Femicide: Causes, Consequences, And Prevention Strategies

Table of Contents
Causes of Femicide
Femicide is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of societal, individual, and systemic factors. Addressing this global crisis requires a comprehensive understanding of these interconnected causes.
Societal Factors
Deeply rooted patriarchal norms and pervasive gender inequality are fundamental drivers of femicide. Misogyny, sexism, and harmful stereotypes that devalue women create an environment where violence is normalized, excused, or even condoned. Cultural norms that tolerate or even celebrate male dominance perpetuate a cycle of violence against women, leading to horrific outcomes like femicide.
- Lack of legal protection: Inadequate laws and weak enforcement against gender-based violence.
- Impunity for perpetrators: A lack of accountability for those who commit violence against women.
- Normalization of violence in media: The portrayal of violence against women in media contributes to its acceptance in society.
- Harmful traditional practices: Certain cultural practices, such as honor killings, directly contribute to femicide.
Individual Factors
While societal structures create fertile ground for femicide, individual factors also play a significant role. Perpetrators often exhibit specific personality traits, such as controlling behavior, extreme jealousy, and a sense of entitlement. Past experiences, including childhood trauma or witnessing domestic violence, can also contribute to violent tendencies. Substance abuse frequently exacerbates these issues. Intimate partner relationships are often the context for femicide, with controlling behavior, possessiveness, and threats of violence escalating to murder. Mental health issues may also play a role in some cases, although it's crucial to avoid using this as a sole explanation for such acts.
- Controlling behavior and possessiveness: A hallmark of many abusive relationships that often precede femicide.
- Past trauma and violence: Witnessing or experiencing violence in childhood can increase the risk of perpetrating violence.
- Substance abuse: Alcohol and drug use can significantly impair judgment and increase aggression.
- Mental health issues: While not a direct cause, underlying mental health conditions can sometimes contribute to violent behavior.
Systemic Issues
Weak law enforcement, ineffective judicial systems, and inadequate access to support services for victims of domestic abuse create systemic vulnerabilities that contribute to femicide. A lack of resources and funding for prevention programs further exacerbates the problem. Impartial investigations and prosecutions are crucial but often absent, leaving women vulnerable and perpetrators unaccountable.
- Inadequate police response: Failure to adequately investigate reports of domestic violence.
- Lack of access to shelters and support services: Women may lack safe places to flee abusive situations.
- Insufficient funding for prevention programs: Limited resources hinder the development and implementation of effective prevention strategies.
- Judicial bias and corruption: Unfair treatment of victims and leniency towards perpetrators in the legal system.
Consequences of Femicide
The consequences of femicide are far-reaching and devastating, impacting families, communities, and society as a whole.
Impact on Families and Communities
The loss of a woman due to femicide shatters families, leaving behind enduring emotional, psychological, and social scars. Children who witness or experience the loss of their mother suffer profound trauma, impacting their mental health and development for years to come. The economic impact on the family can be equally devastating, with the loss of income and increased financial strain. Communities are also negatively affected by the loss of a valued member and the pervasive fear that follows.
- Trauma and grief: Families experience immense emotional distress and prolonged grieving.
- Economic hardship: Loss of income and increased expenses related to funeral costs and legal proceedings.
- Social disruption: Communities grapple with fear, insecurity, and mistrust in the aftermath of femicide.
- Intergenerational trauma: The effects of femicide can extend across generations, impacting families for years to come.
Societal Implications
Femicide normalizes violence against women, erodes trust in institutions meant to protect them, and undermines efforts towards gender equality. It perpetuates a climate of fear, restricting women's freedom and safety. The widespread occurrence of femicide undermines social cohesion, and the cycle of violence continues unchecked.
- Erosion of trust in institutions: A lack of effective responses to violence against women damages trust in law enforcement and the justice system.
- Reduced women's participation in public life: Fear and insecurity limit women's ability to fully participate in society.
- Setback for gender equality initiatives: Femicide hinders progress towards gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Increased social instability: The high rate of femicide destabilizes communities and erodes social trust.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing femicide requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing legal reforms, educational initiatives, and the expansion of comprehensive support services.
