urban Mining Technologies: Advances in technology are making urban mining—the extraction of valuable materials from urban waste— increasingly feasible.
These strategies are critical for a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to rare earth mineral management.
4.3 Technological Advancements and Substitution: Research and development efforts are focused on finding alternative materials and technologies that reduce reliance on rare earth minerals.
- Alternative Magnet Materials: Scientists are exploring alternative magnet materials that could reduce or eliminate the need for rare earth elements.
- Improved Recycling Technologies: Technological advancements are improving the efficiency and effectiveness of rare earth recycling.
These innovations could significantly reduce our dependence on these strategically important minerals.
5. Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Rare Earth Minerals
The strategic importance of rare earth minerals cannot be overstated. Their uneven distribution creates significant geopolitical risks, with the potential for escalating conflict and trade wars. China's near-monopoly presents a significant challenge, emphasizing the urgency of diversification efforts. Sustainable mining practices, robust recycling programs, and technological innovation are essential for mitigating environmental damage and ensuring equitable access to these vital resources. Understanding the complexities surrounding rare earth minerals is crucial to preventing a future crisis. Learn more and get involved today!

Featured Posts
-
 The Knicks Improved Defense A Key Factor In Thibodeaus Success
May 17, 2025
The Knicks Improved Defense A Key Factor In Thibodeaus Success
May 17, 2025 -
 Missed Call Controversy Nba Addresses Knicks Pistons Game Ending
May 17, 2025
Missed Call Controversy Nba Addresses Knicks Pistons Game Ending
May 17, 2025 -
 Mariners Athletics Series Whos On The Injured List March 27 30
May 17, 2025
Mariners Athletics Series Whos On The Injured List March 27 30
May 17, 2025 -
 Strengthening Ties Chinas Ambassador Discusses Potential Trade Deal With Canada
May 17, 2025
Strengthening Ties Chinas Ambassador Discusses Potential Trade Deal With Canada
May 17, 2025 -
 Navigating Japans Steep Bond Curve Strategies For Investors
May 17, 2025
Navigating Japans Steep Bond Curve Strategies For Investors
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Tkrym Astthnayy Llmkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt Fy Aljzayr
May 17, 2025
Tkrym Astthnayy Llmkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt Fy Aljzayr
May 17, 2025 -
 Sbry Abwshealt Tkrym Jzayry Yuthry Alsynma Alerbyt
May 17, 2025
Sbry Abwshealt Tkrym Jzayry Yuthry Alsynma Alerbyt
May 17, 2025 -
 Aljzayr Tukhld Asm Almkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt
May 17, 2025
Aljzayr Tukhld Asm Almkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt
May 17, 2025 -
 Aljzayr Tkrm Almkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt Tkrym Astthnayy Lfnan Mtmyz
May 17, 2025
Aljzayr Tkrm Almkhrj Allyby Sbry Abwshealt Tkrym Astthnayy Lfnan Mtmyz
May 17, 2025 -
 Securing A Stem Future Local Students Awarded Scholarships
May 17, 2025
Securing A Stem Future Local Students Awarded Scholarships
May 17, 2025
