Climate Change Fuels The Spread Of Dangerous Fungi
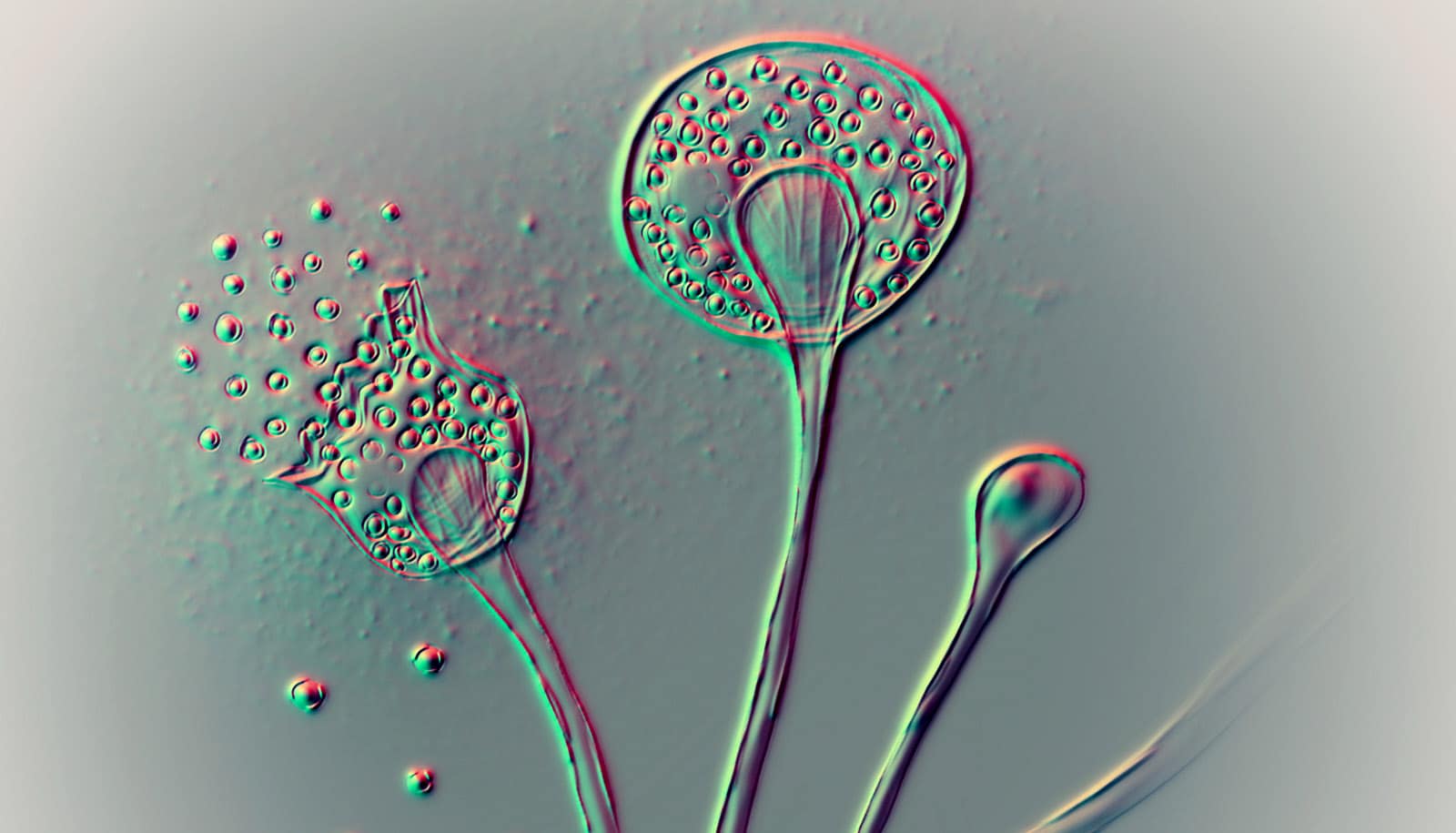
Table of Contents
Warmer Temperatures and Increased Fungal Growth
Higher temperatures significantly accelerate fungal metabolic processes. This means fungi grow and reproduce faster in warmer conditions, leading to increased fungal biomass and a wider geographic distribution. Species like Candida auris, a multi-drug resistant yeast causing serious bloodstream infections, and Aspergillus fumigatus, a common mold that can cause life-threatening lung infections, thrive in warmer environments.
