Quantitative Easing: Greene Suggests A Revised BOE Strategy For Future Economic Crises
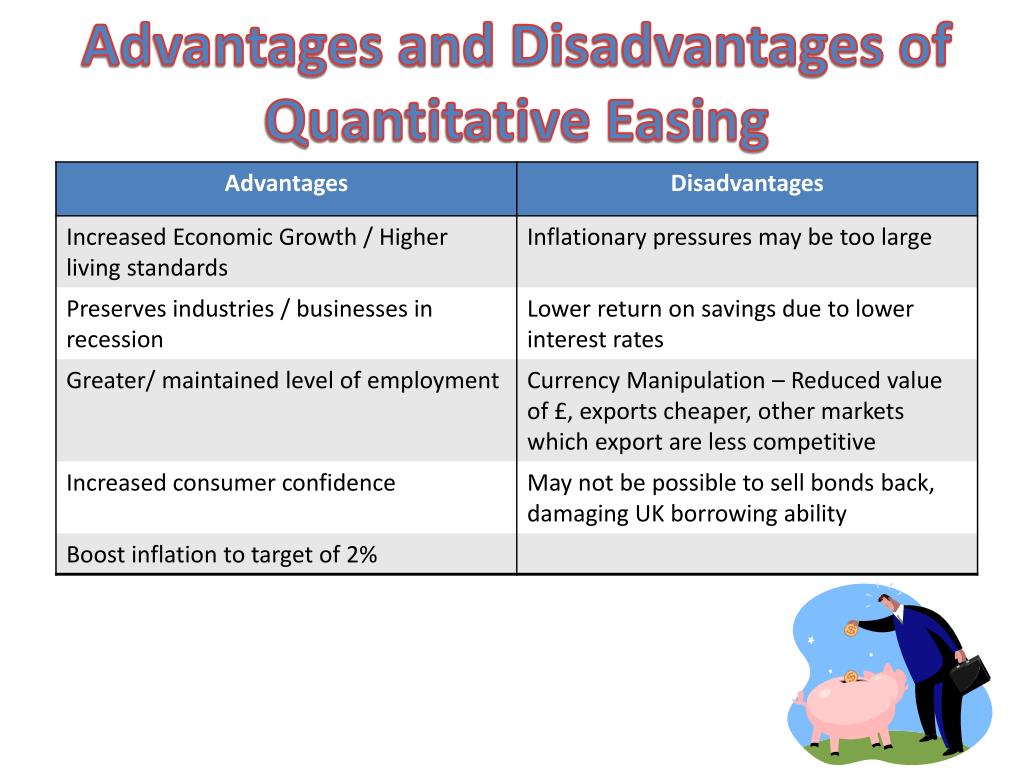
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Quantitative Easing and its Potential Pitfalls
Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy tool where a central bank, in this case the BOE, injects liquidity into the economy by purchasing assets, primarily government bonds, from commercial banks and other financial institutions. The aim is to lower long-term interest rates, increase money supply, and encourage lending and investment, thereby stimulating economic growth. However, QE is not without its critics. Willem Greene, a prominent economist, argues that the BOE's current QE strategy suffers from several significant flaws, hindering its effectiveness and potentially creating new problems. This article aims to dissect Greene's arguments and evaluate the potential implications of his proposed reforms for navigating future economic crises. Keywords throughout this analysis include: quantitative easing, QE, Bank of England, BOE, economic crisis, monetary policy, inflation, asset purchase, financial stability.
2. Main Points: A Critical Analysis of BOE's QE and Greene's Proposed Revisions
2.1. Greene's Critique of Current BOE QE Strategy
2.1.1. Ineffectiveness in Reaching Targeted Sectors: Greene argues that the BOE's current QE approach lacks sufficient targeting, failing to adequately support small businesses and sectors most vulnerable during economic downturns. The benefits have disproportionately flowed to large corporations with easier access to credit markets.
- Limited Impact on Small Businesses: QE primarily affects interest rates on government bonds, with limited direct impact on borrowing costs for smaller firms reliant on bank loans.
- Disproportionate Benefit to Large Corporations: Larger companies can access cheaper funding through bond markets, widening the existing inequality gap.
- Insufficient Stimulus for Real Economic Growth: While QE might inflate asset prices, it may not translate into meaningful increases in employment or investment in the real economy. A recent report from [cite relevant report] highlights this disparity.
2.1.2. Inflationary Risks and Asset Bubbles: Greene expresses serious concerns about the inflationary consequences of QE and the creation of asset bubbles. The injection of large sums of money into the financial system without corresponding increases in the supply of goods and services can fuel inflationary pressures.
- Contribution to Inflationary Pressures: QE-induced liquidity can lead to increased demand, driving up prices, especially in asset markets. The recent rise in [mention specific asset prices affected by QE] illustrates this point.
