Justice Department's Decision: The Impact Of Ending School Desegregation Orders
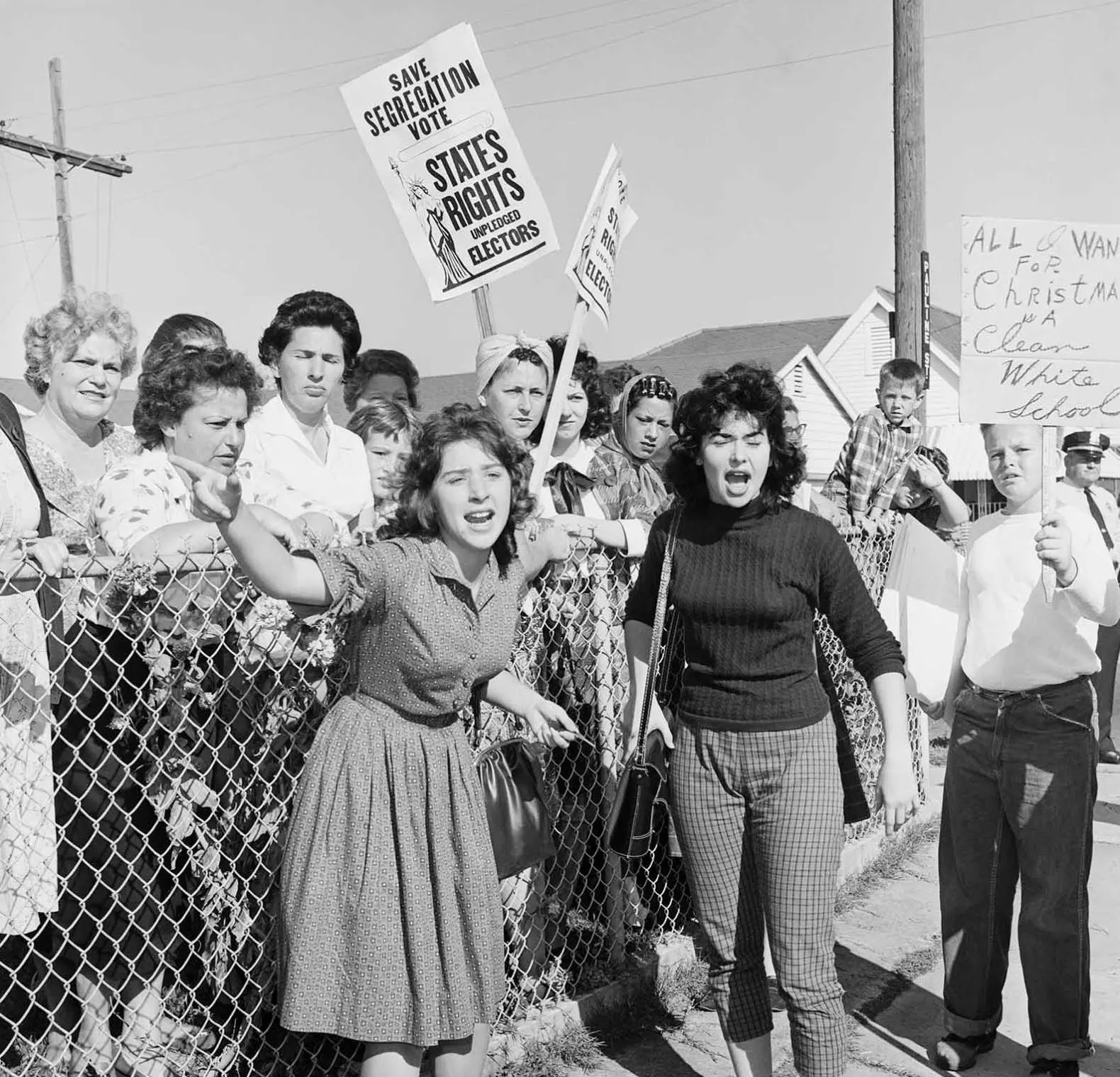

Table of Contents
Historical Context of School Desegregation Orders
The history of school segregation in the United States is a long and complex one, marked by systemic discrimination and the fight for equal educational opportunities. For decades, schools were legally segregated, denying Black students access to the same quality education as their white peers. This injustice fueled decades of activism and legal battles, culminating in the landmark Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which declared state laws establishing separate public schools for Black and white students to be unconstitutional.
However, the Brown decision was just the beginning of a long struggle. Implementation faced significant resistance, leading to the need for federal intervention and the issuance of school desegregation orders by the Justice Department. These orders aimed to dismantle segregationist practices and ensure equal access to education for all students, regardless of race.
- Timeline of significant legal actions:
- 1954: Brown v. Board of Education
- 1964: Civil Rights Act
- 1970s-1990s: Numerous court cases and desegregation orders issued by federal courts.
- Key figures involved in the fight for desegregation: Thurgood Marshall, Martin Luther King Jr., Rosa Parks.
- Examples of successful desegregation efforts: Integration efforts in various school districts across the South and other parts of the country, showcasing the positive impact of desegregation on educational outcomes and social integration.
The Justice Department's Rationale for Ending the Orders
The Justice Department's decision to end school desegregation orders was based on arguments that these orders were no longer necessary or effective in achieving desegregation goals. Their official statement cited various factors, including the significant progress made in desegregating schools and the belief that continued federal oversight was unwarranted. This decision has been met with considerable criticism. Many argue that the progress has been insufficient and that ending these orders risks exacerbating existing racial inequalities.