The impact of rising temperatures on fungal growth is multifaceted:
- Increased prevalence in previously unaffected regions: Fungi are expanding their geographical ranges into areas previously too cold to support their growth.
- Longer growing seasons for fungal pathogens: Warmer temperatures extend the period during which fungi can actively reproduce and spread, increasing the risk of infection.
- Higher infection rates in susceptible populations: Immunocompromised individuals, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to increased fungal activity.
Altered Rainfall Patterns and Humidity: Perfect Breeding Grounds
Changes in rainfall patterns and heightened humidity create perfect breeding grounds for fungal spores. Water availability is crucial for fungal germination and dispersal; increased humidity provides the moist environment necessary for spore growth, while fluctuating rainfall can lead to both concentrated spore populations and wider dispersal. Diseases like histoplasmosis (caused by Histoplasma capsulatum) and coccidioidomycosis (caused by Coccidioides species) are exacerbated by increased humidity and dust storms, respectively, events frequently associated with altered weather patterns.
Extreme weather events further compound the problem:
- Flooding: Creates ideal conditions for waterborne fungi to proliferate and spread.
- Droughts: Concentrate fungal spores in remaining water sources, increasing infection risk for those exposed.
- Increased humidity following extreme weather: Leads to outbreaks of fungal diseases in affected regions.
Impact on Human Health
Climate change significantly increases the risk of fungal infections in humans. Immunocompromised individuals are especially vulnerable, facing a higher risk of severe and potentially fatal infections. The emergence of new fungal diseases and the development of drug-resistant strains further complicate the situation, posing significant challenges to public health.
The specific health risks include:
- Increased rates of respiratory fungal infections: More frequent and intense exposure to fungal spores in warmer, more humid environments.
- Higher incidence of invasive fungal diseases: Weakened immune systems combined with increased fungal exposure leads to a greater likelihood of invasive infections.
- Development of drug-resistant fungal strains: The overuse of antifungal medications is leading to the emergence of resistant strains, making treatment more difficult.
Impact on Ecosystems and Agriculture
Climate change's influence extends beyond human health, significantly impacting ecosystems and agriculture. Fungal pathogens affecting plants and animals are thriving in changing environmental conditions, leading to substantial economic losses and ecological disruption.
The implications for agriculture are severe:
- Loss of biodiversity due to fungal infections: Widespread fungal diseases can decimate plant and animal populations, disrupting ecosystems and reducing biodiversity.
- Disruption of ecosystem services: Fungal diseases impacting pollinators and other beneficial organisms can disrupt crucial ecosystem services.
- Reduced crop yields and food security concerns: Fungal diseases significantly reduce crop yields, threatening global food security, especially in vulnerable regions.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Combating the threat of climate change-fueled fungal diseases requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing mitigation and adaptation strategies. Mitigation focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions to slow climate change, while adaptation strategies emphasize preparedness and response mechanisms to reduce the impact of fungal diseases.
Practical steps include:
- Reducing carbon emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources and implementing sustainable land-use practices are crucial in slowing climate change.
- Improving sanitation and hygiene practices: Basic hygiene measures can help prevent the spread of fungal infections.
- Developing climate-resilient agriculture practices: Implementing drought-resistant crops and integrated pest management strategies can reduce crop losses due to fungal diseases.
- Investing in research and development of new antifungal drugs and treatments: Developing new antifungal drugs and therapies is crucial to combat drug-resistant strains.
- Strengthening public health surveillance and early detection systems: Early detection and rapid response are essential in managing fungal outbreaks.
Conclusion: Addressing the Threat of Climate Change-Fueled Fungal Diseases
The evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates a strong link between climate change and the spread of dangerous fungi. The impact on human health, ecosystems, and agriculture is significant and requires immediate attention. Understanding the complex interplay between climate change and fungal diseases is crucial to developing effective strategies to mitigate this growing threat. We must prioritize research into climate change impacts on fungal growth, enhance public health preparedness against climate-related fungal infections, and advocate for policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve global health infrastructure. Ignoring the connection between climate change and the spread of dangerous fungi risks severe consequences for human and environmental health. Let's act now to address this emerging challenge.

