Global Forest Loss Reaches Record High: Wildfires Fuel The Destruction
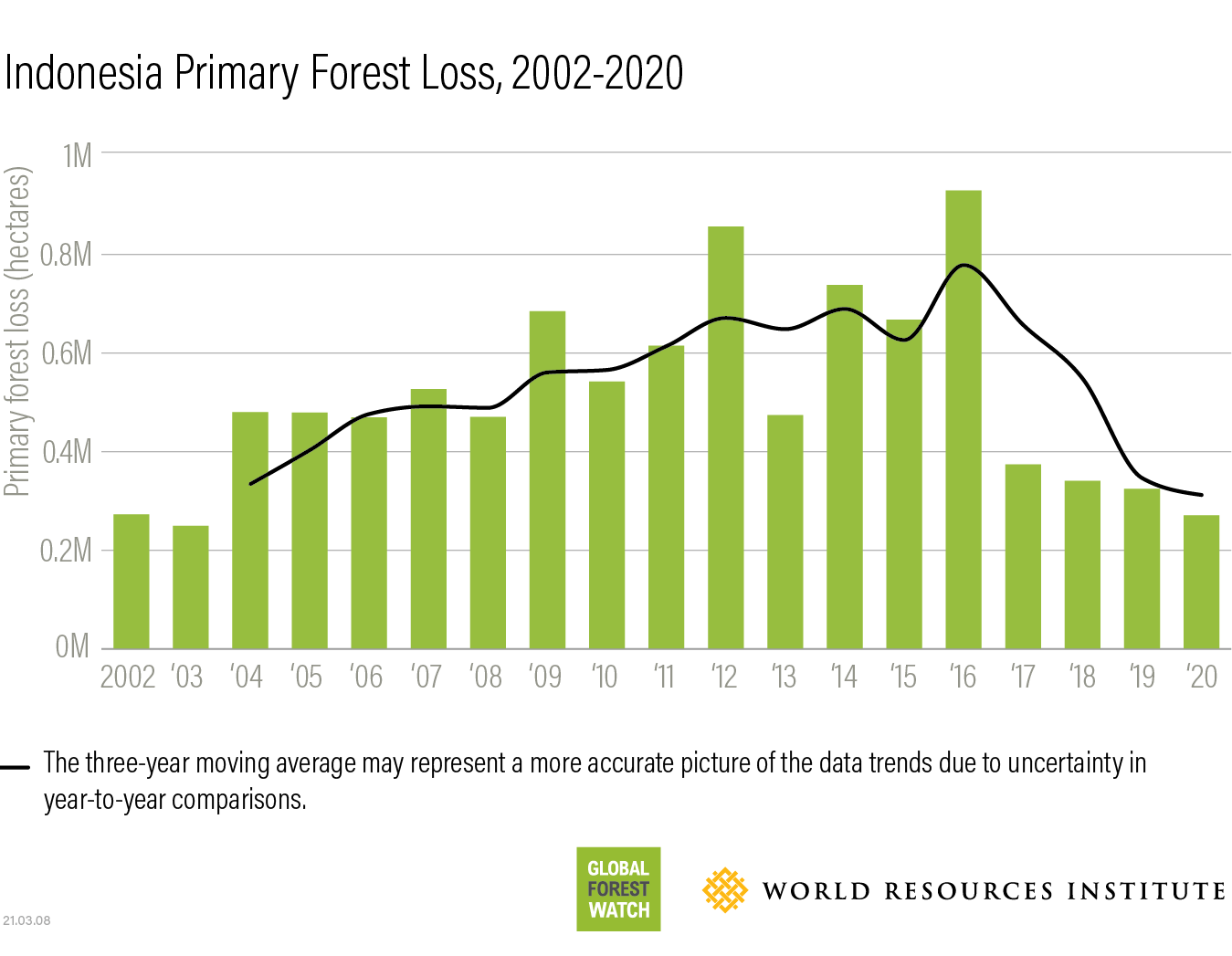
Table of Contents
The Dire Statistics of Global Forest Loss
The current state of global forest loss is deeply concerning. Reports from organizations like the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) paint a grim picture. The sheer scale of deforestation is staggering, with irreversible consequences for biodiversity, climate stability, and human well-being.
