COVID-19 Vaccines: Impact On Long COVID Incidence And Severity
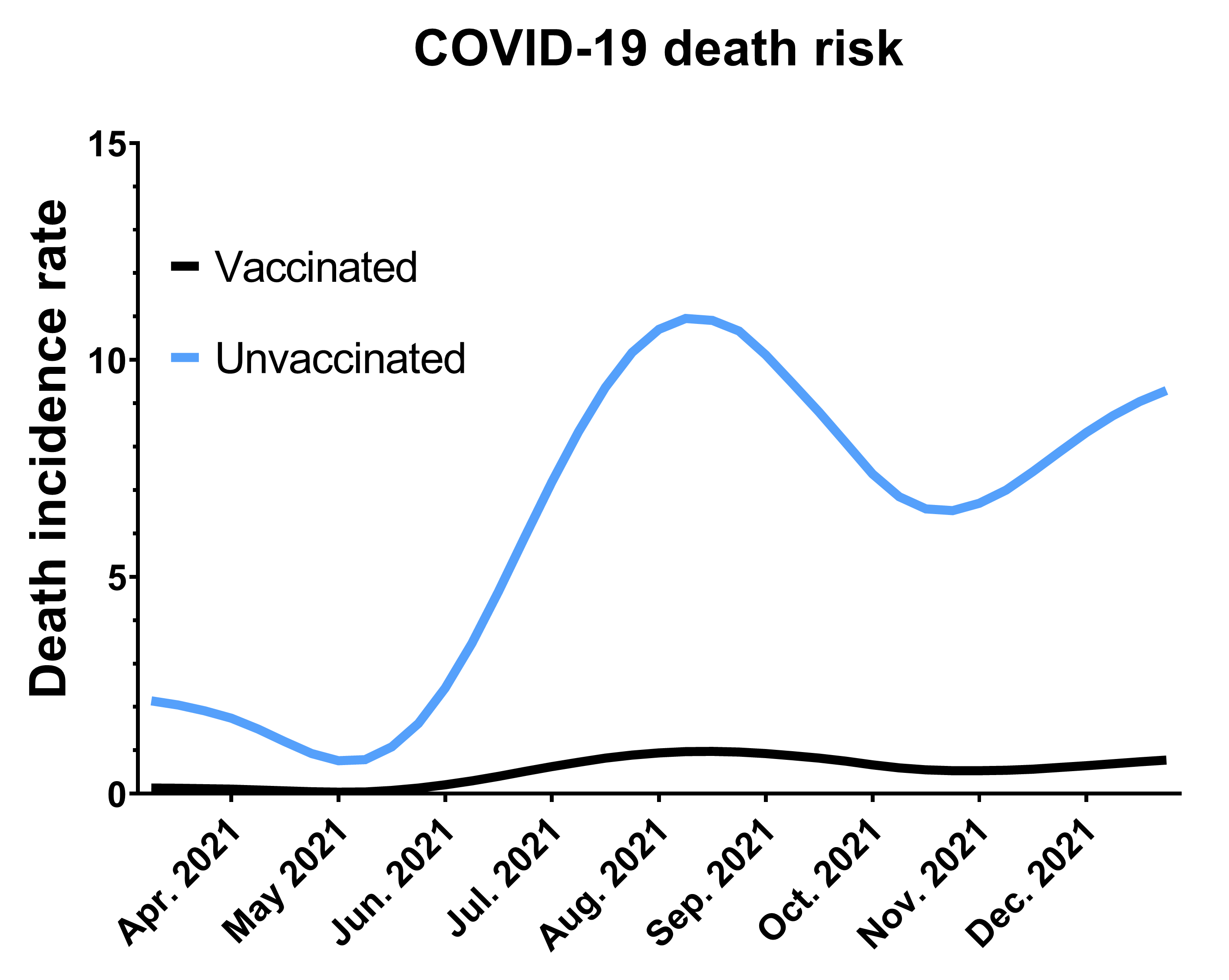
Table of Contents
Vaccine Efficacy in Preventing Long COVID
Numerous studies suggest that COVID-19 vaccines offer significant protection against developing Long COVID. Both mRNA vaccines (like Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna) and viral vector vaccines (like AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson) have demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the risk of this persistent condition.
- Key Findings: Several large-scale epidemiological studies show a substantial percentage reduction in Long COVID risk among vaccinated individuals compared to unvaccinated individuals. While the exact percentages vary based on factors like vaccine type, variant prevalence, and time since vaccination, the overall trend indicates a considerable protective effect. For example, some studies have reported a reduction of up to 50% in Long COVID risk after a full vaccination course.
- Specific Symptom Reduction: Vaccination has been linked to a reduced incidence of specific Long COVID symptoms, including fatigue, brain fog ("brain fog" is also a relevant keyword), shortness of breath, and persistent cough.
- Vaccine Type Comparison: While the effectiveness varies slightly between different vaccine types, the overall protective effect against Long COVID is consistently observed across all authorized vaccines. Ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of the nuances in effectiveness between different vaccines.