Featured Posts
-
 Public Safety Issues In North Myrtle Beach Due To Excess Water Consumption
May 26, 2025
Public Safety Issues In North Myrtle Beach Due To Excess Water Consumption
May 26, 2025 -
 Paris Roubaix 2023 Mathieu Van Der Poel Attacked Seeks Legal Recourse
May 26, 2025
Paris Roubaix 2023 Mathieu Van Der Poel Attacked Seeks Legal Recourse
May 26, 2025 -
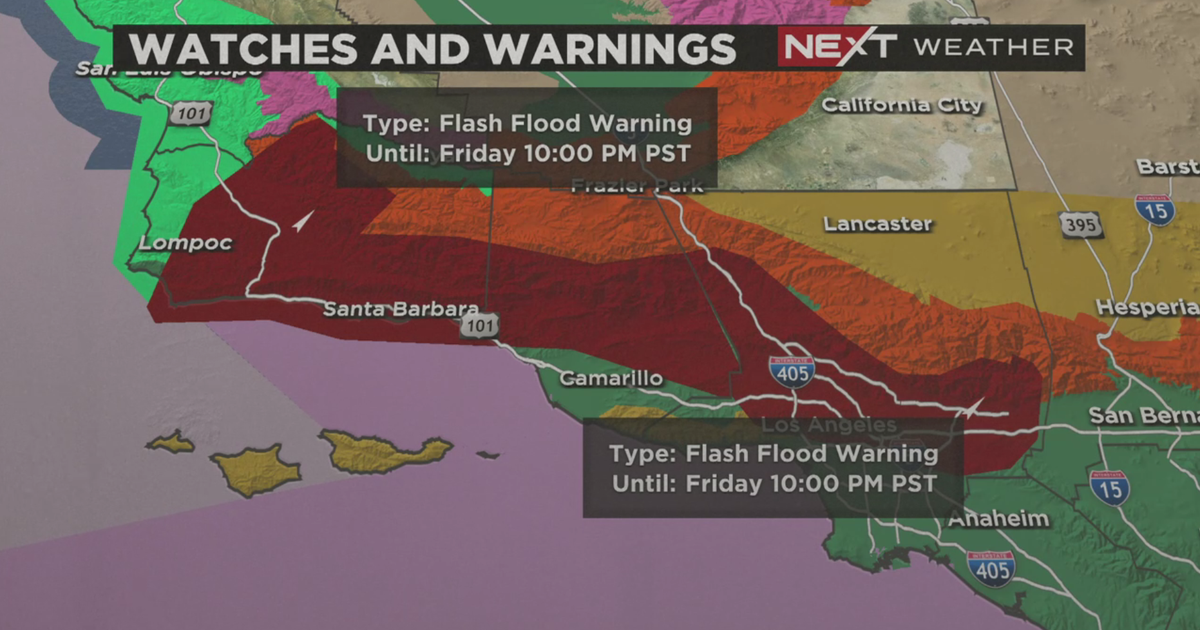 Bradford And Wyoming Counties Flash Flood Warning Until Tuesday
May 26, 2025
Bradford And Wyoming Counties Flash Flood Warning Until Tuesday
May 26, 2025 -
 Link Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Race Sprint Pukul 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025
Link Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Race Sprint Pukul 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025 -
 Uncovering The Truth The Prince His Money Manager And The Monaco Scandal
May 26, 2025
Uncovering The Truth The Prince His Money Manager And The Monaco Scandal
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analysis Mc Kenna Tuanzebe Phillips Cajuste Ipswich Towns Week In Review
May 28, 2025
Analysis Mc Kenna Tuanzebe Phillips Cajuste Ipswich Towns Week In Review
May 28, 2025 -
 Mc Kenna Impresses Tuanzebes Strong Week Phillips And Cajuste Face Challenges Ipswich Town Update
May 28, 2025
Mc Kenna Impresses Tuanzebes Strong Week Phillips And Cajuste Face Challenges Ipswich Town Update
May 28, 2025 -
 Phillips Potential Leeds Return Examining The Transfer Talk
May 28, 2025
Phillips Potential Leeds Return Examining The Transfer Talk
May 28, 2025 -
 Leeds United Transfer News Kalvin Phillips Return On The Cards
May 28, 2025
Leeds United Transfer News Kalvin Phillips Return On The Cards
May 28, 2025 -
 Is A Kalvin Phillips Return To Leeds United On The Cards This Summer
May 28, 2025
Is A Kalvin Phillips Return To Leeds United On The Cards This Summer
May 28, 2025