-
Total area of forest lost in the past year: According to the FAO's most recent assessment, [insert specific data and source here, e.g., "an estimated 10 million hectares of forest were lost in 2022" (FAO, 2023)]. This figure represents a significant increase compared to previous years.
-
Percentage increase compared to previous years: [Insert data and source here, e.g., "This represents a 15% increase from the average annual loss over the previous decade" (Source)].
-
Top countries experiencing significant forest loss: Brazil, Indonesia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo consistently rank among the countries with the highest rates of deforestation, often driven by agricultural expansion, logging, and mining. [Insert additional data and sources here, perhaps mentioning specific regions within these countries].
-
Types of forests most affected: Rainforests, particularly the Amazon and Congo basins, are disproportionately affected due to their high biodiversity and vulnerability to deforestation. Boreal forests in the northern latitudes are also experiencing significant loss due to logging and wildfires.
[Insert a relevant image or infographic here illustrating the data on global forest loss, ideally showing a comparison over time and highlighting key regions.]
Wildfires: A Major Driver of Global Forest Loss
The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires globally are significantly exacerbating the problem of global forest loss. This alarming trend is inextricably linked to climate change.
Climate Change and its Impact on Wildfire Risk
Rising global temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in precipitation patterns are creating ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
- Drier vegetation: Increased heat and reduced rainfall lead to drier vegetation, acting as readily available fuel for wildfires.
- Longer fire seasons: Warmer temperatures extend the fire season, increasing the window of opportunity for wildfires to occur.
- Increased wind speeds: Climate change can also lead to stronger winds, which accelerate the spread of wildfires.
Deforestation and its Contribution to Wildfires
Deforestation itself creates conditions that are highly favorable for wildfires.
- Increased fuel load: The removal of trees leaves behind a dense layer of underbrush and debris, providing ample fuel for intense fires.
- Loss of natural firebreaks: Intact forests often contain natural barriers (rivers, clearings) that help to slow or contain wildfires. Deforestation removes these natural firebreaks, allowing fires to spread more easily.
Human Activities as Wildfire Igniters
Human activities, both accidental and intentional, are a major cause of wildfires.
- Discarded cigarettes: Carelessly discarded cigarettes are a leading cause of wildfires, particularly in dry and windy conditions.
- Agricultural burning: Controlled burns for agricultural purposes can easily get out of control, leading to devastating wildfires.
- Arson: Intentional acts of arson are also a significant cause of wildfires in many regions.
The Devastating Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of global forest loss extend far beyond the simple loss of trees. The ramifications are profound and wide-ranging, affecting biodiversity, climate stability, and human economies.
Biodiversity Loss
The loss of forests leads to the loss of habitat for countless plant and animal species. Many species are driven to extinction as their homes are destroyed.
- Endangered species: Numerous endangered species, including orangutans, tigers, and various bird species, are particularly vulnerable to habitat loss due to deforestation.
- Disrupted ecosystems: The loss of forests disrupts entire ecosystems, leading to cascading effects throughout the food chain.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Forests play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate. Deforestation contributes to climate change in several ways.
- Reduced carbon sinks: Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Deforestation reduces the planet's capacity to absorb CO2, exacerbating greenhouse gas levels.
- Released stored carbon: When forests burn or are cleared, the stored carbon is released into the atmosphere, further contributing to global warming.
Economic Impacts
Global forest loss has significant economic consequences.
- Impact on timber industries: Unsustainable logging practices can lead to the depletion of forest resources, impacting timber industries and local economies.
- Reduced tourism revenue: Loss of forests can negatively affect tourism, as forests are often major tourist attractions.
