Current Status Of The Measles Outbreak Across The United States
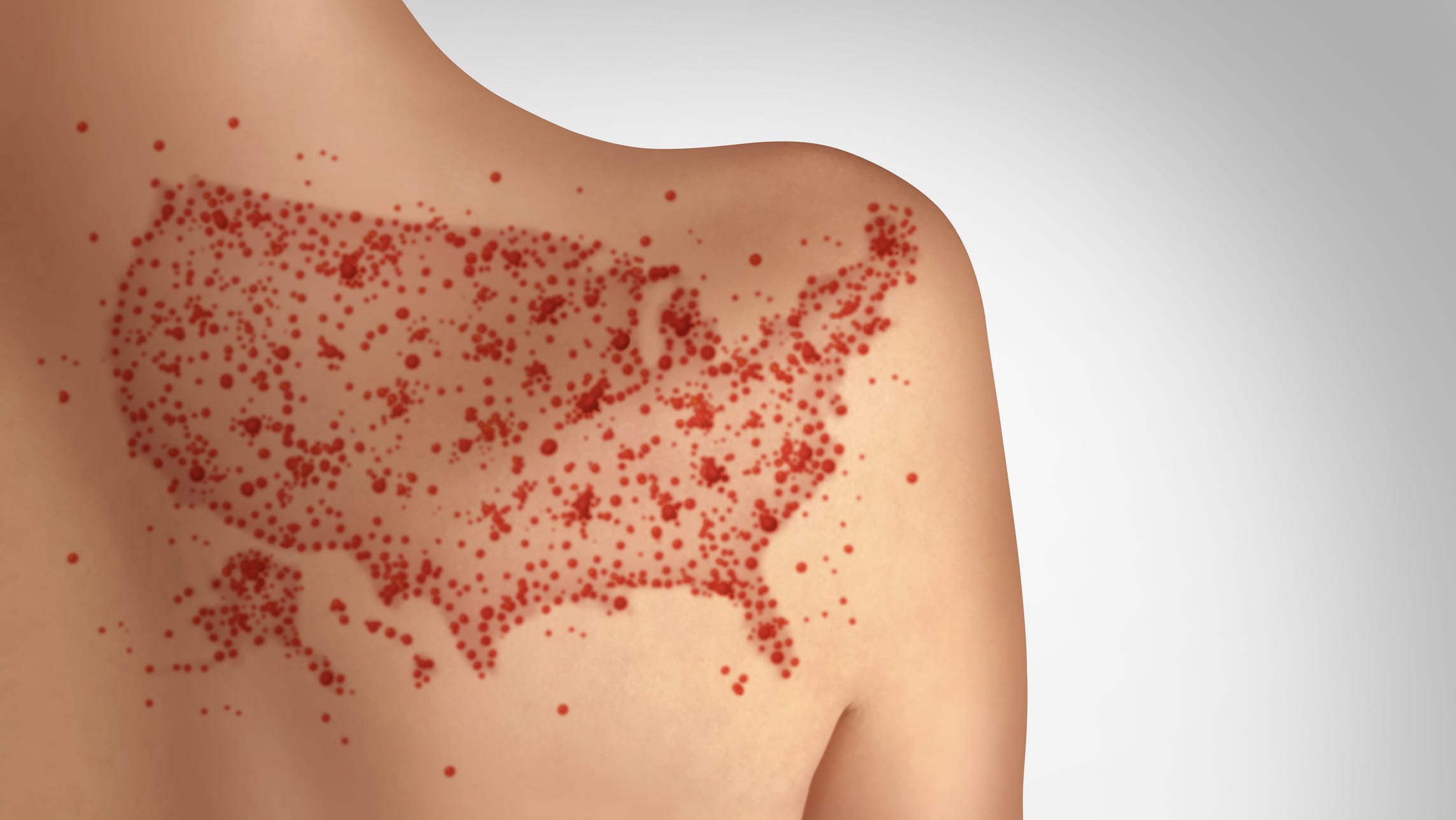
Table of Contents
Geographical Distribution of Measles Cases
The geographical distribution of measles cases across the US is uneven, with certain states experiencing significantly higher infection rates than others. A clear measles map illustrating the state-by-state distribution would reveal clusters of outbreaks, often concentrated in specific regions or communities. Tracking these regional outbreaks is vital for targeted public health interventions. Analyzing the data provides critical insights into the spread patterns and facilitates effective resource allocation.
- California: Reports a significant increase in measles cases this year, prompting intensified public health efforts.
- New York: Experienced a large measles outbreak in recent years, highlighting the potential for rapid spread in densely populated areas.
