Fuel Costs Rise: A 20-Cent Increase In Average Gas Prices
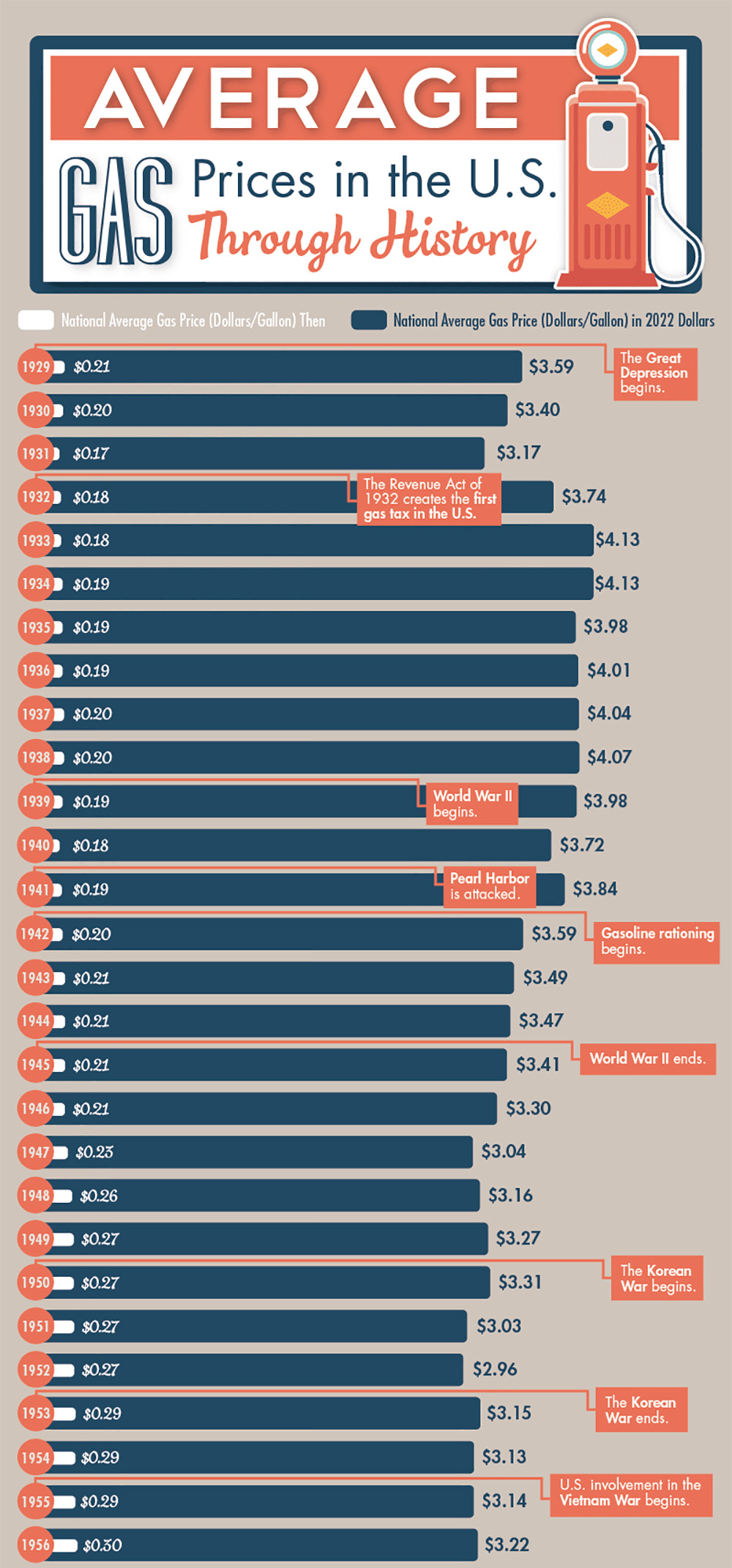
Table of Contents
Reasons Behind the 20-Cent Surge in Fuel Costs
Several factors contribute to this recent spike in gas prices. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial to addressing the issue effectively.
Increased Crude Oil Prices
Global crude oil market fluctuations are a major driver of gas price increases. The global oil market is incredibly sensitive to geopolitical instability and OPEC decisions.
- Geopolitical Events: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, for example, significantly disrupted global oil supplies, leading to price volatility. Other geopolitical tensions around the world can also exert pressure on crude oil prices.
- OPEC Production Quotas: Decisions made by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) regarding oil production quotas directly impact the global supply and, consequently, prices. Reduced production quotas can lead to higher prices, as seen in recent times.
- Seasonal Demand Shifts: Demand for gasoline typically increases during peak travel seasons (summer, holidays), further contributing to price fluctuations.
Refinery Capacity and Production
Issues with refinery output significantly impact the supply of gasoline.
- Maintenance Shutdowns: Planned or unplanned maintenance shutdowns at refineries can temporarily reduce gasoline production, leading to localized price increases.
