How The Student Loan Crisis Will Impact The US Economy

Table of Contents
Reduced Consumer Spending and Aggregate Demand
The sheer weight of student loan repayments significantly reduces disposable income for millions of Americans. This decrease in available funds directly impacts consumer spending, a cornerstone of US economic growth.
Lower Disposable Income
High monthly student loan payments leave less money for other essential expenses and discretionary spending. This translates to a dampening effect on aggregate demand.
- Delayed major purchases: Many young adults postpone significant purchases like homes, cars, and even starting a family due to student loan debt.
- Reduced discretionary spending: Entertainment, travel, and dining out are often the first casualties as individuals prioritize loan repayments.
- Impact on savings: Building savings for retirement or emergencies becomes significantly more challenging, further hindering long-term economic stability.
According to the Federal Reserve, a significant percentage of borrowers allocate a substantial portion (often 20% or more) of their monthly income to student loan repayments. This leaves little room for the kind of spending that fuels economic growth. This decreased consumer spending negatively affects businesses of all sizes, but especially small businesses.
Impact on Small Businesses
Small businesses, which form the backbone of the US economy and employ a significant portion of the workforce, are particularly vulnerable to reduced consumer spending. They rely heavily on local consumer demand, and a downturn in spending directly impacts their revenue and ability to thrive.
- Reduced sales and revenue: Less consumer spending translates directly to lower sales for small businesses, leading to reduced revenue and potentially layoffs.
- Difficulty in expansion: Small businesses struggle to invest in growth and expansion when faced with reduced demand.
- Increased risk of closure: Many small businesses are forced to close their doors due to the inability to cope with sustained low consumer spending.
Impact on Economic Growth and Investment
The student loan crisis casts a long shadow over future economic growth by stifling entrepreneurial activity and reducing investment in education and human capital.
Stifled Entrepreneurial Activity
The substantial burden of student loan debt discourages young people from pursuing entrepreneurial ventures. The financial risk associated with starting a business becomes too daunting when already grappling with significant student loan repayments.
- High barrier to entry: The financial resources needed to launch a new business are often unavailable to individuals burdened by student loan debt.
- Reduced risk tolerance: The weight of existing debt can lead to a more risk-averse approach, hindering innovation and the creation of new businesses.
- Delayed career progression: Many individuals delay pursuing their entrepreneurial aspirations, hindering the creation of jobs and economic growth.
Data indicates a decline in the number of new businesses started by young adults, suggesting a direct correlation between student loan debt and reduced entrepreneurial activity.
Reduced Investment in Education and Human Capital
The student loan crisis also poses a significant threat to future investment in education and human capital. The fear of accumulating even more debt discourages many from pursuing further education or professional development.
- Declining college enrollment: The cost of higher education, combined with the prospect of substantial student loan debt, leads to a decline in college enrollment and advanced degree pursuits.
- Reduced skill development: Fewer individuals pursue professional development opportunities, leading to a decline in the overall skillset of the workforce.
- Impact on long-term productivity: A less-skilled and less-educated workforce negatively impacts long-term economic productivity and growth.
Increased Risk of Defaults and Financial Instability
The escalating rates of student loan delinquency and default present a growing risk to both individuals and the broader financial system.
Delinquency and Default Rates
The rising number of borrowers struggling to make their student loan payments indicates a serious problem. Defaulting on student loans has severe consequences:
- Damaged credit score: Default severely damages an individual's credit score, limiting access to credit for future purchases and opportunities.
- Wage garnishment: The government can garnish wages to recoup defaulted student loan debt, significantly impacting an individual's financial stability.
- Collection agencies: Default often leads to aggressive collection efforts, adding to the financial and emotional burden.
Data reveals a concerning upward trend in student loan delinquency and default rates, raising alarms about the potential for a broader financial crisis.
Systemic Risk to the Financial System
The interconnectedness of the student loan market with other financial institutions poses a systemic risk. Widespread defaults could destabilize the financial system:
- Impact on banks and lenders: High default rates can lead to significant losses for banks and other lending institutions.
- Potential for a broader financial crisis: A cascading effect of defaults could negatively impact other sectors of the economy, triggering a much larger economic downturn.
Inflationary Pressures
Government interventions, such as loan forgiveness programs, while intended to alleviate the burden of student loan debt, may have unintended inflationary consequences.
Government Intervention and Inflation
Large-scale loan forgiveness programs represent a significant injection of money into the economy. This could potentially lead to:
- Increased demand-pull inflation: The sudden influx of cash could increase demand for goods and services, pushing up prices.
- Impact on interest rates: Government borrowing to fund forgiveness programs could increase interest rates, affecting borrowing costs across the board.
Finding effective solutions to the student loan crisis is paramount for the long-term health of the US economy. We need innovative solutions to mitigate the risks associated with this growing burden and prevent further negative impacts on our national economic health. Addressing the student debt crisis requires a multifaceted approach involving policymakers, lenders, and individuals to create a more sustainable and equitable system. Effective solutions are needed to prevent the student loan crisis from further destabilizing the US economy.

