Putin's War Economy: A Restructured Russia
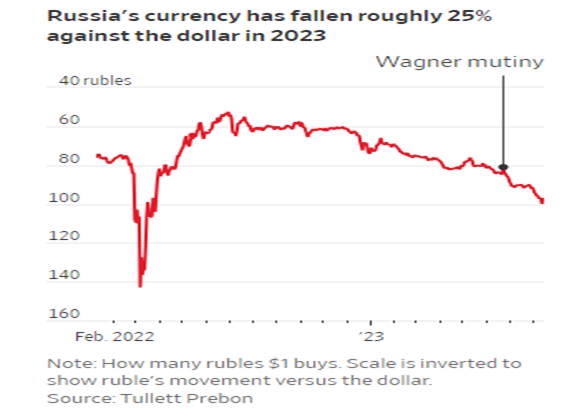
Table of Contents
Sanctions and Their Immediate Impact on the Russian Economy
The immediate aftermath of the sanctions imposed on Russia saw a dramatic shift in its economic landscape. The repercussions were felt across numerous sectors, leading to significant challenges for the Kremlin.
The Energy Sector Under Pressure
Russia's economy is heavily reliant on energy exports, primarily oil and natural gas. Sanctions targeting these exports aimed to cripple Russia's revenue streams and limit its ability to fund the war effort.
- Reduced export revenue: The sanctions significantly reduced Russia's oil and gas export revenue, impacting its budget and foreign currency reserves.
- Diversification of energy markets: Facing restrictions from Western markets, Russia has sought to redirect its energy exports towards Asia, particularly China and India. This shift, however, comes with its own set of challenges, including the need for new infrastructure and potential price fluctuations.
- Investment in renewable energy: While seemingly contradictory to its current reliance on fossil fuels, Russia has also shown some interest in developing alternative energy sources, although progress in this area has been slow.
- Impact on energy prices globally: The disruption to the global energy market caused by the sanctions and Russia's response has led to volatile energy prices worldwide, impacting consumers and businesses globally. This unintended consequence highlights the interconnectedness of the global economy and the far-reaching effects of Putin's war economy.
Financial Sector Instability and Capital Flight
The financial sector experienced immediate and severe pressure following the imposition of sanctions. The swift actions taken by Western nations aimed to isolate Russian banks from the global financial system.
- Ruble devaluation: The ruble experienced a significant devaluation against major currencies, fueling inflation and impacting the purchasing power of Russian citizens.
- Inflation: The combination of sanctions, reduced import availability, and ruble devaluation led to a sharp increase in inflation, further straining the Russian economy.
- Limitations on international transactions: Sanctions severely restricted Russian banks' access to the SWIFT international payment system, hindering international transactions and causing significant disruptions to trade.
- Reliance on domestic financing: Faced with limited access to international capital markets, Russia has increasingly relied on domestic financing, which, in turn, may lead to increased pressure on the domestic financial system.
Adaptation and Resilience Strategies in Putin's War Economy
Despite the severe challenges posed by sanctions, Russia has implemented several adaptation strategies to mitigate the impact on its economy and maintain some level of stability. These strategies, however, are not without limitations.
Import Substitution and Domestic Production
Facing restrictions on imports, Russia has focused on boosting domestic production and reducing its reliance on foreign goods. This involves a massive effort to rebuild its domestic industrial capacity and supply chains.
- Investment in domestic manufacturing: The Russian government has invested heavily in several domestic industries to increase their output and reduce import dependency.
- Technological limitations: Russia faces significant challenges in achieving self-sufficiency due to technological limitations and a lack of advanced manufacturing capabilities in many sectors.
- Quality control issues: The rapid expansion of domestic production has also raised concerns about quality control and the competitiveness of domestically produced goods in the global market.
- Increased consumer prices: The shift towards domestic production often results in higher prices for consumers as domestically produced goods may be more expensive or less efficient than imported alternatives.
Strengthening Ties with Allied Nations
To offset the impact of Western sanctions, Russia has strengthened its economic ties with countries like China, increasing trade and investment collaborations.
