Malaysia Faces US Solar Import Duties: Impact On The Industry
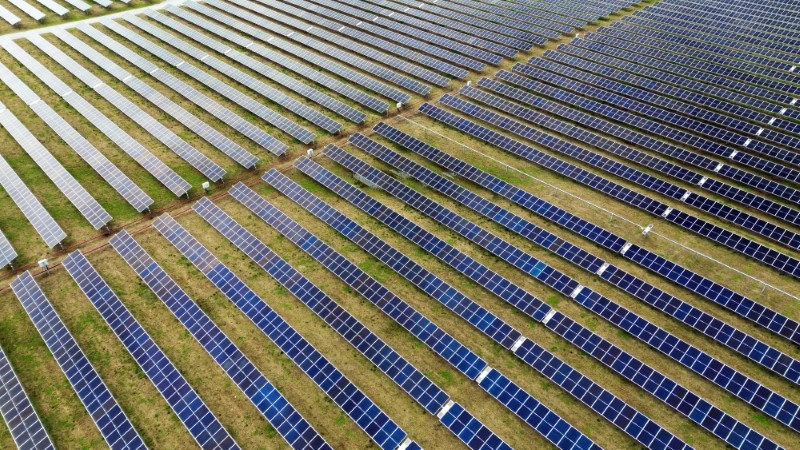

Table of Contents
Disruption to Malaysia's Solar Supply Chain
The imposition of US solar import duties creates a major disruption to Malaysia's solar supply chain. This is largely due to Malaysia's reliance on imported solar panels and components, many of which originate from or transit through the US. The increased costs and potential delays significantly impact the viability and timelines of numerous solar energy projects.
-
Increased costs of solar panels due to tariffs, impacting project viability: The added tariffs directly translate to higher costs for Malaysian businesses importing solar panels. This makes projects less financially attractive, potentially leading to delays or cancellations. The rise in prices affects both large-scale solar farms and smaller residential installations.
-
Potential delays in solar energy project completion due to supply chain bottlenecks: Tariffs can cause bottlenecks in the supply chain, leading to delays in the delivery of essential components. This not only pushes back project completion dates but also increases overall project costs due to extended timelines.
-
Reduced competitiveness of Malaysian solar companies in regional markets: Higher input costs make Malaysian solar companies less competitive compared to their counterparts in countries unaffected by the US tariffs. This impacts their ability to bid for and win projects in the regional market.
-
Exploration of alternative sourcing options, potentially impacting quality and reliability: The search for alternative suppliers may compromise quality and reliability. Finding suitable alternatives that meet the same standards and provide consistent supply can be challenging and time-consuming.
-
Need for diversification of supply chains to reduce reliance on US-sourced components: This crisis highlights the vulnerability of relying heavily on a single source for crucial components. Diversifying supply chains is crucial to mitigating future risks. This includes exploring partnerships with manufacturers in other regions like Southeast Asia and China.
Economic Impact on Malaysian Businesses
The economic consequences of these US solar import duties on Malaysia are considerable and far-reaching. The impact extends beyond the immediate solar energy sector, affecting related industries and the broader economy.
-
Reduced profitability for Malaysian solar businesses due to higher input costs: The increased cost of solar panels directly reduces the profitability of Malaysian solar businesses, impacting their margins and long-term sustainability.
-
Potential job losses in the solar energy sector: Reduced profitability may force companies to downsize, leading to job losses across various roles within the industry, from installation crews to engineers and project managers.
-
Increased prices for consumers purchasing solar panels and related services: The higher costs are eventually passed on to consumers, making solar energy adoption less affordable and potentially hindering the growth of the sector.
-
Impact on foreign direct investment in Malaysia's solar energy sector: The increased uncertainty and higher costs may deter foreign investors from committing to projects in Malaysia, slowing down the growth of the renewable energy sector.
-
Potential ripple effects across related industries: The impact extends to related industries, such as those involved in construction, finance, and logistics, affecting their revenue and employment prospects.
Government Response and Policy Implications
The Malaysian government has a critical role to play in mitigating the negative impacts of these tariffs. Effective policy responses are crucial to protect the domestic solar industry and promote the country's renewable energy goals.
-
Government's role in negotiating trade agreements to lessen the impact of tariffs: Negotiating trade agreements or seeking exemptions from the US tariffs are essential to lessening the burden on Malaysian businesses.
-
Potential for government subsidies or tax incentives to support the solar industry: Providing subsidies or tax incentives can help offset the increased costs for Malaysian solar businesses, making projects more financially viable.
-
Review and adjustment of existing renewable energy policies in light of the new challenges: Existing renewable energy policies may need revision to account for the new economic realities and ensure the continued growth of the sector.
-
Exploration of alternative energy sources to lessen dependence on solar imports: Diversifying energy sources to reduce reliance on imported solar panels can enhance energy security.
-
Strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities for solar components: Investing in domestic solar component manufacturing can reduce reliance on imports and boost local economic growth.
Opportunities for Growth Amidst Challenges
While the situation presents considerable challenges, it also creates opportunities for growth and innovation within the Malaysian solar energy industry.
-
Potential boost to domestic solar panel manufacturing in Malaysia: The higher costs of imports could incentivize investment in domestic solar panel manufacturing, creating jobs and reducing reliance on foreign suppliers.
-
Increased focus on research and development in solar technology: This crisis could spur innovation in solar technology, potentially leading to the development of more cost-effective and efficient solar panels.
-
Opportunities for strategic partnerships with other countries to secure solar panel supplies: Developing strategic partnerships with countries not affected by the US tariffs can ensure a stable supply of solar panels.
-
Exploring innovative financing models to support solar energy projects: Innovative financing models, such as crowdfunding or green bonds, could help attract investment in solar projects despite the increased costs.
Conclusion
The imposition of US solar import duties poses a significant challenge to Malaysia's solar energy industry, potentially disrupting supply chains, impacting businesses, and affecting the nation's renewable energy goals. However, the crisis also presents opportunities for growth through increased domestic manufacturing, technological innovation, and strategic policy adjustments. Understanding the complexities of Malaysia's response to US solar import duties is crucial. Stay informed about the evolving situation and advocate for policies that support the growth of the Malaysian solar energy industry and its contribution to a sustainable future. Learn more about the impacts of Malaysia's US solar import duties and the ways forward.

Featured Posts
-
 More Accurate Gene Repair Advances In Crispr Technology
May 30, 2025
More Accurate Gene Repair Advances In Crispr Technology
May 30, 2025 -
 Mealm Alastqlal Fy Alwtn Alerby
May 30, 2025
Mealm Alastqlal Fy Alwtn Alerby
May 30, 2025 -
 Shock For Glastonbury Attendees Huge Act Pulled From Festival Lineup
May 30, 2025
Shock For Glastonbury Attendees Huge Act Pulled From Festival Lineup
May 30, 2025 -
 Cts Eventim Q1 Results Significant Increase In Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Q1 Results Significant Increase In Adjusted Ebitda And Revenue
May 30, 2025 -
 The Untold Story Daniel Cormiers Confrontation With Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025
The Untold Story Daniel Cormiers Confrontation With Jon Jones Publicist
May 30, 2025
