NATO Spending And The Global Increase In Military Expenditure
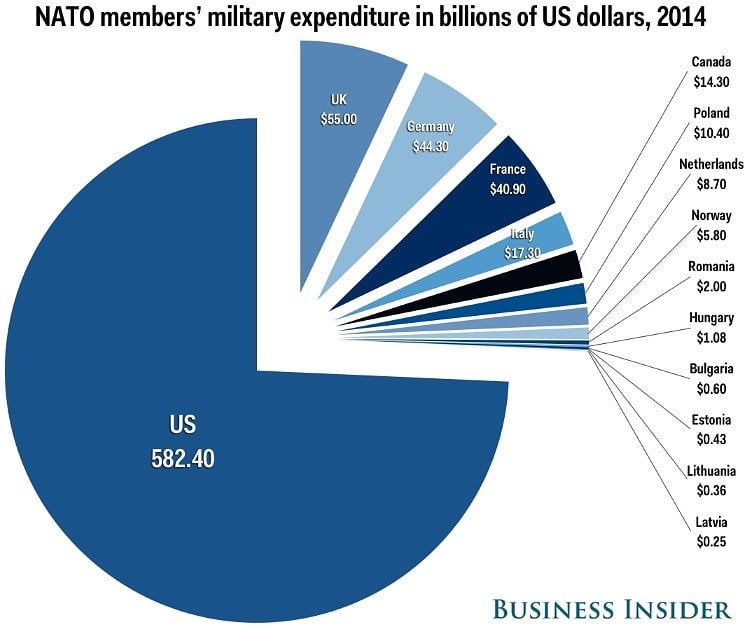
Table of Contents
NATO's Role in the Surge of Military Expenditure
Increased Defense Budgets within NATO Member States
Since 2014, and especially following Russia's annexation of Crimea, we've seen a significant increase in defense budgets among NATO members. Eastern European countries, in particular, have experienced substantial growth in their military spending. This is largely driven by a perceived threat from Russia and a need to modernize their armed forces to meet contemporary challenges.
- Poland: Poland has significantly boosted its military budget, focusing on acquiring advanced weaponry and strengthening its land forces.
- Romania: Romania has also increased its defense spending, modernizing its air force and investing in cyber security capabilities.
- Baltic States (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania): These nations have made considerable investments in defense to deter potential aggression and enhance their national security.
These increases reflect a recognition of the evolving security environment and a commitment to collective defense within the NATO alliance. The rationale behind these increases is multifaceted, encompassing:
- Deterrence: Increased military spending aims to deter potential aggressors and protect national sovereignty.
- Modernization: Many NATO members are modernizing their armed forces with advanced technologies to maintain a credible defense posture.
- Alliance Solidarity: The increased spending reflects a stronger commitment to collective security within the NATO framework.
NATO's Collective Defense Spending Targets
NATO members have adopted a target of spending 2% of their Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on defense. While some nations have exceeded this target, many others lag behind. Achieving this target is crucial for maintaining collective security and ensuring the alliance's ability to respond effectively to threats. Failure to meet this target can undermine the alliance’s credibility and potentially leave some members vulnerable.
- Meeting the 2% Target: Countries like the United States and Greece exceed the 2% GDP target.
- Falling Short: Several European nations are still below the 2% threshold, highlighting the ongoing challenge of meeting the collective defense goals.
The implications of meeting or failing to meet this target are significant, impacting:
- Military Capabilities: Adequate funding is necessary to maintain advanced weaponry, training, and personnel.
- Interoperability: Harmonized spending levels enhance interoperability and seamless cooperation between member states' armed forces.
- Political Signaling: Meeting the target demonstrates a commitment to collective security and strengthens the alliance’s deterrence capabilities.
Global Factors Influencing Military Expenditure
The Impact of Geopolitical Instability
Regional conflicts, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine and protracted conflicts in the Middle East, have significantly contributed to the global rise in military expenditure. Rising tensions between major global powers fuel an arms race, further escalating the cost. Terrorism and asymmetric warfare also contribute to increased defense spending, prompting nations to invest in counter-terrorism strategies and intelligence gathering.
- Ukraine Conflict: The war in Ukraine has drastically increased military spending across Europe, as countries bolster their defenses in response to Russian aggression.
- Middle East Conflicts: Ongoing conflicts in the Middle East continue to drive military expenditure in the region and among global powers involved.
