Declining Measles Cases In The United States: Understanding The Trends
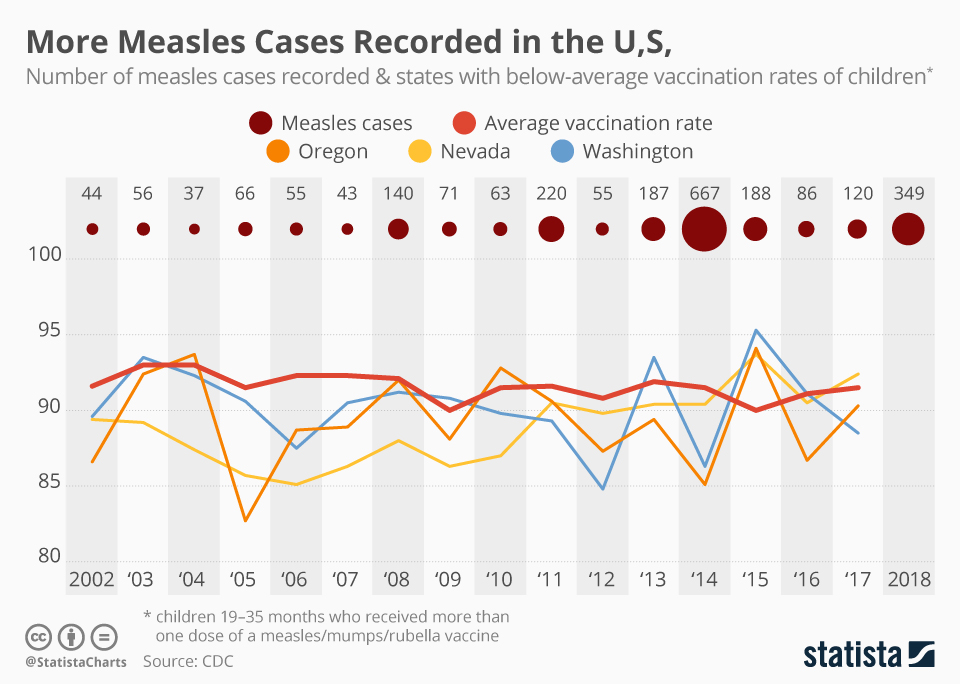
Table of Contents
H2: The Impact of the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella (MMR) Vaccine
The MMR vaccine stands as a cornerstone in the fight against measles. Its effectiveness in preventing measles infection is undeniable.
H3: Vaccine Effectiveness
The MMR vaccine boasts an impressive efficacy rate, significantly reducing the risk of contracting measles.
- Studies show a greater than 97% reduction in measles cases is attributable to widespread MMR vaccination.
- High vaccination rates create herd immunity, protecting even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
- The CDC reports that vaccine uptake rates in the US have fluctuated over time, with periods of higher and lower coverage, impacting the overall prevalence of measles.
However, challenges remain in achieving complete vaccination coverage. Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation and distrust, continues to pose a significant obstacle. Additionally, access to healthcare and vaccination services remains uneven across different socioeconomic groups, creating disparities in vaccination rates.
H2: Public Health Initiatives and Surveillance
Robust public health infrastructure and surveillance programs have played a crucial role in minimizing measles outbreaks.
H3: Enhanced Surveillance Programs
Improved disease surveillance and reporting systems have been instrumental in rapidly identifying and containing outbreaks.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and state health departments diligently track measles cases, facilitating prompt responses.
- Rapid case investigation and contact tracing are essential in preventing further spread within communities.
- Targeted public health campaigns effectively raise awareness about measles, its dangers, and the importance of vaccination.
These initiatives ensure early detection and facilitate rapid response to outbreaks, minimizing their impact and preventing widespread transmission. The ability to swiftly identify and isolate cases is key to controlling outbreaks and protecting vulnerable populations.
H2: Improved Healthcare Access and Infrastructure
Enhanced access to healthcare, particularly in underserved communities, has contributed significantly to the decline in measles cases.
H3: Increased Access to Healthcare
Improved access to healthcare directly translates into increased vaccination rates.
- Increased access to healthcare ensures timely vaccination for children, reducing the risk of infection.
- Community health clinics and outreach programs actively work to improve vaccination coverage in vulnerable populations.
- Persistent socioeconomic disparities contribute to uneven vaccination rates, highlighting the need for targeted interventions.
Addressing healthcare disparities is paramount to improving overall public health outcomes and preventing the resurgence of vaccine-preventable diseases like measles.
H2: Global Impact and Travel Restrictions
Global measles control efforts and international collaborations have had a significant impact on the US situation.
H3: Global Measles Control Efforts
International cooperation in vaccine development and distribution is crucial to global measles eradication efforts, indirectly benefiting the US.
- International travel restrictions and quarantine measures imposed during outbreaks help to prevent the import of measles cases.
- Global collaborations facilitate the sharing of best practices and resources in measles prevention and control.
- Containing measles globally prevents its reintroduction into the United States.
The interconnectedness of global health underscores the critical importance of international collaboration in disease control. The success of one nation in controlling measles benefits the global community, reducing the risk of re-emergence and outbreaks.
3. Conclusion
The dramatic decline in measles cases in the United States is a result of the synergistic effect of several factors: the high efficacy of the MMR vaccine, robust public health initiatives and surveillance, improved healthcare access, and global efforts to control measles. Maintaining this progress requires continued commitment to vaccination, robust public health infrastructure, and sustained international collaboration.
Understanding the factors behind the declining measles cases in the United States underscores the critical role of continued vaccination efforts. Learn more about protecting yourself and your community from measles today! Visit the CDC website () for more information on measles prevention and vaccination.

Featured Posts
-
 Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025
Alcaraz Vs Musetti A Monte Carlo Masters Showdown In 2025
May 30, 2025 -
 Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reasons For Investor Calm
May 30, 2025
Stock Market Valuations Bof As Reasons For Investor Calm
May 30, 2025 -
 Isere Les Attaques Contre Les Prisons Et La Visite Ministerielle Sous Le Feu Des Critiques
May 30, 2025
Isere Les Attaques Contre Les Prisons Et La Visite Ministerielle Sous Le Feu Des Critiques
May 30, 2025 -
 Is Bruno Fernandes Moving To Al Hilal Latest Transfer News
May 30, 2025
Is Bruno Fernandes Moving To Al Hilal Latest Transfer News
May 30, 2025 -
 Tunnel De Tende Date D Ouverture Confirmee Pour Juin Par Le Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025
Tunnel De Tende Date D Ouverture Confirmee Pour Juin Par Le Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025