- Specific points from the Justice Department's statement: Emphasis on local control of schools, belief that previous goals have been substantially achieved, and concerns about the cost and effectiveness of continued federal monitoring.
- Expert opinions supporting or opposing the decision: Analysis of statements from education experts, civil rights advocates, and legal scholars on both sides of the debate.
- Potential legal challenges to the decision: Discussion of the possibility of lawsuits and appeals challenging the Justice Department's decision and the legal grounds for such challenges.
Potential Impacts on Affected School Districts
The decision to end school desegregation orders has significant implications for affected school districts. The most immediate concern is the potential for re-segregation, reversing decades of progress and exacerbating racial disparities in educational outcomes. Districts that previously operated under desegregation orders may experience a shift towards more racially homogenous schools, potentially leading to unequal access to resources and opportunities.
- Examples of districts likely to be significantly impacted: Identification of specific school districts previously subject to desegregation orders and their likely future trajectory.
- Potential scenarios for increased segregation: Analysis of various scenarios for increased segregation, including the potential for "white flight" and the concentration of minority students in under-resourced schools.
- Economic consequences of the decision: Discussion of the potential economic impacts on both segregated and integrated schools and communities.
Impact on Student Achievement and Educational Equity
The potential impact on student achievement and educational equity is perhaps the most critical consequence of ending school desegregation orders. Research consistently demonstrates that diverse learning environments benefit all students, promoting critical thinking, cultural understanding, and improved academic performance. Re-segregation risks widening the achievement gap between white and minority students, perpetuating cycles of inequality and limiting social mobility.
- Statistical data on achievement gaps: Presentation of statistical data highlighting the existing achievement gap and the potential for it to widen with increased segregation.
- Expert opinions on the importance of diverse learning environments: Citations of research and expert opinions supporting the benefits of diversity in education.
- Potential strategies to mitigate negative impacts: Discussion of possible strategies to counteract the negative consequences of re-segregation, including targeted interventions, resource allocation, and community engagement.
Political and Social Ramifications of the Decision
The Justice Department's decision has sparked significant political and social reactions. The decision has become a focal point in the ongoing national conversation about race, inequality, and the role of government in addressing social injustices. Advocacy groups and community organizations are mobilizing to oppose the decision and advocate for continued efforts to ensure equitable access to education.
- Statements from key political figures: Review of public statements made by political leaders from both sides of the issue.
- Public opinion polls and surveys: Analysis of public opinion data regarding the decision and its impact.
- Activities of relevant advocacy groups: Discussion of the responses and activities of various civil rights organizations and community groups in the wake of the Justice Department's decision.
Conclusion
The Justice Department's decision to end school desegregation orders represents a significant turning point in the ongoing struggle for racial equality in education. The potential consequences are substantial, including increased segregation, widening achievement gaps, and the exacerbation of existing social and economic inequalities. While the Justice Department argues that their actions reflect progress, critics argue that ending federal oversight jeopardizes decades of progress and risks reversing hard-won gains in educational equity. It is crucial to stay informed about the ongoing developments and engage in constructive discussions about the future of school desegregation and the enduring fight for equitable education for all students. Learn more about the impact of the School Desegregation Orders and advocate for policies promoting equitable education for all students.

Featured Posts
-
 100 Year Old Actress Priscilla Pointer Starring In Carrie Passes Away
May 02, 2025
100 Year Old Actress Priscilla Pointer Starring In Carrie Passes Away
May 02, 2025 -
 Actor Michael Sheens 100 000 Gift 900 Peoples 1 Million Debt Paid Off
May 02, 2025
Actor Michael Sheens 100 000 Gift 900 Peoples 1 Million Debt Paid Off
May 02, 2025 -
 La Laport 3 20
May 02, 2025
La Laport 3 20
May 02, 2025 -
 April 30 2025 Lottery Results Winning Numbers
May 02, 2025
April 30 2025 Lottery Results Winning Numbers
May 02, 2025 -
 Office365 Data Breach Nets Millions For Cybercriminal Federal Charges Filed
May 02, 2025
Office365 Data Breach Nets Millions For Cybercriminal Federal Charges Filed
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Katapolemisi Tis Diafthoras Stis Poleodomies Bimata Gia Tin Epanidrysi Toy Kratoys Dikaioy
May 03, 2025
Katapolemisi Tis Diafthoras Stis Poleodomies Bimata Gia Tin Epanidrysi Toy Kratoys Dikaioy
May 03, 2025 -
 Tensions Rise Tory Chairman Condemns Farage Faces Reform Uk Showdown
May 03, 2025
Tensions Rise Tory Chairman Condemns Farage Faces Reform Uk Showdown
May 03, 2025 -
 Rekordt Na Lakazet Lion Na Pt Za Vtoroto Myasto
May 03, 2025
Rekordt Na Lakazet Lion Na Pt Za Vtoroto Myasto
May 03, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Growth
May 03, 2025
The Impact Of Nigel Farage On Reform Uks Growth
May 03, 2025 -
 Signing And Exchange Of Notes Grant Assistance To Mauritius
May 03, 2025
Signing And Exchange Of Notes Grant Assistance To Mauritius
May 03, 2025
