Climate Change And The Rise Of Deadly Fungi: A Growing Threat
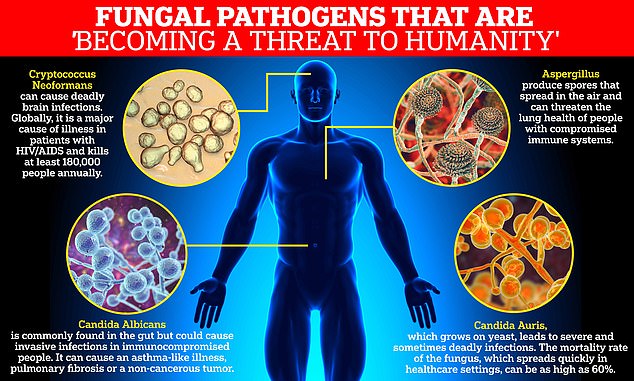
Table of Contents
The Impact of Climate Change on Fungal Growth and Distribution
Climate change significantly alters environmental conditions, creating ideal breeding grounds for fungal pathogens. Two key factors are at play:
Temperature and Humidity
Rising global temperatures and increased humidity create optimal conditions for fungal growth and spore dispersal. Many fungi thrive in warmer, wetter conditions.
- Examples: Species like Aspergillus fumigatus, a common cause of opportunistic infections, show increased growth rates at higher temperatures.
- Optimal Ranges: Many pathogenic fungi demonstrate optimal growth between 25-30°C and high humidity (above 80%). Climate change is pushing more regions into these ranges.
- Vulnerable Regions: Tropical and subtropical regions are particularly vulnerable, experiencing more frequent and intense heat waves and periods of high humidity, leading to increased fungal outbreaks.
Altered Ecosystems
Climate change disrupts ecosystems, weakening plant and animal hosts and making them more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Weakened Hosts: Stress from drought, heat, or flooding compromises the immune systems of plants and animals, increasing their vulnerability to fungal pathogens.
- Geographic Expansion: Warmer temperatures allow fungi to expand their geographic ranges, invading previously unaffected areas. This can lead to the emergence of new diseases in regions not previously exposed.
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss: The destruction of natural habitats disrupts ecological balances, potentially increasing the prevalence of certain fungi and creating opportunities for new fungal diseases to emerge.
Increased Exposure to Fungal Spores
Changes in weather patterns and increased air pollution contribute to greater human exposure to fungal spores.
- Extreme Weather Events: Increased frequency and intensity of storms, floods, and wildfires disperse fungal spores over wider areas, increasing human exposure.
- Air Quality: Climate change exacerbates air pollution, which can further contribute to respiratory problems, making individuals more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Vulnerable Populations: Immunocompromised individuals, the elderly, and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to increased fungal spore exposure.
Examples of Deadly Fungi Thriving in a Changing Climate
Several deadly fungi are exhibiting increased prevalence and virulence due to climate change:
Candida auris
This highly drug-resistant fungus is a growing concern globally. Its rise is partly attributed to climate change-induced environmental shifts.
- Characteristics: C. auris is highly resistant to multiple antifungal drugs, making treatment challenging.
- Transmission: It spreads easily in healthcare settings, leading to outbreaks and high mortality rates.
- Geographic Spread: Its geographic range is expanding, potentially linked to increased temperatures and humidity.
Coccidioides species
The geographic range of Coccidioides, the fungus causing coccidioidomycosis (valley fever), is expanding due to climate change.
- Symptoms: Valley fever symptoms range from mild flu-like illness to severe pneumonia.
- Increased Prevalence: Areas previously unaffected by valley fever are now experiencing increased cases, likely due to changing climatic conditions.
- Vulnerable Populations: Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of severe complications.
Other Emerging Fungal Threats
Other fungi, such as Cryptococcus gattii and various Aspergillus species, are also showing increased prevalence linked to climate change, impacting both human and environmental health. Their spread highlights the broad and interconnected nature of this threat.