Featured Posts
-
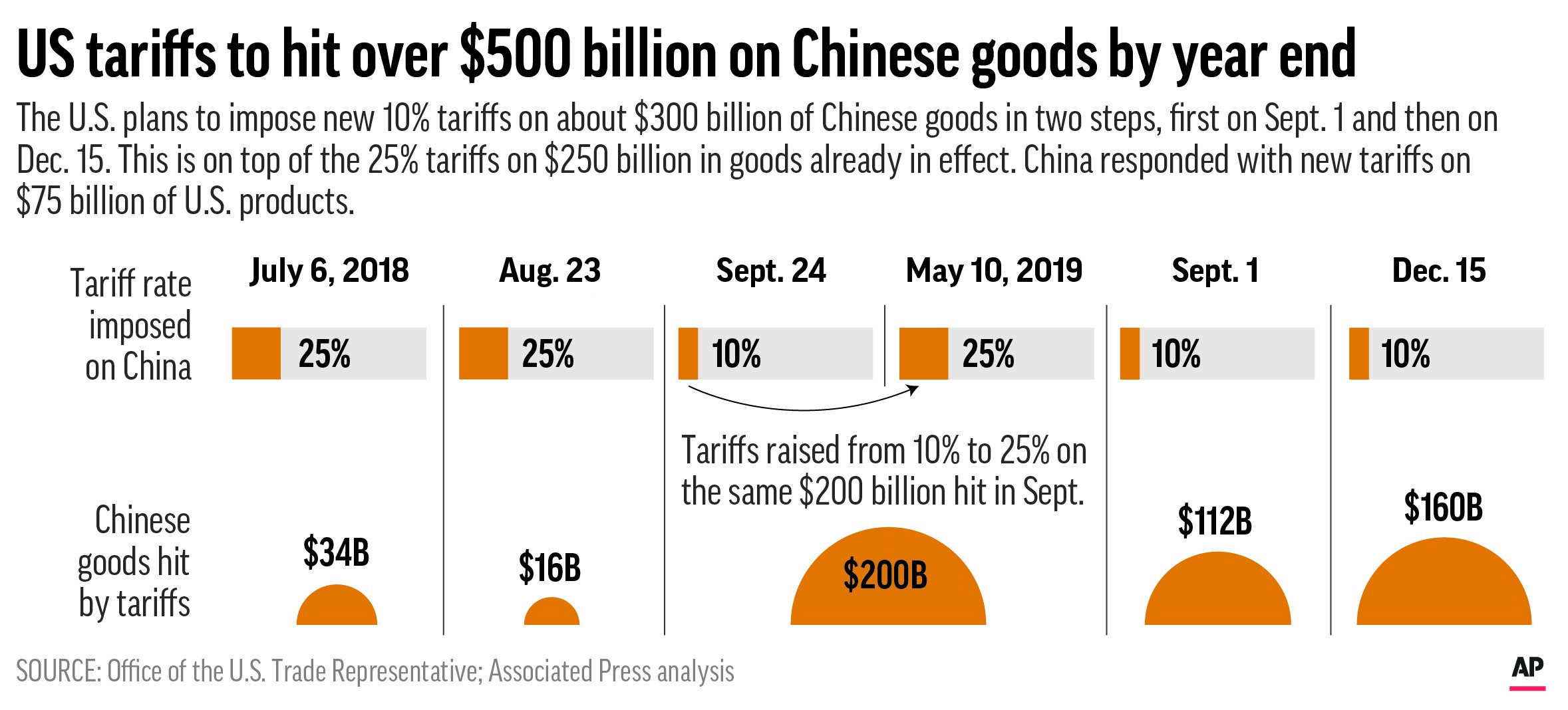 Trump Extends Eu Tariff Deadline New Date July 9th
May 28, 2025
Trump Extends Eu Tariff Deadline New Date July 9th
May 28, 2025 -
 Metro Detroit To See Sunshine After Cool Monday Morning
May 28, 2025
Metro Detroit To See Sunshine After Cool Monday Morning
May 28, 2025 -
 Hugh Jackman Wolverine Avengers Doomsday Fact Or Fiction A Deep Dive Into The Casting Rumors
May 28, 2025
Hugh Jackman Wolverine Avengers Doomsday Fact Or Fiction A Deep Dive Into The Casting Rumors
May 28, 2025 -
 Prakiraan Cuaca Bandung 22 April Hujan Siang Hari
May 28, 2025
Prakiraan Cuaca Bandung 22 April Hujan Siang Hari
May 28, 2025 -
 Manchester United Star Alejandro Garnacho Chelsea Bid Response
May 28, 2025
Manchester United Star Alejandro Garnacho Chelsea Bid Response
May 28, 2025
