Gas Prices Surge: Nearly 20-Cent Increase Per Gallon
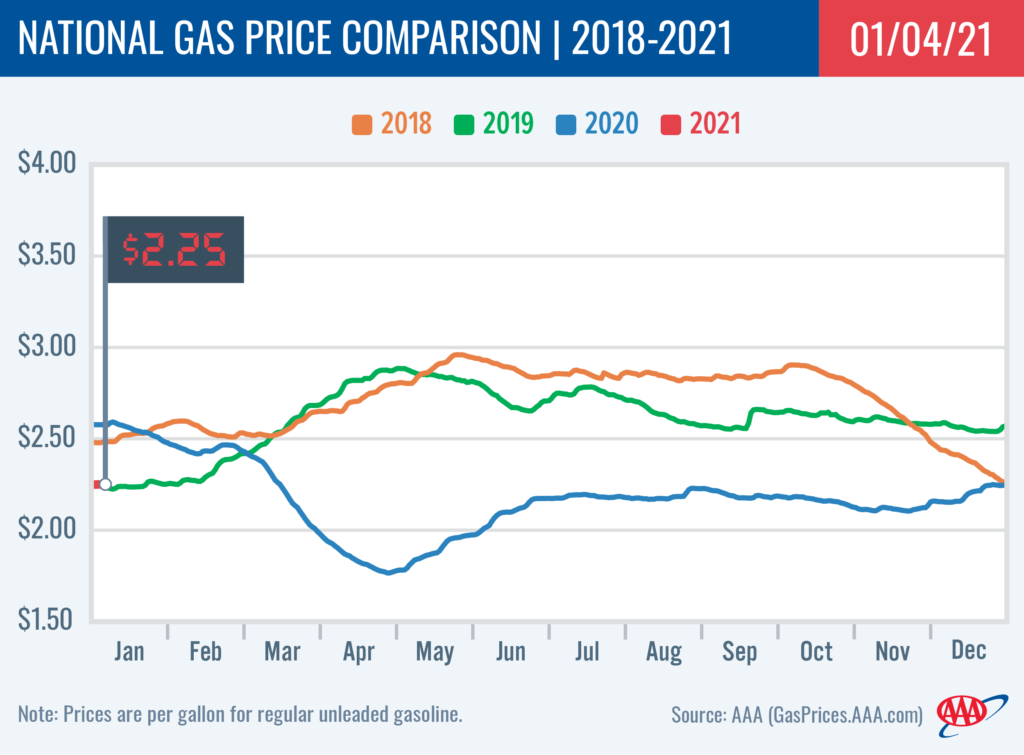
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the Nearly 20-Cent Gas Price Increase
Several interconnected factors contribute to this significant increase in gas prices.
Crude Oil Price Volatility
Global crude oil markets are notoriously volatile, and fluctuations directly translate into changes at the gas pump. Recent price increases are largely attributed to:
- Geopolitical Instability: Tensions in various regions, such as ongoing conflicts and political uncertainty, disrupt oil production and supply chains, leading to higher prices. For example, sanctions on major oil-producing countries can significantly impact global supply.
- OPEC+ Decisions: Decisions made by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies (OPEC+) regarding oil production quotas directly influence global supply and consequently, prices. Reductions in production often lead to price increases.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Unexpected events like extreme weather, pipeline closures, or logistical bottlenecks can disrupt the flow of crude oil, causing shortages and price spikes.
The correlation between crude oil prices and gasoline prices is almost always direct. A 10% increase in crude oil prices typically leads to a noticeable increase in gas prices at the pump, often within a few weeks.
Increased Demand
Increased demand for gasoline, especially during peak travel seasons, also contributes to higher prices. This is largely due to:
- Summer Travel: The summer months see a significant surge in leisure travel, leading to higher gasoline consumption. Road trips and vacations contribute significantly to this seasonal demand increase.
- Economic Recovery: A robust economy translates to increased consumer spending, including on gasoline. More people commuting to work and businesses transporting goods contribute to this demand.
- Increased Freight Transportation: The rise in e-commerce and global trade puts a significant strain on freight transportation networks, boosting the demand for fuel.
The following chart illustrates the relationship between seasonal demand and gasoline prices: (Insert chart here showing seasonal peaks in gas prices)
Refinery Issues & Capacity Constraints
Unexpected refinery shutdowns, planned maintenance, or capacity limitations can significantly impact gasoline supply, leading to price increases.
- Refinery Shutdowns: Unforeseen events like fires, explosions, or equipment failures at refineries can temporarily reduce the amount of gasoline produced, resulting in higher prices. Specific examples of recent refinery issues (if any) should be mentioned here, linking to relevant news articles for verification.
- Planned Maintenance: Regular maintenance at refineries is essential, but when multiple refineries undergo maintenance simultaneously, it can lead to reduced output and price increases.
