Is The Venture Capital Secondary Market Overheated? A Current Analysis
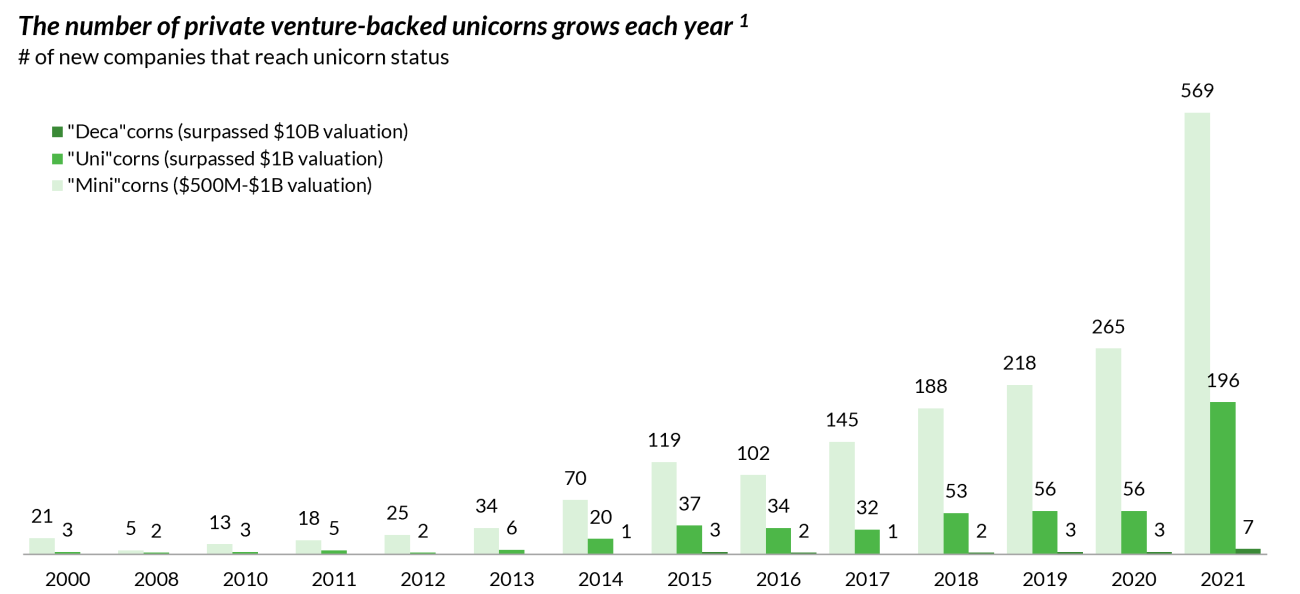
Table of Contents
Increased Transaction Volume and Valuation Multiples
The sheer volume of secondary transactions is undeniable evidence of increased market activity.
Rising Transaction Numbers
The number of venture capital secondary deals closed has experienced exponential growth. While precise figures vary depending on the data provider, a consistent trend shows year-over-year increases, particularly in the late 2010s and early 2020s.
- Notable Transactions: Several multi-billion dollar secondary transactions involving high-profile tech companies have dominated headlines, further fueling perceptions of a booming market.
- Year-over-Year Growth: Data from sources like Preqin and PitchBook show double-digit percentage growth in deal volume for several consecutive years, indicating a significant expansion of the market.
- Geographic Distribution: While the US remains the dominant market for venture capital secondary transactions, activity in Europe and Asia is also increasing, suggesting a global trend.
Inflated Valuations?
A key question is whether valuations in secondary deals are justified or reflect an inflated market. Many argue that valuations in the secondary market are exceeding those observed in primary markets, leading to concerns about a potential bubble.
- Primary vs. Secondary Valuations: Direct comparisons are difficult due to data limitations, but anecdotal evidence suggests that some secondary transactions involve premiums over recent primary rounds, potentially driven by the desire for immediate liquidity.
- Discount Rates: The discount rates applied in secondary transactions play a critical role in determining valuations. Lower discount rates, often reflecting higher investor confidence, can lead to higher valuations.
- Examples of High Valuations: Specific examples of deals with unusually high valuations compared to comparable primary transactions can be used to illustrate the potential for overvaluation in certain segments of the market. However, these examples need to be considered in context, taking into account factors such as growth trajectory and market conditions.
Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
Macroeconomic forces have significantly influenced the venture capital secondary market.
Interest Rate Hikes and Inflation
Rising interest rates and persistent inflation have created a complex environment for the secondary market.
- Impact on LP Liquidity Needs: Higher interest rates might incentivize LPs to seek liquidity from their venture capital holdings to reinvest at higher returns elsewhere.
- Effect on Discount Rates: Increased inflation and interest rates generally lead to higher discount rates, potentially dampening valuations in the secondary market.
- Potential for Decreased Deal Flow: A combination of higher rates and economic uncertainty might lead to a decrease in the overall number of transactions, as both buyers and sellers become more cautious.
Recessionary Fears and Market Volatility
Broader economic uncertainty and recessionary fears have cast a shadow over the venture capital secondary market.