Legal and Policy Reforms
Stronger laws, stricter enforcement, and improved judicial systems are crucial for holding perpetrators accountable. Comprehensive legislation addressing domestic violence and femicide, including mandatory reporting and protection orders, is essential. Improving the training and response of law enforcement agencies is also vital.
- Strengthening legislation against gender-based violence: Enacting and enforcing laws that specifically address femicide.
- Improving judicial processes: Ensuring fair and efficient investigations and prosecutions of femicide cases.
- Implementing mandatory reporting protocols: Requiring healthcare professionals, educators, and others to report suspected cases of domestic violence.
- Providing specialized training for law enforcement: Equipping law enforcement with the skills to effectively respond to and investigate cases of violence against women.
Educational Initiatives
Challenging harmful gender norms and stereotypes through comprehensive education campaigns is paramount. Educating boys and men about healthy relationships, consent, and the consequences of violence is crucial. Schools and communities play a vital role in fostering gender equality and challenging patriarchal attitudes.
- Gender equality education in schools: Integrating gender equality education into school curricula.
- Public awareness campaigns: Raising public awareness about femicide and its prevention.
- Bystander intervention training: Equipping individuals with the skills to intervene safely when witnessing violence.
- Men's engagement programs: Engaging men in the prevention of gender-based violence.
Support Services and Resources
Accessible and comprehensive support services are critical for survivors of domestic violence and those at risk of femicide. Shelters, hotlines, counseling services, and legal aid are vital, requiring increased funding and resources. Early intervention and support programs can help break the cycle of violence.
- Expanding access to shelters and safe houses: Providing safe and accessible shelter for survivors of domestic violence.
- Increasing funding for victim support organizations: Ensuring adequate resources for organizations that provide support to victims of violence.
- Providing legal aid and representation: Offering free or low-cost legal services to victims of violence.
- Developing early intervention programs: Identifying and supporting individuals at risk of becoming perpetrators or victims of violence.