- Limitations and Ongoing Research: It's crucial to acknowledge the limitations of current studies. The ongoing evolution of the virus and its variants necessitates continuous monitoring and research to assess the long-term effectiveness of vaccines against emerging strains. Furthermore, the definition and diagnostic criteria for Long COVID remain an area of active development, which can affect the consistency of results across studies. Many studies are still ongoing to further validate and refine these findings.
Impact of Vaccination on Long COVID Severity
Even in individuals who contract COVID-19 after vaccination, studies indicate that vaccination significantly impacts the severity of Long COVID symptoms.
- Reduced Symptom Duration and Intensity: Vaccinated individuals experiencing Long COVID tend to report shorter symptom durations and less intense symptom experiences compared to their unvaccinated counterparts. This reduction in severity can significantly impact a patient's ability to return to their normal daily activities.
- Vaccinated vs. Unvaccinated: Comparisons between vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals with Long COVID reveal notable differences:
- Average Duration of Symptoms: Vaccinated individuals often experience a shorter duration of Long COVID symptoms.
- Prevalence of Debilitating Symptoms: The prevalence of debilitating symptoms like severe fatigue, persistent cognitive impairment ("brain fog"), and chronic pain is often lower in vaccinated individuals.
- Impact on Quality of Life: Overall, vaccinated individuals tend to experience a less significant reduction in their quality of life compared to unvaccinated individuals suffering from Long COVID.
Specific Vaccine Types and Their Impact on Long COVID
While all authorized COVID-19 vaccines demonstrate a protective effect against Long COVID, subtle differences in efficacy may exist. For example, studies might show slightly different levels of protection against specific Long COVID symptoms offered by Pfizer-BioNTech compared to Moderna or AstraZeneca. The inclusion of booster shots is also crucial, as these often significantly enhance protection against both initial infection and Long COVID. However, currently there's no definitive consensus on which vaccine provides the most comprehensive protection against Long COVID. Ongoing research is continually providing updated data and analyses on each vaccine’s efficacy.
Unanswered Questions and Future Research
Despite significant progress, several questions about the long-term impact of COVID-19 vaccines on Long COVID remain unanswered.
- Long-Term Studies: Longitudinal studies tracking vaccinated individuals over several years are essential to fully understand the vaccine's long-term protective effect. This includes understanding whether protection wanes over time, requiring booster doses.
- Variant-Specific Efficacy: The continuous emergence of new COVID-19 variants necessitates ongoing research to assess the efficacy of vaccines against emerging strains and their potential impact on Long COVID.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Research into therapeutic interventions for Long COVID is ongoing. Further investigation will determine whether vaccines offer additional protection to patients receiving such therapies.
Conclusion: COVID-19 Vaccines and the Fight Against Long COVID
In summary, the evidence strongly suggests that COVID-19 vaccines play a significant role in reducing both the incidence and severity of Long COVID. While further research is needed to address unanswered questions, the available data clearly support the crucial role of vaccination in protecting against this debilitating condition. The benefits of vaccination extend beyond immediate protection from acute infection; they also offer substantial protection against the long-term consequences of COVID-19. Stay updated on the latest research from reputable sources like the CDC and WHO, and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice on COVID-19 vaccination. Protect yourself from Long COVID – get vaccinated today! [Link to CDC website] [Link to WHO website]

Featured Posts
-
 Zaragoza Recibe Reconocimiento Europeo Por Su Patrimonio Cultural
May 29, 2025
Zaragoza Recibe Reconocimiento Europeo Por Su Patrimonio Cultural
May 29, 2025 -
 Meet Taylor Deardens Parents
May 29, 2025
Meet Taylor Deardens Parents
May 29, 2025 -
 Game 3 Cavaliers Defeat Pacers 126 104 Mitchell Scores 43
May 29, 2025
Game 3 Cavaliers Defeat Pacers 126 104 Mitchell Scores 43
May 29, 2025 -
 Partnership Announced Fincantieri And Tuis Uk Cruise Expansion
May 29, 2025
Partnership Announced Fincantieri And Tuis Uk Cruise Expansion
May 29, 2025 -
 Analyzing Albertas Oil Industry Levy Addressing Orphan Well Liabilities
May 29, 2025
Analyzing Albertas Oil Industry Levy Addressing Orphan Well Liabilities
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Part Time Position For Former Fox19 Meteorologist In Cleveland
May 31, 2025
Part Time Position For Former Fox19 Meteorologist In Cleveland
May 31, 2025 -
 Cleveland Guardians Home Opener Weather Patterns Over The Years
May 31, 2025
Cleveland Guardians Home Opener Weather Patterns Over The Years
May 31, 2025 -
 Fox19 Meteorologist Finds New Part Time Role In Cleveland
May 31, 2025
Fox19 Meteorologist Finds New Part Time Role In Cleveland
May 31, 2025 -
 Former Fox19 Meteorologist Takes Part Time Cleveland Job
May 31, 2025
Former Fox19 Meteorologist Takes Part Time Cleveland Job
May 31, 2025 -
 Cleveland Browns Draft Mel Kiper Jr S Top Pick At No 2 Overall
May 31, 2025
Cleveland Browns Draft Mel Kiper Jr S Top Pick At No 2 Overall
May 31, 2025
