Global Forest Loss: A Record-Breaking Year Of Wildfire Devastation
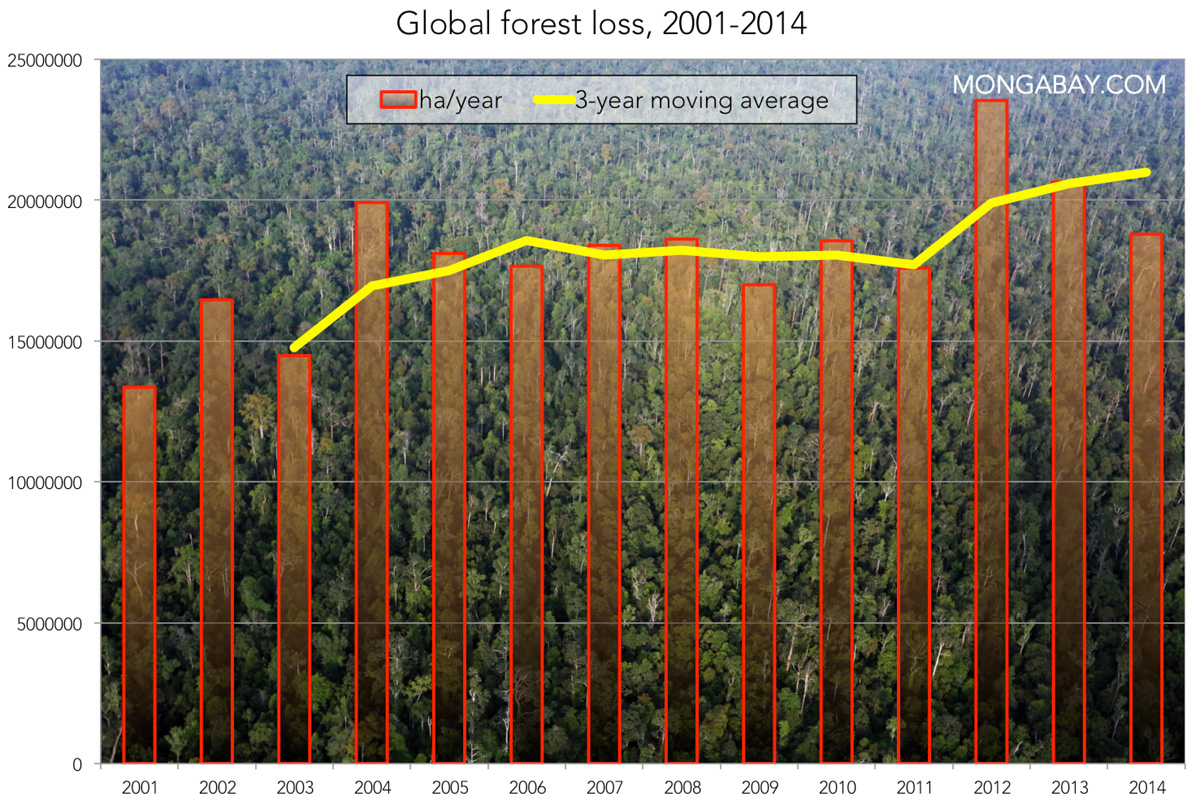
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires on Global Forests
Wildfires are a major driver of global forest loss, causing widespread destruction and irreparable damage to ecosystems worldwide. 2023 saw a catastrophic increase in wildfire activity, with significant blazes in regions like Canada, Australia, and Siberia. For instance, the Canadian wildfires of 2023 burned millions of hectares of boreal forest, releasing an unprecedented amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Similarly, vast swathes of forest in Australia and Siberia were consumed, resulting in significant biodiversity loss and long-term ecological damage. The key impacts of these devastating events include:
- Loss of biodiversity and habitat destruction: Wildfires decimate plant and animal populations, leading to habitat loss and species extinction. Many endangered species are particularly vulnerable to these events.
- Increased carbon emissions and climate change acceleration: Burning forests release massive amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change and creating a vicious cycle of increasingly intense wildfires. This contributes significantly to global warming and further intensifies the greenhouse effect.
- Soil erosion and water contamination: The destruction of forest cover leaves the soil exposed to erosion, leading to land degradation and water pollution. Ash and debris from wildfires contaminate water sources, impacting both aquatic life and human populations.
- Economic losses: The timber industry, tourism sector, and local communities suffer significant economic losses due to wildfire damage, impacting livelihoods and regional economies.
Underlying Causes of Increased Wildfire Activity
The increased frequency and intensity of wildfires are driven by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Climate change and rising temperatures: Global warming, characterized by rising temperatures and prolonged heat waves, creates drier conditions that increase the risk of wildfires. Increased drought severity also plays a significant role.
- Deforestation and land-use change: The conversion of forests for agriculture, logging, and urbanization reduces the natural resilience of ecosystems to wildfires and creates more flammable landscapes. This is a significant factor in global forest loss statistics.
- Drought conditions and dry vegetation: Prolonged periods of drought lead to dry vegetation, which acts as readily available fuel for wildfires, making them more easily ignited and harder to control.