- Texas and Ohio: Have also seen notable increases in reported cases, indicating the widespread nature of the current measles outbreak.
- Tracking the spread of measles: Requires robust surveillance systems and close collaboration between state and local health departments. Data analysis is crucial for understanding the dynamics of the outbreak and guiding targeted interventions.
Demographics Affected by the Measles Outbreak
The measles outbreak disproportionately affects specific demographic groups, underscoring the vulnerability of certain populations. Understanding these vulnerabilities is essential for designing effective prevention and control strategies. The unvaccinated, particularly children under five years old, represent the most vulnerable group.
- Unvaccinated children under five years old: Are at the highest risk of severe complications from measles, including pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death.
- Outbreaks disproportionately affect communities: With limited access to healthcare, highlighting existing health inequities.
- Adults who received only one MMR dose: May have insufficient immunity and are at increased risk of contracting measles.
- Immunocompromised individuals: Are particularly vulnerable to severe measles complications due to their weakened immune systems.
Factors Contributing to the Measles Outbreak
The resurgence of measles in the US is a complex issue fueled by a convergence of factors. A decline in vaccination rates, fueled by vaccine hesitancy and the spread of misinformation, plays a significant role. The anti-vaccine movement and the proliferation of inaccurate information through social media platforms pose significant challenges to public health efforts.
- The spread of misinformation through social media: Is a major contributor to vaccine hesitancy and undermines public trust in established science.
- Decreased vaccination rates: Weaken community immunity, creating opportunities for the virus to spread rapidly.
- Lack of access to healthcare: Contributes to outbreaks in underserved communities, where vaccination rates may be lower.
- Erosion of herd immunity: Leaves vulnerable populations at greater risk of infection.
Public Health Response to the Measles Outbreak
Public health officials are actively working to contain the measles outbreak and prevent further spread. This involves a multi-pronged approach encompassing vaccination campaigns, public awareness initiatives, contact tracing, and quarantine measures. A coordinated and robust response is essential to control the outbreak effectively.
- Public health officials are conducting vaccination campaigns: In affected areas to increase vaccination rates among susceptible populations.
- Contact tracing is implemented: To identify and isolate infected individuals and their close contacts to prevent further transmission.
- Educational campaigns: Aim to combat misinformation, promote vaccine uptake, and emphasize the importance of measles prevention.
- Quarantine measures: May be implemented in specific situations to limit the spread of the virus.
The Importance of Measles Vaccination
The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is a safe and highly effective way to prevent measles. Vaccination is the most effective strategy for protecting individuals and communities from this highly contagious disease. Addressing concerns about vaccine safety with accurate information is critical.
- The MMR vaccine is safe and highly effective: In preventing measles, significantly reducing the risk of infection and severe complications.
- Vaccination is the most effective way: To protect individuals and communities from measles and to achieve herd immunity.
- Herd immunity protects vulnerable populations: Who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons.
Conclusion
The current measles outbreak in the United States represents a serious public health concern. The uneven geographical distribution, the vulnerability of specific demographic groups, and the factors contributing to the resurgence highlight the need for a multifaceted approach. Vaccination remains the most effective tool for preventing measles, and combating misinformation is critical to increasing vaccination rates and protecting communities. We must work together to improve access to vaccines, address vaccine hesitancy, and promote accurate information about measles prevention. Get vaccinated against measles, talk to your healthcare provider about the MMR vaccine, and share accurate information to help prevent measles in your community. Stay informed about the latest updates on US measles cases to remain vigilant and proactive in protecting yourself and your loved ones.

Featured Posts
-
 A Scheme For Benicio Del Toro The Story Behind The Gift
May 30, 2025
A Scheme For Benicio Del Toro The Story Behind The Gift
May 30, 2025 -
 Tunnel De Tende Date D Ouverture Confirmee Pour Juin Par Le Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025
Tunnel De Tende Date D Ouverture Confirmee Pour Juin Par Le Ministre Tabarot
May 30, 2025 -
 Epcot Flower And Garden Festival 2024 Dates Events And More
May 30, 2025
Epcot Flower And Garden Festival 2024 Dates Events And More
May 30, 2025 -
 Venue Virtual De Ticketmaster Revolucion En La Compra De Entradas
May 30, 2025
Venue Virtual De Ticketmaster Revolucion En La Compra De Entradas
May 30, 2025 -
 Fbi Most Wanted Season 6 Sneak Peek Remy And The Widower
May 30, 2025
Fbi Most Wanted Season 6 Sneak Peek Remy And The Widower
May 30, 2025
