Ozempic For Everyone? Exploring GLP-1 Receptor Agonists And Their Expanding Use
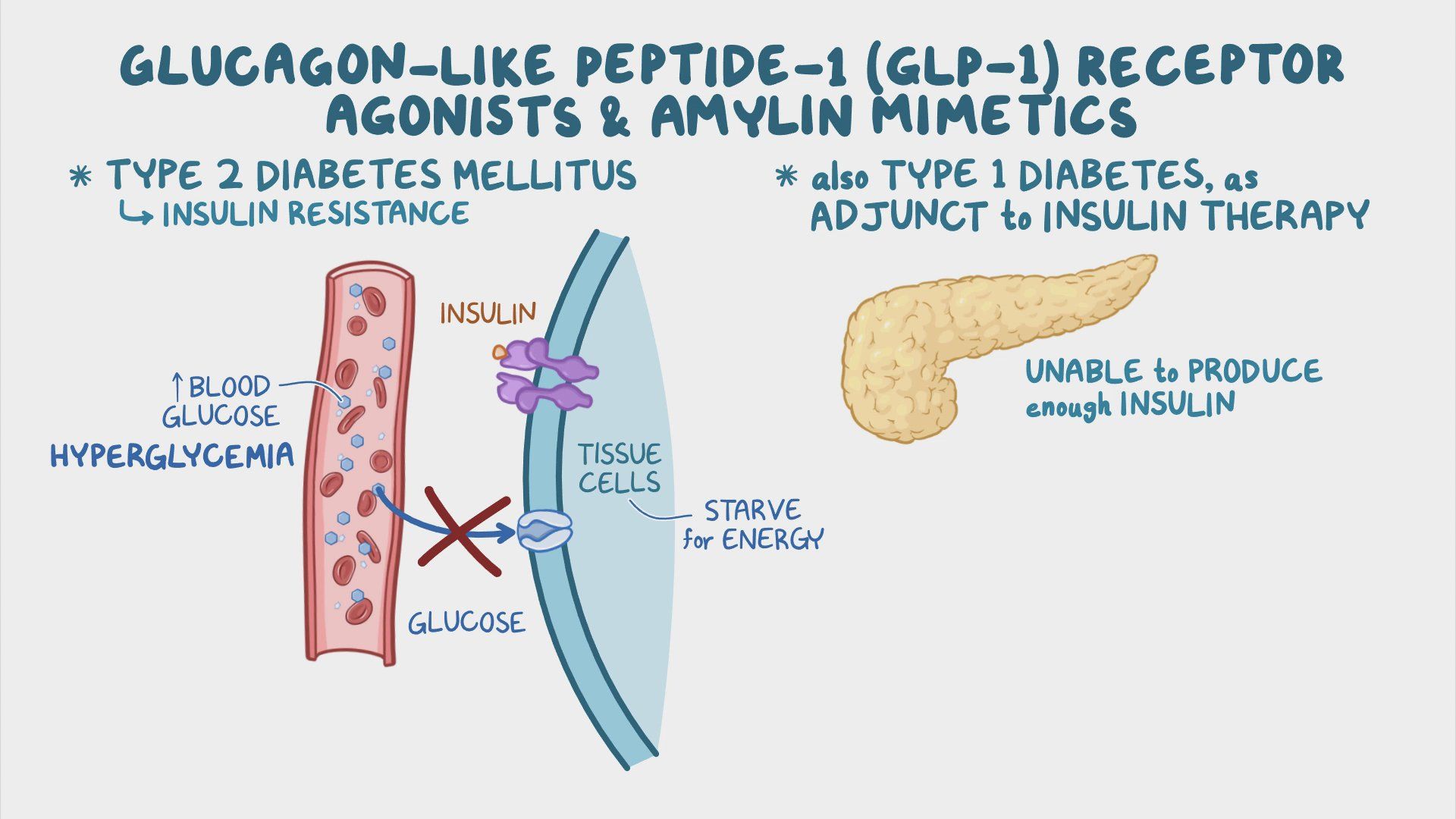
Table of Contents
Understanding GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a class of medications that mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a naturally occurring hormone in the body. They work primarily through three key mechanisms:
-
Mechanism of Action:
- Glucose-Dependent Insulin Secretion: GLP-1 agonists stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas, but only when blood sugar levels are elevated. This prevents hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), a common side effect of some other diabetes medications.
- Appetite Suppression: They act on the brain to reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness, leading to reduced food intake and weight loss.
- Slowed Gastric Emptying: This slows down the rate at which food leaves the stomach, contributing to increased satiety and improved blood sugar control.