- Capacity Constraints: A lack of sufficient refining capacity to meet the demand for gasoline can also contribute to higher prices.
Impact of the Gas Price Surge on Consumers and the Economy
The recent "Gas Prices Surge" has a significant impact on both consumers and the broader economy.
Increased Transportation Costs
Higher gas prices directly translate to increased transportation costs for individuals and businesses:
- Commuting Costs: Daily commuters face higher expenses, reducing their disposable income.
- Grocery Shopping: The cost of transporting goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumers at the grocery store.
- Logistics and Businesses: Businesses experience higher costs associated with transporting goods and services, potentially leading to price increases for consumers.
- Tourism: Increased travel costs can discourage tourism and affect related industries.
The impact on low-income families is particularly acute, as a larger percentage of their budget is allocated to transportation expenses.
Inflationary Pressures
Higher gas prices contribute to overall inflation, affecting the prices of various goods and services:
- Ripple Effect: Increased transportation costs influence the prices of food, raw materials, and other consumer goods.
- Increased Production Costs: Higher fuel costs increase production costs for various industries, which are often passed on to consumers.
- Potential Interest Rate Hikes: Central banks might respond to inflation by raising interest rates, which could impact borrowing costs and economic growth.
The impact of gas prices on inflation is a complex issue, requiring a multifaceted approach to analysis.
Potential Future Trends and Predictions for Gas Prices
Predicting future gas prices is challenging, but several factors offer insights.
Short-Term Outlook
The near-term outlook for gas prices is uncertain, with experts offering a range of predictions: (insert expert opinions and predictions here, linking to reputable sources). Several factors will influence short-term trends, including geopolitical events, OPEC+ decisions, and potential refinery issues.
Long-Term Outlook and Mitigation Strategies
In the long term, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and addressing price volatility is crucial. Mitigation strategies include:
- Renewable Energy Sources: Transitioning to renewable energy sources can reduce reliance on oil and gas.
- Fuel Efficiency Improvements: Investing in more fuel-efficient vehicles and improving transportation infrastructure can reduce gasoline consumption.
- Alternative Transportation Methods: Promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking can reduce reliance on private vehicles.
- Government Policies: Governments can implement policies to promote energy efficiency, support renewable energy development, and encourage the adoption of alternative transportation methods.
- Electric Vehicles: The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is expected to significantly reduce demand for gasoline in the long term.
Conclusion
The recent "Gas Prices Surge," with its near 20-cent increase per gallon, is driven by a combination of crude oil price volatility, increased demand, and refinery issues. This price hike has significant implications for consumers, increasing transportation costs and contributing to inflationary pressures. While short-term predictions are uncertain, long-term mitigation strategies focusing on renewable energy and alternative transportation methods are essential to address gas price volatility and reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Stay updated on the latest developments in gas prices and plan accordingly. Keep an eye on future gas price surges and take steps to manage your fuel costs.

Featured Posts
-
 Nissan And Fords Joint Venture Impact On The Electric Vehicle Landscape
May 22, 2025
Nissan And Fords Joint Venture Impact On The Electric Vehicle Landscape
May 22, 2025 -
 Stijgende Huizenprijzen Abn Amros Prognose Ondanks Economische Tegenvallers
May 22, 2025
Stijgende Huizenprijzen Abn Amros Prognose Ondanks Economische Tegenvallers
May 22, 2025 -
 Bbc Antiques Roadshow Leads To Us Couples Arrest In The Uk
May 22, 2025
Bbc Antiques Roadshow Leads To Us Couples Arrest In The Uk
May 22, 2025 -
 La Temporada De La Redencion De Javier Baez Salud Y Resultados
May 22, 2025
La Temporada De La Redencion De Javier Baez Salud Y Resultados
May 22, 2025 -
 Zhreb Za Ligata Na Natsii Makedoni A Gi Dozna Potentsi Alnite Protivnitsi
May 22, 2025
Zhreb Za Ligata Na Natsii Makedoni A Gi Dozna Potentsi Alnite Protivnitsi
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ten Hag Linked With Juventus After Motta Sacking
May 23, 2025
Ten Hag Linked With Juventus After Motta Sacking
May 23, 2025 -
 Maguire On Being Stripped Of Man Utd Captaincy
May 23, 2025
Maguire On Being Stripped Of Man Utd Captaincy
May 23, 2025 -
 Novedades En La Lista De Convocados De Instituto Como Jugara Ante Lanus
May 23, 2025
Novedades En La Lista De Convocados De Instituto Como Jugara Ante Lanus
May 23, 2025 -
 Manchester United Captaincy Maguires Response To Removal
May 23, 2025
Manchester United Captaincy Maguires Response To Removal
May 23, 2025 -
 El Once De Instituto Ante Lanus Analisis De La Lista De Convocados
May 23, 2025
El Once De Instituto Ante Lanus Analisis De La Lista De Convocados
May 23, 2025
