Measles Elimination In Canada: A Looming Threat
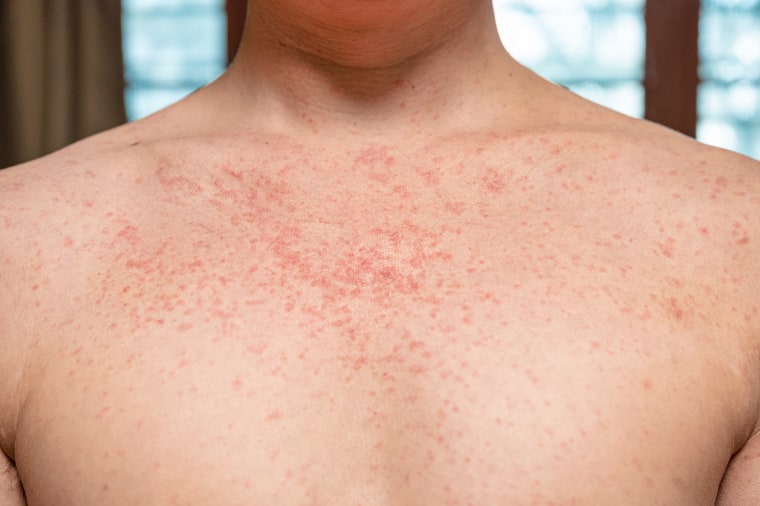
Table of Contents
H2: Declining Vaccination Rates: A Primary Concern
The primary driver behind the potential return of measles is the worrying decline in vaccination rates across Canada. This decrease in MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccination uptake poses a significant risk to public health.
H3: Factors Contributing to Vaccine Hesitancy:
Several factors contribute to vaccine hesitancy, hindering the progress towards Measles Elimination in Canada.
- Misinformation and Anti-vaccine Sentiment: The spread of misinformation through social media and online platforms fuels distrust in vaccines. False claims linking vaccines to autism and other health problems continue to circulate despite overwhelming scientific evidence to the contrary.
- Parental Concerns about Vaccine Safety: Despite extensive research demonstrating the safety and efficacy of vaccines, some parents remain concerned about potential side effects. These concerns often stem from a lack of understanding of the scientific process and risk assessment.
- Access to Healthcare and Vaccine Affordability: Limited access to healthcare services, particularly in remote or underserved communities, can create barriers to vaccination. While vaccines are largely publicly funded in Canada, affordability can still be a concern for some families.
Specific Examples: Recent studies show lower vaccination rates in certain provinces, particularly among specific demographic groups. For example, pockets of lower vaccination uptake have been observed in communities with higher concentrations of immigrant populations due to language barriers or cultural beliefs about vaccination. These variations highlight the need for targeted public health interventions.
H3: The Consequences of Low Vaccination Rates:
Low vaccination rates directly undermine herd immunity, a critical factor in preventing measles outbreaks.
- Breakdown of Herd Immunity: Herd immunity protects even those who cannot be vaccinated (infants, immunocompromised individuals) by preventing the virus from spreading widely. When vaccination rates drop below a critical threshold, the risk of outbreaks increases dramatically.
- Increased Vulnerability of Infants and Immunocompromised Individuals: Infants under six months old are too young to receive the MMR vaccine, making them especially vulnerable. Similarly, individuals with weakened immune systems are at high risk of severe complications.
- Economic Burden: Measles outbreaks impose a significant economic burden on healthcare systems, including costs associated with hospitalization, treatment, and lost productivity.
Potential Consequences: Measles can lead to serious complications, including: * Pneumonia * Encephalitis (brain inflammation) * Otitis media (middle ear infection) * Diarrhea * Death
H2: The Threat of Measles Outbreaks and Their Impact
The consequences of declining vaccination rates are already evident in the form of recent measles outbreaks across Canada.