- Risk Aversion: Increased risk aversion among investors can lead to lower valuations and fewer transactions, as buyers become more selective and demand higher discounts.
- Potential for a Pullback: Market volatility can trigger a pullback in deal activity, as uncertainty makes it harder to price assets accurately.
- Strategic Implications: Recessionary fears force LPs and GPs to reassess their strategies, potentially leading to more strategic, rather than purely opportunistic, secondary transactions.
Shifting Investor Sentiment and Strategies
The behavior of both limited partners (LPs) and general partners (GPs) is crucial to understanding the market's dynamics.
Increased LP Demand for Liquidity
LPs, including pension funds and endowments, are often seeking ways to manage their portfolios and generate returns.
- Reasons for LP Liquidity Needs: Portfolio rebalancing, capital calls from other investments, and the need to meet specific funding targets are all drivers of LP demand for liquidity.
- Strategies for Managing Liquidity Needs: Secondary transactions provide a mechanism for LPs to access liquidity without forcing the sale of entire company stakes.
Strategic Objectives of General Partners (GPs)
GPs also have strategic reasons to participate in secondary transactions.
- Fund Restructuring: Secondary sales can help GPs restructure their portfolios, focusing on their most promising investments.
- Capital Raising: Secondary sales can provide GPs with capital to support existing portfolio companies or to invest in new opportunities.
- Benefits and Drawbacks: While secondary sales offer liquidity and strategic advantages, they can also dilute the GP's ownership and potentially impact future fund performance.
Signs of an Overheated Market (or Lack Thereof)
Determining whether the market is truly overheated requires careful consideration of several factors.
Potential Warning Signs
Several indicators might suggest an overheated market.
- Unsustainable Valuation Increases: Rapid and significant increases in valuations, particularly if not supported by strong fundamental performance, are a potential warning sign.
- Increased Competition Among Buyers: Fierce competition for deals, leading to higher prices, suggests potential overvaluation.
- Speculative Trading: The emergence of speculative trading, driven by FOMO rather than fundamental analysis, can be a harbinger of a market correction.
Counterarguments and Market Resilience
Arguments against an overheated market also exist.
- Increased Institutional Participation: Increased participation from sophisticated institutional investors suggests a level of market maturity and validation.
- Sophisticated Pricing Mechanisms: The development of more sophisticated pricing methodologies and data-driven valuation models can help to mitigate the risk of overvaluation.
- Resilience of Underlying Portfolio Companies: Strong underlying performance of portfolio companies can support higher valuations, even in a volatile market.
Conclusion
The evidence regarding whether the venture capital secondary market is overheated is mixed. While the increased transaction volume and, in some cases, elevated valuations are cause for concern, several factors mitigate the risk of an imminent collapse. Increased institutional participation, sophisticated pricing mechanisms, and the underlying strength of many portfolio companies suggest a degree of market resilience. However, the impact of macroeconomic factors, such as rising interest rates and recessionary fears, remains a significant uncertainty. Understanding the current dynamics of the venture capital secondary market is crucial for both LPs and GPs. Further research into specific deal structures and market trends will be essential to effectively navigate this evolving landscape. The future of the secondary market for venture capital investments remains to be seen, and careful monitoring is crucial for all participants.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Spelling Bee February 12 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee February 12 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Podcast Production Reimagined Ais Role In Processing Repetitive Scatological Texts
Apr 29, 2025
Podcast Production Reimagined Ais Role In Processing Repetitive Scatological Texts
Apr 29, 2025 -
 How Ai Thinks A Look At The Limits Of Artificial Intelligence
Apr 29, 2025
How Ai Thinks A Look At The Limits Of Artificial Intelligence
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Chinas Huawei Unveils New Ai Chip Technology Closing The Gap On Nvidia
Apr 29, 2025
Chinas Huawei Unveils New Ai Chip Technology Closing The Gap On Nvidia
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Outlaw Music Festival Bob Dylan And Billy Strings Coming To Portland
Apr 29, 2025
Outlaw Music Festival Bob Dylan And Billy Strings Coming To Portland
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Donald Trump Calls For Pete Rose Pardon And Hall Of Fame Induction
Apr 29, 2025
Donald Trump Calls For Pete Rose Pardon And Hall Of Fame Induction
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Pete Rose Pardon Donald Trumps Presidential Gamble
Apr 29, 2025
The Pete Rose Pardon Donald Trumps Presidential Gamble
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Will Trump Pardon Pete Rose The Impact On Baseball And Sports Betting
Apr 29, 2025
Will Trump Pardon Pete Rose The Impact On Baseball And Sports Betting
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trump Promises Pete Rose A Posthumous Pardon Following Mlb Criticism
Apr 29, 2025
Trump Promises Pete Rose A Posthumous Pardon Following Mlb Criticism
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Trumps Potential Pardon Of Pete Rose A Look At The Mlb Betting Ban
Apr 29, 2025
Trumps Potential Pardon Of Pete Rose A Look At The Mlb Betting Ban
Apr 29, 2025