- Increased trade volume with China: Trade between Russia and China has increased significantly, with China becoming a major buyer of Russian energy resources and other commodities.
- Infrastructure projects: Russia and China are engaged in several large-scale infrastructure projects designed to further enhance their economic cooperation.
- Development of new trade routes (e.g., Silk Road): The expansion of the Silk Road Economic Belt initiative provides alternative trade routes, helping Russia reduce its dependence on traditional Western trade channels.
The Long-Term Outlook for Putin's War Economy
The long-term implications of Putin's war economy are complex and uncertain. The success of Russia's adaptation strategies will significantly influence its future economic trajectory.
Structural Changes and Economic Diversification
The sanctions-induced restructuring is likely to lead to profound structural changes in the Russian economy.
- Increased technological dependence: Russia's attempts to achieve self-sufficiency may lead to increased technological dependence on its allies, particularly China.
- Reduced economic integration with the West: The long-term impact of sanctions could be a further decoupling of the Russian economy from the Western world.
- Long-term economic stagnation or recovery potential: The future of Russia's economy hinges on several factors including the success of its import substitution strategy, the geopolitical situation, and the effectiveness of its economic reforms.
Social and Political Consequences
The economic hardship caused by sanctions and the war effort could have significant social and political consequences.
- Inflation, poverty, inequality: The economic downturn is likely to exacerbate existing inequalities, leading to increased poverty and social unrest.
- Public opinion on the war and economic situation: The ongoing war and its economic consequences could trigger significant shifts in public opinion, posing potential challenges to the Russian government's stability.
Conclusion
Putin's war economy represents a significant departure from Russia's previous economic trajectory. The sanctions imposed following the invasion of Ukraine have forced a radical restructuring, impacting energy exports, the financial sector, and domestic production. While Russia has demonstrated resilience through import substitution and closer ties with allied nations, the long-term outlook remains uncertain. The success of Putin's war economy will hinge on its ability to achieve sustainable economic diversification, mitigate social consequences, and navigate the complexities of a changing global landscape. Further research and analysis are needed to fully understand the evolving dynamics of Putin's War Economy and its long-term implications. To stay informed about the latest developments in this critical area, continue to follow expert analysis on Putin's War Economy and its evolving strategies.

Featured Posts
-
 Ajax In Gesprek Met Heitinga Over Trainerschap
May 29, 2025
Ajax In Gesprek Met Heitinga Over Trainerschap
May 29, 2025 -
 Vote Now Bay Area High School Athlete Of The Week
May 29, 2025
Vote Now Bay Area High School Athlete Of The Week
May 29, 2025 -
 Mstqbl Jwnathan Tah Hl Syleb Me Bayrn Mywnykh
May 29, 2025
Mstqbl Jwnathan Tah Hl Syleb Me Bayrn Mywnykh
May 29, 2025 -
 Next Starship Launch Date Space X And Texas Engine Tests
May 29, 2025
Next Starship Launch Date Space X And Texas Engine Tests
May 29, 2025 -
 Aragon 58 Centros Escolares Con Listas De Espera Soluciones Y Consejos
May 29, 2025
Aragon 58 Centros Escolares Con Listas De Espera Soluciones Y Consejos
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Trump And Musk A New Chapter Begins
May 31, 2025
Trump And Musk A New Chapter Begins
May 31, 2025 -
 Who Is The Overweight Friend In Donald Trumps Viral Story
May 31, 2025
Who Is The Overweight Friend In Donald Trumps Viral Story
May 31, 2025 -
 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanie Vrkhu Klasiraneto Mu
May 31, 2025
Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Vliyanie Vrkhu Klasiraneto Mu
May 31, 2025 -
 The Truth About Donald Trump And His Friend Debunking The Elon Musk Rumors
May 31, 2025
The Truth About Donald Trump And His Friend Debunking The Elon Musk Rumors
May 31, 2025 -
 15 To Uchastie Na Grigor Dimitrov Na Rolan Garos Kakvo Da Ochakvame
May 31, 2025
15 To Uchastie Na Grigor Dimitrov Na Rolan Garos Kakvo Da Ochakvame
May 31, 2025