- Cyber Warfare: The growing threat of cyberattacks has prompted increased investment in cybersecurity defenses.
Technological Advancements and Modernization
The development of advanced weaponry, cyber warfare capabilities, and space-based technologies significantly impacts military budgets. Research and development in the defense sector is expensive, requiring substantial investment to maintain a technological edge. This technological competition fuels an ongoing increase in military expenditure, creating a cycle of investment and counter-investment.
- Advanced Fighter Jets: The cost of developing and procuring advanced fighter jets like the F-35 contributes significantly to military expenditure.
- Cybersecurity: Investing in cybersecurity infrastructure and personnel to combat cyber threats represents a major cost for many nations.
- Space-Based Assets: Developing and maintaining space-based surveillance and communication systems represents a significant financial commitment.
Economic and Social Consequences of Increased Military Expenditure
Opportunity Costs of Military Spending
High levels of military expenditure create opportunity costs, diverting resources from essential sectors such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This can lead to reduced economic growth, impacting a nation's overall development and prosperity. Prioritizing defense over other societal needs can have significant social implications.
- Reduced Investment in Education: High military spending can mean less investment in education, hindering human capital development.
- Healthcare Cuts: Military spending may lead to cuts in healthcare budgets, negatively impacting public health.
- Infrastructure Neglect: Limited funds may be available for infrastructure development, hindering economic growth and societal progress.
The Arms Trade and its Global Impact
The international arms trade plays a significant role in fueling global military expenditure. Arms exports can destabilize regions and exacerbate conflicts, leading to a cycle of violence and increased military spending. The ethical considerations of arms sales, especially to countries with poor human rights records, are increasingly debated.
- Major Arms Exporters: Countries like the United States, Russia, and China are major players in the global arms trade.
- Regional Instability: Arms sales to conflict zones can prolong violence and increase the demand for weaponry.
- Ethical Concerns: The sale of weapons to authoritarian regimes raises ethical concerns regarding human rights and international stability.
Conclusion
The global increase in military expenditure is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. NATO spending plays a significant role in this trend, driven by geopolitical instability, technological advancements, and the commitment to collective defense. This increased spending has substantial economic and social implications, diverting resources from vital sectors and raising ethical concerns related to the arms trade. Understanding the complexities of military expenditure, its drivers, and its consequences is crucial. Continue your research to gain a more comprehensive view of this critical issue, exploring resources from organizations like the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) and the NATO website.

Featured Posts
-
 Enexis Wachtlijst Van Meer Dan 1000 Limburgse Ondernemers
May 01, 2025
Enexis Wachtlijst Van Meer Dan 1000 Limburgse Ondernemers
May 01, 2025 -
 Windstar Cruises A Foodies Voyage
May 01, 2025
Windstar Cruises A Foodies Voyage
May 01, 2025 -
 The Ukraine Wars Impact On Global Military Spending And European Defense Budgets
May 01, 2025
The Ukraine Wars Impact On Global Military Spending And European Defense Budgets
May 01, 2025 -
 Key Contributions From Judge And Goldschmidt Secure Yankees Win
May 01, 2025
Key Contributions From Judge And Goldschmidt Secure Yankees Win
May 01, 2025 -
 Offensive Struggles Doom Skenes Despite Strong Pitching
May 01, 2025
Offensive Struggles Doom Skenes Despite Strong Pitching
May 01, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Inadequate Police Accountability Review Sparks Outrage Among Campaigners
May 01, 2025
Inadequate Police Accountability Review Sparks Outrage Among Campaigners
May 01, 2025 -
 Police Accountability Review Campaigners Voice Deep Concerns
May 01, 2025
Police Accountability Review Campaigners Voice Deep Concerns
May 01, 2025 -
 Campaigners Raise Serious Concerns About Police Accountability Review
May 01, 2025
Campaigners Raise Serious Concerns About Police Accountability Review
May 01, 2025 -
 Deep Concern Expressed By Campaigners Regarding Police Accountability Review
May 01, 2025
Deep Concern Expressed By Campaigners Regarding Police Accountability Review
May 01, 2025 -
 Lack Of Police Accountability Campaigners Express Deep Worry
May 01, 2025
Lack Of Police Accountability Campaigners Express Deep Worry
May 01, 2025