Mitigating the Threat of Climate Change-Driven Fungal Infections
Addressing this growing threat requires a multi-pronged approach:
Climate Change Mitigation
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to curb climate change and its impact on fungal diseases.
- Individual Actions: Adopting sustainable practices like reducing carbon footprint, using public transport, and conserving energy.
- Governmental Policies: Implementing policies to transition to renewable energy sources and improve energy efficiency.
- International Cooperation: Global cooperation is essential for effective climate change mitigation efforts.
Improved Surveillance and Diagnosis
Enhanced monitoring and improved diagnostic tools are critical for early detection and management of fungal infections.
- Early Detection Strategies: Implementing robust surveillance systems to track fungal outbreaks and identify emerging threats.
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests: Developing rapid and accurate diagnostic tests to facilitate timely treatment.
- Global Data Sharing: Fostering international collaboration on data sharing to improve global understanding of fungal disease patterns.
Development of New Antifungal Treatments
Research and development of new and effective antifungal drugs are urgently needed.
- Challenges: Developing new antifungals is challenging due to the complex nature of fungal cells and the risk of toxicity.
- Research Funding: Increased investment in antifungal drug research is critical.
- Novel Approaches: Exploring novel therapeutic approaches, such as immunotherapy and combination therapies.
Conclusion
The strong link between Climate Change and the Rise of Deadly Fungi is undeniable. The increasing prevalence and virulence of fungal pathogens pose a significant threat to human and environmental health. Urgent action is needed to mitigate climate change, improve surveillance and diagnosis of fungal infections, and develop new antifungal treatments. By advocating for climate action and supporting research into antifungal treatments, we can work together to protect ourselves and future generations from this growing threat. Understanding the complex interplay between climate change and fungal diseases is crucial for building a resilient future.

Featured Posts
-
 Death Of Hells Angels Biker Prompts Memorial Service
May 25, 2025
Death Of Hells Angels Biker Prompts Memorial Service
May 25, 2025 -
 Southern Vacation Hotspot Responds To Negative Safety Rating After Shooting Incident
May 25, 2025
Southern Vacation Hotspot Responds To Negative Safety Rating After Shooting Incident
May 25, 2025 -
 Funeral Held For Hells Angels Member Killed In Motorcycle Accident
May 25, 2025
Funeral Held For Hells Angels Member Killed In Motorcycle Accident
May 25, 2025 -
 130 Years After Dreyfus Affair French Parliament Considers Posthumous Promotion
May 25, 2025
130 Years After Dreyfus Affair French Parliament Considers Posthumous Promotion
May 25, 2025 -
 Hsv Aufstieg In Hamburg Die Rueckkehr In Die Bundesliga
May 25, 2025
Hsv Aufstieg In Hamburg Die Rueckkehr In Die Bundesliga
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Baffie Et Ardisson Polemique Sur Les Blagues Tele
May 25, 2025
Baffie Et Ardisson Polemique Sur Les Blagues Tele
May 25, 2025 -
 Thierry Ardisson Et Laurent Baffie La Verite Sur Leur Dispute
May 25, 2025
Thierry Ardisson Et Laurent Baffie La Verite Sur Leur Dispute
May 25, 2025 -
 Laurent Baffie Thierry Ardisson Defend Ses Blagues Controversees
May 25, 2025
Laurent Baffie Thierry Ardisson Defend Ses Blagues Controversees
May 25, 2025 -
 Ardisson Et Baffie Fin D Une Amitie Accusations De Connerie Et De Machisme
May 25, 2025
Ardisson Et Baffie Fin D Une Amitie Accusations De Connerie Et De Machisme
May 25, 2025 -
 Thierry Ardisson Et Laurent Baffie Une Brouille Durable
May 25, 2025
Thierry Ardisson Et Laurent Baffie Une Brouille Durable
May 25, 2025