- Human negligence and accidental ignition: Human activities, including carelessly discarded cigarettes, power lines, and intentional arson, are also responsible for many wildfires.
The Environmental Consequences of Extensive Global Forest Loss
The environmental consequences of extensive global forest loss extend far beyond the immediate damage caused by wildfires. These impacts include:
- Disruption of the carbon cycle and increased greenhouse gas emissions: Forests play a vital role in carbon sequestration. Their destruction disrupts the carbon cycle, leading to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and accelerating climate change.
- Loss of biodiversity and extinction of species: The destruction of forest habitats leads to biodiversity loss, threatening numerous plant and animal species with extinction. This loss diminishes ecological resilience and stability.
- Changes in regional climate patterns: Deforestation can alter regional climate patterns, impacting rainfall, temperature, and wind patterns, potentially leading to more extreme weather events.
- Impact on air and water quality: Wildfires release pollutants into the atmosphere, affecting air quality and human health. They also contaminate water sources, affecting aquatic ecosystems and drinking water supplies.
Economic Impacts and Societal Costs of Forest Fires
The economic and societal costs associated with wildfires and forest loss are substantial:
- Damage to property and infrastructure: Wildfires can destroy homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure, leading to significant financial losses and displacement of communities.
- Loss of livelihoods: Farmers, forest workers, and tourism operators are particularly vulnerable to economic hardship caused by wildfires, leading to job losses and poverty.
- Increased healthcare costs: Exposure to wildfire smoke can cause respiratory illnesses and other health problems, increasing healthcare costs and burdening healthcare systems.
- Costs of firefighting and disaster relief: The costs of fighting wildfires and providing disaster relief are substantial, placing a strain on government budgets and resources.
Mitigation Strategies and Conservation Efforts to Combat Global Forest Loss
Addressing the threat of global forest loss requires a multi-pronged approach that includes:
- Improved forest management practices: Implementing controlled burns and other forest management techniques can help reduce the risk of large, destructive wildfires.
- Strengthening fire prevention measures: Public awareness campaigns and stricter regulations can help prevent human-caused wildfires.
- Investing in early warning systems and fire suppression technologies: Early detection and rapid response are crucial for effectively controlling wildfires. Improved technology and monitoring systems are essential.
- Combating deforestation and promoting sustainable forestry: Sustainable forestry practices and reducing deforestation are essential for preserving forest ecosystems and reducing the risk of wildfires.
- International cooperation and collaborative efforts: Global collaboration is vital for sharing best practices, coordinating efforts, and providing financial and technical assistance to countries affected by wildfires.
Conclusion: Addressing the Urgent Threat of Global Forest Loss
The record-breaking scale of global forest loss in 2023 underscores the urgent need for comprehensive action. The devastating impacts of wildfires, driven by climate change, deforestation, and human negligence, have far-reaching environmental and economic consequences. To mitigate future devastation, we must prioritize improved forest management, strengthen fire prevention measures, combat deforestation, invest in early warning systems, and foster international cooperation. Support organizations dedicated to forest conservation, advocate for stronger environmental policies, and promote responsible land management practices to combat global forest loss and protect our planet's invaluable forests. Learn more about the issue and take personal action to reduce your carbon footprint – the future of our forests depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 Lego Master Manny Garcia Inspires Students At Veterans Memorial Elementary School
May 25, 2025
Lego Master Manny Garcia Inspires Students At Veterans Memorial Elementary School
May 25, 2025 -
 Finding Your Dream Country Home For Under 1 Million
May 25, 2025
Finding Your Dream Country Home For Under 1 Million
May 25, 2025 -
 16 Million Fine For T Mobile Three Year Data Breach Settlement
May 25, 2025
16 Million Fine For T Mobile Three Year Data Breach Settlement
May 25, 2025 -
 Escape To The Country Making The Move To A Rural Area
May 25, 2025
Escape To The Country Making The Move To A Rural Area
May 25, 2025 -
 Carolina Country Music Fest 2025 Tickets Sold Out
May 25, 2025
Carolina Country Music Fest 2025 Tickets Sold Out
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Has Armando Iannucci Lost His Touch A Critical Examination
May 25, 2025
Has Armando Iannucci Lost His Touch A Critical Examination
May 25, 2025 -
 Armando Iannuccis Creative Evolution A Loss Of Sharpness
May 25, 2025
Armando Iannuccis Creative Evolution A Loss Of Sharpness
May 25, 2025 -
 The Diminishing Edge Analyzing Armando Iannuccis Recent Work
May 25, 2025
The Diminishing Edge Analyzing Armando Iannuccis Recent Work
May 25, 2025 -
 The Best British Pop Films Of All Time A Ranked List
May 25, 2025
The Best British Pop Films Of All Time A Ranked List
May 25, 2025 -
 Comparing Cityscapes Glasgows Unexpected Resemblance To Los Angeles In A New Thriller
May 25, 2025
Comparing Cityscapes Glasgows Unexpected Resemblance To Los Angeles In A New Thriller
May 25, 2025