Conclusion
Femicide is a devastating global crisis fueled by a complex interplay of societal, individual, and systemic factors. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting families, communities, and the progress towards gender equality. Preventing femicide requires a collective and sustained effort encompassing legal reforms, comprehensive education, and robust support services. Ending femicide demands urgent action, challenging ingrained patriarchal norms and ensuring accountability for perpetrators while simultaneously providing vital support to survivors. Learn more about how you can contribute to preventing femicide and support organizations working to end violence against women. Together, we can create a safer world for all.

Featured Posts
-
 Cartoon Network And Looney Tunes Unite In New 2025 Animated Short
May 21, 2025
Cartoon Network And Looney Tunes Unite In New 2025 Animated Short
May 21, 2025 -
 Liverpool Juara Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Prediksi Dan Daftar Juara Premier League Terakhir
May 21, 2025
Liverpool Juara Liga Inggris 2024 2025 Prediksi Dan Daftar Juara Premier League Terakhir
May 21, 2025 -
 Understanding The Name Of Peppa Pigs New Baby Sister
May 21, 2025
Understanding The Name Of Peppa Pigs New Baby Sister
May 21, 2025 -
 Nederlandse Bankieren Vereenvoudigd Een Praktische Handleiding Voor Tikkie
May 21, 2025
Nederlandse Bankieren Vereenvoudigd Een Praktische Handleiding Voor Tikkie
May 21, 2025 -
 David Walliams What Happened On Britains Got Talent
May 21, 2025
David Walliams What Happened On Britains Got Talent
May 21, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ragbrai And Beyond Exploring Scott Savilles Cycling Life
May 21, 2025
Ragbrai And Beyond Exploring Scott Savilles Cycling Life
May 21, 2025 -
 Prepare For Mild Temperatures And Dry Conditions
May 21, 2025
Prepare For Mild Temperatures And Dry Conditions
May 21, 2025 -
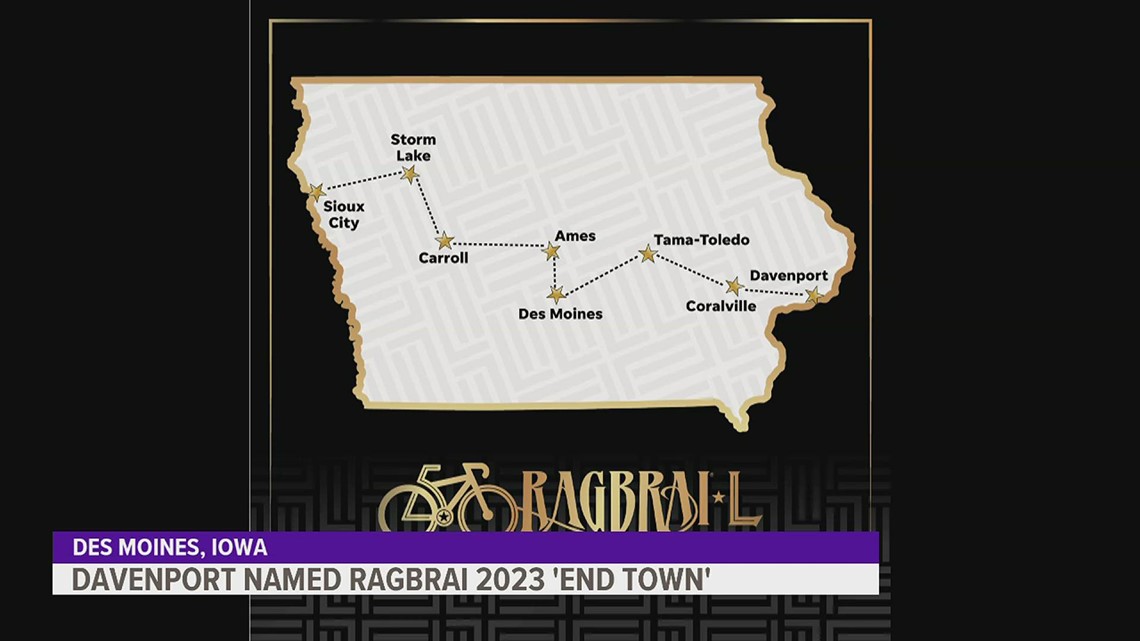 From Ragbrai To Daily Rides Scott Savilles Passion For Cycling
May 21, 2025
From Ragbrai To Daily Rides Scott Savilles Passion For Cycling
May 21, 2025 -
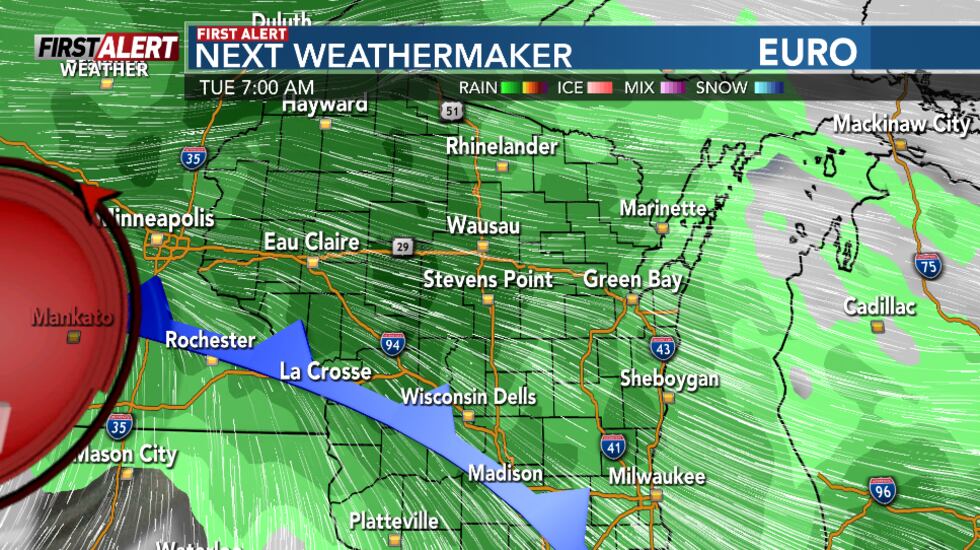 How To Predict Breezy And Mild Weather For Your Next Trip
May 21, 2025
How To Predict Breezy And Mild Weather For Your Next Trip
May 21, 2025 -
 Expecting Mild Temperatures Low Rain Probability This Week
May 21, 2025
Expecting Mild Temperatures Low Rain Probability This Week
May 21, 2025