- Asset Bubbles: The increased liquidity can inflate asset prices beyond their fundamental value, creating unsustainable bubbles that can burst with devastating consequences, as seen in the housing market crash of [cite relevant historical example].
2.1.3. Equity and Distributional Concerns: Greene highlights the unequal distribution of benefits from QE, exacerbating existing socioeconomic inequalities.
- Wealth Concentration: The gains from QE disproportionately accrue to asset holders, widening the gap between the rich and the poor.
- Exacerbation of Inequality: While QE aims to boost overall economic activity, its benefits are not evenly distributed, potentially increasing social tensions.
2.2. Greene's Proposed Revisions for a More Effective QE Strategy
2.2.1. Targeted QE for Specific Sectors: Greene advocates for a shift towards targeted QE, focusing on direct support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and other vulnerable sectors.
- Direct Lending and Grants: Instead of solely purchasing government bonds, the BOE could directly lend to or provide grants to SMEs struggling to access credit.
- Sector-Specific Programs: Targeted programs could be designed to support specific industries hit hard during a crisis, such as tourism or manufacturing.
- Improved Allocation Efficiency: This approach could ensure that the stimulus reaches those who need it most, maximizing its effectiveness.
2.2.2. Enhanced Transparency and Accountability: Greene emphasizes the need for greater transparency and accountability in the BOE's QE operations.
- Clearer Communication of QE Goals and Mechanisms: The BOE should improve communication with the public regarding its QE decisions, explaining their rationale and potential consequences.
- Independent Audits and Oversight: Independent audits of the QE program should be conducted to ensure its effectiveness and prevent misuse.
- Public Reporting Requirements: Regular public reports detailing the impact of QE would improve accountability.
2.2.3. Integration of Fiscal Policy: Greene suggests coordinating monetary policy (QE) with fiscal policy to maximize their combined impact.
- Synergistic Policy Measures: Fiscal stimulus, such as infrastructure spending, can complement QE, increasing the overall effectiveness of economic support.
- Coordinated Policy Response: A coordinated approach between the Treasury and the BOE can ensure a more effective response to economic shocks.
- Examples of Coordinated Actions: For instance, the government could invest in infrastructure projects while the BOE uses QE to lower borrowing costs.
2.3. Potential Impact and Challenges of Greene's Revised Strategy
2.3.1. Economic Benefits and Risks: Implementing Greene’s proposals could lead to several benefits.
- Increased Economic Growth: Targeted QE could boost economic activity by channeling support to struggling businesses.
- Reduced Inequality: A more targeted approach could mitigate the wealth concentration effects of QE.
However, risks remain:
- Increased Inflation: Direct lending or grants could increase aggregate demand, potentially leading to higher inflation.
- Unintended Consequences: Targeting specific sectors might lead to unintended consequences, such as distorting market allocations.
2.3.2. Political and Practical Challenges: Implementing Greene's revised strategy faces various challenges.
- Political Opposition: Targeted QE might face political resistance due to concerns about government intervention in markets.
- Logistical Difficulties: Implementing targeted programs requires significant administrative capacity and expertise.
- Risk of Misallocation: Ensuring effective targeting and preventing corruption require robust oversight mechanisms.
3. Conclusion: The Future of Quantitative Easing and the Need for Reform
Willem Greene's critique of the BOE's current QE strategy highlights several key weaknesses: its limited effectiveness in reaching targeted sectors, its potential for creating inflation and asset bubbles, and its contribution to wealth inequality. His proposed revisions – focusing on targeted QE, enhanced transparency, and better coordination with fiscal policy – offer a compelling alternative for future economic crises. While the implementation faces political and practical challenges, the potential benefits of a more effective and equitable QE strategy are significant. Further research and open discussion are crucial to refine these proposals and develop robust, future-proof quantitative easing strategies that better serve the needs of the entire economy. The need to refine our understanding and application of quantitative easing is paramount to effectively navigate future economic downturns. Let's explore the potential of improved quantitative easing strategies to foster a more resilient and equitable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Yankees Cortes Throws Scoreless Gem Against Reds
Apr 23, 2025
Yankees Cortes Throws Scoreless Gem Against Reds
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Brewers Defeat Reds Nestor Cortes Pivotal Role
Apr 23, 2025
Brewers Defeat Reds Nestor Cortes Pivotal Role
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Analyse Complete Du Marche Boursier Bfm Bourse Du 24 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025
Analyse Complete Du Marche Boursier Bfm Bourse Du 24 Fevrier 2024
Apr 23, 2025 -
 Valeur Ajoutee D Infotel Un Succes Client Le 17 Fevrier
Apr 23, 2025
Valeur Ajoutee D Infotel Un Succes Client Le 17 Fevrier
Apr 23, 2025 -
 The China Factor Analyzing The Automotive Industrys Shifting Landscape
Apr 23, 2025
The China Factor Analyzing The Automotive Industrys Shifting Landscape
Apr 23, 2025