- Unexpected Outages: Unexpected outages due to equipment failure, natural disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances can further exacerbate the situation, causing supply chain disruptions and higher prices.
- Capacity Constraints: A lack of sufficient refinery capacity to meet current demand can also push prices higher.
Increased Demand and Seasonal Factors
Increased driving due to economic growth or seasonal factors plays a role in the rising demand for fuel.
- Seasonal Driving Trends: Summer vacations and holiday travel periods usually see a spike in fuel consumption, increasing demand and driving up prices.
- Economic Indicators: Strong economic growth often translates to increased consumer spending, including more driving and higher fuel consumption.
The Impact of Rising Fuel Costs on Consumers and Businesses
The 20-cent increase in fuel costs has a wide-ranging impact, affecting household budgets, businesses, and various industries.
Impact on Household Budgets
Higher gas prices directly impact consumers' disposable income.
- Reduced Spending Power: Increased fuel costs force many households to cut back on other expenses, impacting their overall spending habits.
- Budgeting Challenges: Families are finding it harder to manage their budgets as a larger portion of their income is now allocated to fuel.
- Inflationary Pressure: Rising fuel costs contribute to overall inflation, impacting the cost of living.
Effect on Transportation and Logistics
The transportation and logistics sectors are particularly vulnerable to fuel price hikes.
- Increased Shipping Costs: Businesses face increased shipping costs, impacting the price of goods and services.
- Higher Transportation Costs: Higher fuel costs translate to higher transportation costs for businesses, affecting profitability and potentially leading to price increases for consumers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Rising fuel costs can contribute to supply chain disruptions as businesses grapple with increased transportation expenses.
Ripple Effect on Other Industries
The impact extends beyond transportation, affecting various other sectors.
- Agriculture: Higher fuel costs increase the cost of farming and transportation of agricultural products, potentially impacting food prices.
- Tourism: Increased fuel prices can discourage travel, negatively impacting the tourism sector.
- Overall Economic Growth: Persistently high fuel costs can hinder overall economic growth by increasing the cost of production and transportation across various industries.
Potential Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the issue of rising fuel costs requires a multifaceted approach involving government intervention, energy efficiency, and a shift towards alternative fuels.
Government Intervention and Policies
Governments can play a vital role in mitigating the impact of fuel price volatility.
- Fuel Subsidies: Targeted fuel subsidies can provide temporary relief to vulnerable populations.
- Tax Relief: Reducing fuel taxes can lower the overall cost of fuel for consumers and businesses.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves: Utilizing strategic petroleum reserves can help stabilize prices during periods of supply disruptions.
Energy Efficiency and Conservation
Improving fuel efficiency is crucial in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Public Transport: Encouraging the use of public transportation can significantly reduce individual fuel consumption.
- Carpooling: Carpooling reduces the number of vehicles on the road, leading to lower fuel consumption.
- Fuel-Efficient Vehicles: Investing in fuel-efficient vehicles or hybrid/electric cars can significantly reduce fuel costs in the long run.
Alternative Fuels and Renewable Energy
Transitioning to alternative fuels and renewable energy sources is essential for long-term sustainability.
- Electric Vehicles: The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial in reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
- Biofuels: Exploring and utilizing biofuels as a sustainable alternative can contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Investing in solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources can help diversify our energy portfolio and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Conclusion
The recent 20-cent increase in average gas prices highlights the vulnerability of our economy to fuel price volatility. Fuel costs rise due to a complex interplay of factors, including increased crude oil prices, refinery capacity issues, and increased demand. This surge significantly impacts household budgets, businesses, and various industries. To mitigate the effects, a combination of government policies, energy efficiency measures, and a transition to alternative fuels and renewable energy is crucial. Stay informed about future changes in fuel costs and take steps to reduce your fuel consumption. Share this article to help spread awareness about rising fuel costs!