- Impacts on local communities: Many communities depend on forests for their livelihoods, and deforestation can lead to poverty and displacement.
Soil Erosion and Water Cycle Disruption
Deforestation leads to soil erosion, desertification, and changes in rainfall patterns.
- Increased soil erosion: Trees help to bind the soil together. Deforestation leaves the soil exposed to erosion, leading to land degradation.
- Desertification: Severe soil erosion can lead to desertification, turning fertile land into barren wasteland.
- Changes in rainfall patterns: Forests play a role in regulating the water cycle. Deforestation can lead to changes in rainfall patterns, impacting agriculture and water resources.
Combating Global Forest Loss: Solutions and Strategies
Addressing the crisis of global forest loss requires a multifaceted approach involving various stakeholders and strategies.
- Improved forest management practices: Sustainable forest management practices, including selective logging and replanting, can help to minimize forest loss.
- Sustainable forestry techniques: Promoting sustainable forestry certification schemes helps to ensure that timber is sourced from responsibly managed forests.
- Reforestation and afforestation efforts: Planting trees in deforested areas and establishing new forests can help to restore forest cover.
- Early wildfire detection and response systems: Investing in advanced technology for early wildfire detection and deploying rapid response teams can help to minimize wildfire damage.
- Community engagement and education: Raising public awareness about the importance of forests and engaging local communities in forest conservation efforts is essential.
- International cooperation and policy changes: International cooperation and strong policies are crucial for effective forest conservation.
- Addressing climate change: Mitigating climate change is essential to reducing the risk of wildfires and slowing deforestation.
Conclusion:
The record-high levels of global forest loss, fueled by devastating wildfires, present an urgent and critical threat to our planet's future. The consequences of continued deforestation are far-reaching and devastating, impacting biodiversity, climate stability, and human well-being. Understanding the critical threat of global forest loss is the first step towards impactful action. Learn more, get involved with organizations dedicated to forest conservation, and advocate for policies that protect our planet's vital forests. Let's work together to prevent further destruction and safeguard the future of our forests.

Featured Posts
-
 Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Nonton Online Pukul 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025
Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris 2025 Sprint Race Nonton Online Pukul 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025 -
 Jangan Lewatkan Jadwal Tayang Moto Gp Argentina 2025 Di Trans7
May 26, 2025
Jangan Lewatkan Jadwal Tayang Moto Gp Argentina 2025 Di Trans7
May 26, 2025 -
 F1 Drivers Press Conference What You Need To Know
May 26, 2025
F1 Drivers Press Conference What You Need To Know
May 26, 2025 -
 55 Let Naomi Kempbell Redkie I Goryachie Foto
May 26, 2025
55 Let Naomi Kempbell Redkie I Goryachie Foto
May 26, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Et X Un Outil Pour L Ascension De L Extreme Droite Europeenne
May 26, 2025
Elon Musk Et X Un Outil Pour L Ascension De L Extreme Droite Europeenne
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Illegal Caribou Hunt At Remote Lodge Rcmp Investigation Underway Near Manitoba Nunavut Border
May 30, 2025
Illegal Caribou Hunt At Remote Lodge Rcmp Investigation Underway Near Manitoba Nunavut Border
May 30, 2025 -
 Rcmp Investigate Illegal Caribou Hunting Near Manitoba Nunavut Border
May 30, 2025
Rcmp Investigate Illegal Caribou Hunting Near Manitoba Nunavut Border
May 30, 2025 -
 Snowfall Warning Issued For Parts Of Western Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Snowfall Warning Issued For Parts Of Western Manitoba
May 30, 2025 -
 Enhanced Emergency Care Advanced Paramedics Arrive In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Enhanced Emergency Care Advanced Paramedics Arrive In Rural And Northern Manitoba
May 30, 2025 -
 Joy Smith Foundation Launching A Media And Photo Advisory
May 30, 2025
Joy Smith Foundation Launching A Media And Photo Advisory
May 30, 2025