H3: Recent Outbreaks and their Geographic Distribution:
Several measles outbreaks have been reported in Canada in recent years, demonstrating the vulnerability of communities with lower vaccination rates. These outbreaks highlight the challenges in containing the highly contagious virus, particularly in areas with significant international travel. [Insert map showing geographic spread of measles cases if available]. The outbreaks often originate from imported cases, emphasizing the global nature of this health threat.
H3: The Severity of Measles Infection:
Measles is a highly contagious virus transmitted through respiratory droplets. Infection can lead to serious health consequences.
- Symptoms: Symptoms typically include fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic rash.
- Complications: Severe complications can include pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death, particularly in young children and immunocompromised individuals. Long-term effects can include hearing loss and developmental disabilities.
- Contagiousness: Measles is incredibly contagious, with a high transmission rate. A single infected individual can easily spread the virus to many others.
Specific Symptoms and Complications: * High fever * Koplik's spots (small white spots inside the mouth) * Severe cough * Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
H2: Strengthening Vaccination Programs and Public Health Initiatives
Addressing the threat of measles requires a multifaceted approach that strengthens vaccination programs and public health initiatives.
H3: Improving Vaccine Access and Affordability:
Increased access to vaccines is crucial for boosting vaccination rates.
- Government Initiatives: Increased funding for vaccination programs, including targeted outreach to underserved communities, is vital.
- Addressing Vaccine Safety Concerns: Transparent communication and educational resources, developed by trusted healthcare professionals and public health agencies, are essential to counter misinformation and address parental concerns.
- Role of Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers play a critical role in educating patients, addressing their concerns, and promoting vaccination.
H3: Combating Misinformation and Promoting Vaccine Confidence:
Combating misinformation and building vaccine confidence requires a multi-pronged strategy.
- Evidence-Based Information: Public health officials must actively disseminate accurate and evidence-based information through various channels, including social media, traditional media, and community events.
- Social Media Engagement: Utilizing social media platforms to counter misinformation and engage directly with individuals who express vaccine hesitancy.
- Community Leaders and Influencers: Involving trusted community leaders, faith-based organizations, and influencers to promote vaccination can significantly enhance the reach and impact of public health messages.
Strategies to Combat Misinformation: * Fact-checking websites * Public service announcements * Social media campaigns
3. Conclusion:
The resurgence of measles in Canada poses a significant threat to public health. Declining vaccination rates, coupled with the highly contagious nature of the virus and the spread of misinformation, create a perfect storm for outbreaks. Achieving and maintaining Measles Elimination in Canada requires a collective effort to increase vaccination coverage, counter vaccine hesitancy, and enhance access to healthcare services. Protecting our communities from the threat of measles requires a collective effort. Let's work together towards Measles Elimination in Canada by prioritizing vaccination. Get vaccinated, encourage your family and friends to get vaccinated, and support public health initiatives aimed at increasing vaccination rates and promoting evidence-based information.

Featured Posts
-
 Kawasaki W175 Vs Honda St 125 Dax Mana Yang Lebih Baik
May 30, 2025
Kawasaki W175 Vs Honda St 125 Dax Mana Yang Lebih Baik
May 30, 2025 -
 Pacific Rim 2 What Could Have Been Exploring Del Toros Vision
May 30, 2025
Pacific Rim 2 What Could Have Been Exploring Del Toros Vision
May 30, 2025 -
 Emma Raducanu Cruises To Miami Open Round Of 16
May 30, 2025
Emma Raducanu Cruises To Miami Open Round Of 16
May 30, 2025 -
 Fwz Tarykhy Llmksyk Fy Jyrw Iytalya Qst Njah Dyl Twrw
May 30, 2025
Fwz Tarykhy Llmksyk Fy Jyrw Iytalya Qst Njah Dyl Twrw
May 30, 2025 -
 From Dental School To Jacob Alons Career Story
May 30, 2025
From Dental School To Jacob Alons Career Story
May 30, 2025