Featured Posts
-
 Vanja Mijatovic Promenila Ime Detalji O Promeni Imena
May 22, 2025
Vanja Mijatovic Promenila Ime Detalji O Promeni Imena
May 22, 2025 -
 Massive Fire At Franklin County Pa Chicken Farm 600 Foot Barn In Flames
May 22, 2025
Massive Fire At Franklin County Pa Chicken Farm 600 Foot Barn In Flames
May 22, 2025 -
 Route 581 Closed Following Box Truck Crash What We Know
May 22, 2025
Route 581 Closed Following Box Truck Crash What We Know
May 22, 2025 -
 Market Reaction Explaining Core Weave Inc Crwv S Thursday Stock Drop
May 22, 2025
Market Reaction Explaining Core Weave Inc Crwv S Thursday Stock Drop
May 22, 2025 -
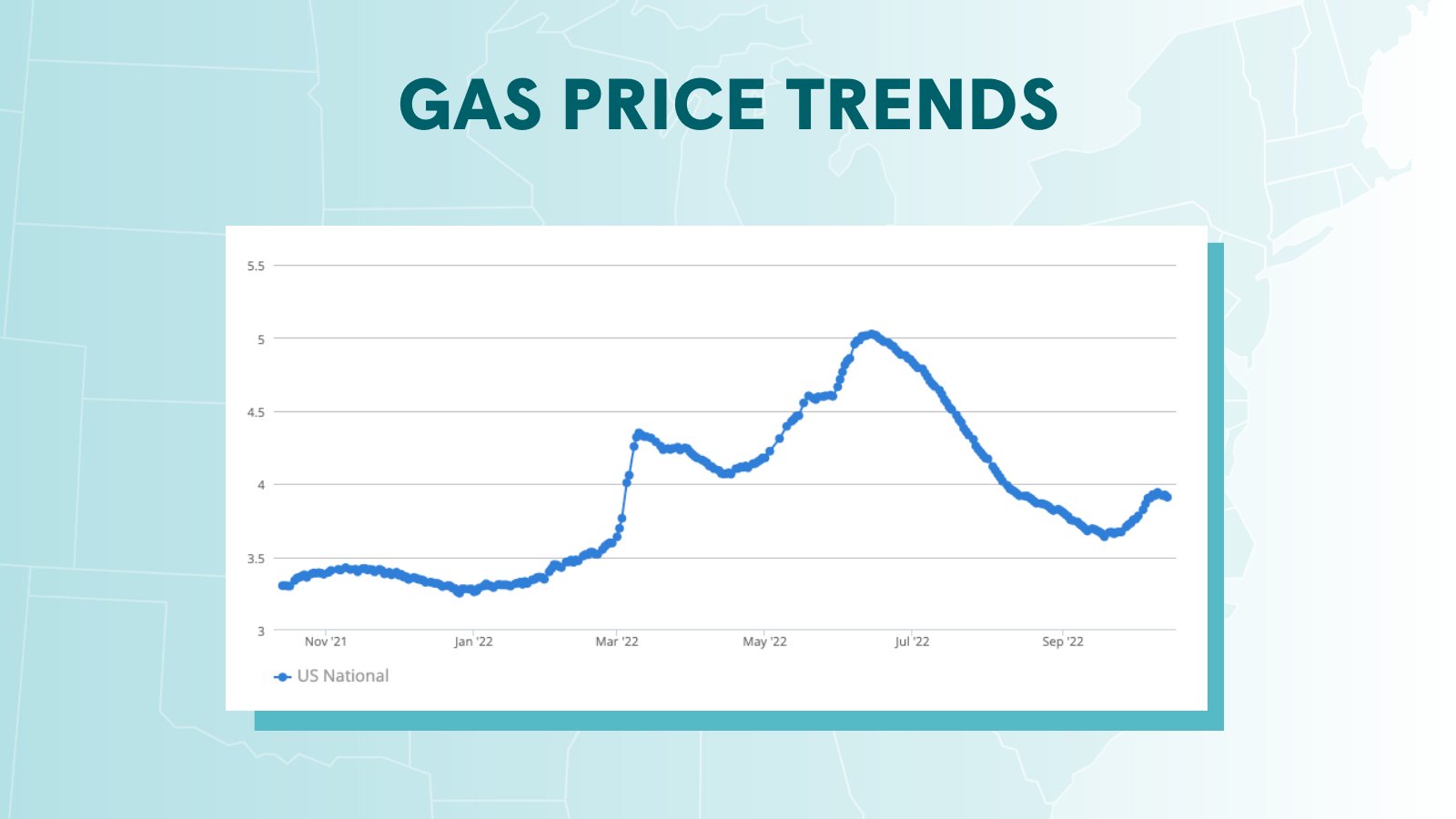 Weekly Virginia Gas Price Update From Gas Buddy
May 22, 2025
Weekly Virginia Gas Price Update From Gas Buddy
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Sobrecarga De Partidos La Real Sociedad Sufre Las Consecuencias Del Calendario Fifa
May 22, 2025
Sobrecarga De Partidos La Real Sociedad Sufre Las Consecuencias Del Calendario Fifa
May 22, 2025 -
 Khrvatska Protiv Shpani A Finaleto Na Ln Resheno Po Penali
May 22, 2025
Khrvatska Protiv Shpani A Finaleto Na Ln Resheno Po Penali
May 22, 2025 -
 El Impacto Del Calendario Fifa En La Real Sociedad Cansancio Y Riesgo De Lesiones
May 22, 2025
El Impacto Del Calendario Fifa En La Real Sociedad Cansancio Y Riesgo De Lesiones
May 22, 2025 -
 La Real Sociedad Y El Incesante Calendario Fifa Un Problema Sin Solucion
May 22, 2025
La Real Sociedad Y El Incesante Calendario Fifa Un Problema Sin Solucion
May 22, 2025 -
 El Virus Fifa La Real Sociedad Sin Respiro Tras La Avalancha De Partidos
May 22, 2025
El Virus Fifa La Real Sociedad Sin Respiro Tras La Avalancha De Partidos
May 22, 2025