-
Types of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Several GLP-1 receptor agonists are available, each with slightly different properties and administration methods:
- Semaglutide: Available in both injectable (Ozempic, Wegovy) and oral (Rybelsus) forms.
- Liraglutide: Available as an injectable medication (Victoza, Saxenda).
- Dulaglutide: Available as an injectable medication (Trulicity).
- Exenatide: Available as an injectable medication (Byetta, Bydureon).
-
Key Benefits: The benefits extend beyond blood sugar control:
- Significant Weight Loss: Many users experience substantial weight loss, a significant advantage for those with obesity or overweight conditions.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Effective in managing type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: Some studies suggest potential cardiovascular benefits, including reduced risk of cardiovascular events in certain patient populations.
Approved Uses of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
While initially approved for type 2 diabetes management, the applications of GLP-1 receptor agonists are expanding:
-
Type 2 Diabetes: GLP-1 receptor agonists are a cornerstone of type 2 diabetes treatment, often used in combination with other medications or as monotherapy. They help improve glycemic control and reduce the need for insulin.
-
Obesity and Weight Management: The FDA has approved several GLP-1 receptor agonists, such as Wegovy (semaglutide), for chronic weight management in adults with and without type 2 diabetes. This approval reflects the significant weight loss potential of these drugs.
-
Other Potential Applications: Research is ongoing to explore the potential of GLP-1 receptor agonists in other areas:
- Heart Failure: Studies suggest a potential role in improving outcomes in patients with heart failure. [Citation needed - Insert relevant scientific publication here]
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Preliminary evidence suggests benefits in reducing liver fat and improving liver function. [Citation needed - Insert relevant scientific publication here]
- Alzheimer's Disease: Some research explores a possible link between GLP-1 receptor agonists and neuroprotection in Alzheimer's disease. [Citation needed - Insert relevant scientific publication here]
The Expanding Use and Accessibility Debate
The increasing popularity of GLP-1 receptor agonists has led to several challenges:
-
Increased Demand and Supply Constraints: The high demand, fueled by both medical necessity and cosmetic uses, has resulted in shortages and difficulties accessing these medications.
-
Cost and Insurance Coverage: GLP-1 receptor agonists are expensive, posing a significant financial barrier for many patients. Insurance coverage varies widely, further limiting accessibility.
-
Ethical Considerations: The use of these medications primarily for weight loss in individuals without diabetes or other significant health conditions raises ethical questions about resource allocation and the potential for misuse.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
While generally well-tolerated, GLP-1 receptor agonists can cause side effects:
-
Common Side Effects: The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These are usually mild and transient.
-
Long-Term Effects: Long-term studies are still ongoing to fully assess the potential long-term consequences of GLP-1 receptor agonist use.
-
Patient Selection and Monitoring: Careful patient selection and close monitoring by healthcare professionals are crucial to minimize risks and ensure safe and effective use. Patients with a history of pancreatitis should exercise particular caution.
Conclusion
GLP-1 receptor agonists, including Ozempic and Wegovy, represent a significant advancement in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Their mechanisms of action offer multiple benefits, but their expanding use necessitates careful consideration of accessibility, cost, and potential side effects. While the promise of these medications is considerable, responsible prescribing and patient monitoring are crucial. Further research is needed to fully understand their long-term effects and to determine the appropriate scope of their application. If you are considering GLP-1 receptor agonists for diabetes management or weight loss, consult your doctor to discuss your individual needs and risk factors. They can help determine if GLP-1 receptor agonists are the right treatment option for you. Remember to discuss all potential benefits and risks of GLP-1 receptor agonists with your healthcare provider before starting any treatment.

Featured Posts
-
 Every Mlb Teams Starting Left Fielder Ranked For The 2025 Season
May 28, 2025
Every Mlb Teams Starting Left Fielder Ranked For The 2025 Season
May 28, 2025 -
 Falling Car Sales In Europe A Reflection Of Economic Troubles
May 28, 2025
Falling Car Sales In Europe A Reflection Of Economic Troubles
May 28, 2025 -
 Broadstairs Resident Wins 105 000 On The National Lottery Mauritius Trip Planned
May 28, 2025
Broadstairs Resident Wins 105 000 On The National Lottery Mauritius Trip Planned
May 28, 2025 -
 Fans React To Hugh Jackmans Possible Role In Blake Livelys Legal Case
May 28, 2025
Fans React To Hugh Jackmans Possible Role In Blake Livelys Legal Case
May 28, 2025 -
 Le Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go Vaut Il Son Prix De 967 50 E
May 28, 2025
Le Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go Vaut Il Son Prix De 967 50 E
May 28, 2025
