Casper Faces Zebra Mussel Infestation: A Local Discovery
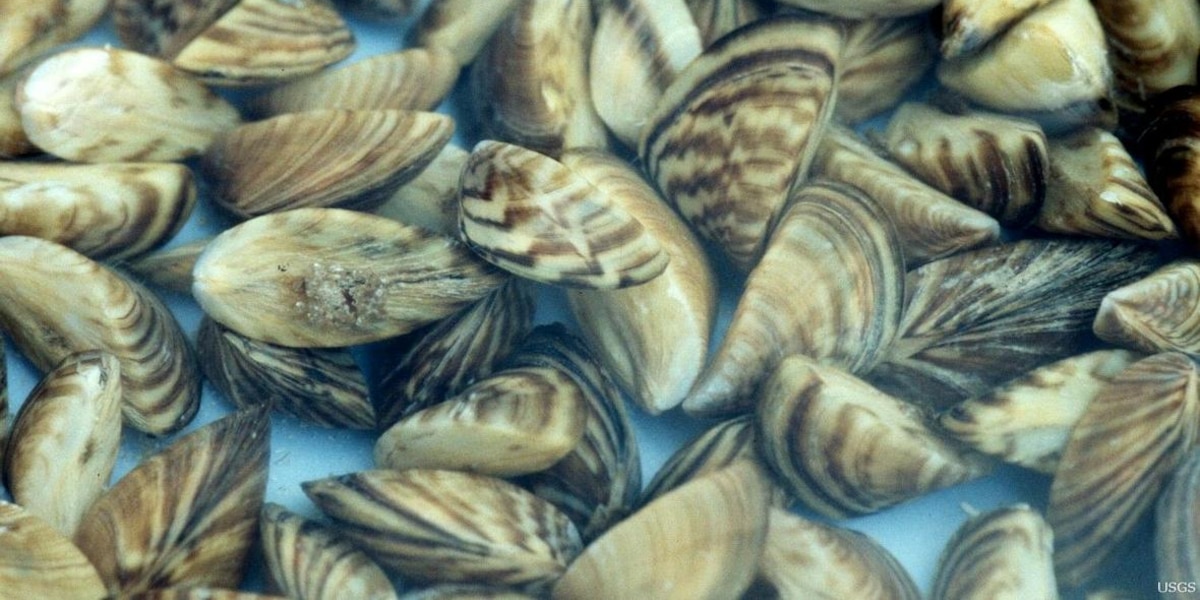

Table of Contents
The Threat of Zebra Mussel Infestation in Casper
Understanding Zebra Mussels
Zebra mussels ( Dreissena polymorpha) are small freshwater mollusks with a remarkable ability to rapidly reproduce and spread. Their invasive nature poses a significant threat to Casper's waterways.
- Native Habitat: Native to the Black and Caspian Seas in Eurasia.
- Invasive Species Status: Designated as an invasive species in North America and many other regions.
- Reproductive Strategies: They are prolific breeders, with a single female capable of producing millions of microscopic larvae annually. These larvae are dispersed by currents and can attach to various surfaces.
- Preferred Habitats: They thrive in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, attaching to hard surfaces such as rocks, pipes, and boat hulls.
- Negative Impacts: Zebra mussels clog water intake pipes, causing costly damage to infrastructure. They also outcompete native mussels for food and habitat, disrupting the entire ecosystem. Their sharp shells can also injure swimmers and wildlife.
The Ecological Impact on Casper's Waterways
The ecological consequences of a zebra mussel infestation in Casper could be severe. The introduction of this invasive species disrupts the delicate balance of the local ecosystem.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Zebra mussels outcompete native mussels and other filter-feeding organisms, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
- Disruption of Food Webs: The alteration of the food web can impact fish populations that rely on native mussels as a food source.
- Impact on Fish Populations: Changes in water clarity and the availability of food can negatively affect fish populations.
- Potential for Algal Blooms: By filtering large quantities of water, zebra mussels can increase water clarity, potentially leading to increased sunlight penetration and promoting algal blooms. This further disrupts the balance of the ecosystem. Specific impacts on Casper's unique ecosystem, such as the North Platte River, require further study.
Economic Consequences for Casper
The economic impact of a zebra mussel infestation in Casper could be substantial, affecting various sectors reliant on clean and functional water infrastructure.
- Costs of Water Treatment: Clogged water intake pipes require costly cleaning and maintenance, increasing the burden on taxpayers.
- Repairs to Infrastructure: Damage to water pipes, irrigation systems, and other infrastructure necessitates significant repair costs.
- Potential Impact on Tourism and Recreation: The presence of zebra mussels can negatively impact recreational activities like swimming, boating, and fishing, potentially decreasing tourism revenue.
- Potential Impact on Fishing Industries: The disruption of aquatic life can lead to decreased fish populations, affecting local fishing industries. The full economic impact is still being assessed, but it is likely to be substantial given the rapid spread of these invasive mussels.
Current Efforts to Combat the Zebra Mussel Infestation in Casper
Local and State Response
Both local and state agencies are actively involved in addressing the zebra mussel infestation in Casper. These efforts are crucial in mitigating the long-term damage.
- Monitoring Efforts: Regular water sampling and surveys are conducted to monitor the extent of the infestation.
- Control Measures: Various control measures are being explored, including the use of chlorine or other chemical treatments, as well as physical removal methods.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educational campaigns are underway to inform the public about zebra mussels and preventive measures.
- Collaboration with Other Agencies: Effective management requires collaboration among local, state, and federal agencies. Specific details of the Casper response are still developing, but the commitment to address the issue is evident.
Community Involvement and Prevention Strategies
Community participation is essential in preventing the further spread of zebra mussels in Casper.
- Boat Cleaning Protocols: Thoroughly cleaning and inspecting boats before and after use in infested waters is critical. This includes draining all water from bilges and livewells.
- Proper Disposal of Bait: Never dispose of live bait in waterways.
- Reporting Sightings: Reporting any sightings of zebra mussels to the appropriate authorities is crucial for early detection and intervention.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Opportunities for community members to participate in monitoring and removal efforts can significantly contribute to the control of this invasive species. Citizens are encouraged to engage actively in these efforts.
Long-Term Strategies and Outlook for Casper
Research and Monitoring
Continued research and monitoring are vital for understanding the long-term ecological and economic impacts of the zebra mussel infestation in Casper.
- Ongoing Monitoring Programs: Continuous monitoring of water bodies is crucial to track the spread of zebra mussels and assess the effectiveness of control measures.
- Research on Control Techniques: Research into novel and effective control techniques is ongoing.
- Collaboration with Researchers: Collaboration with universities and research institutions can provide valuable insights and support for management efforts.
Predicting Future Impacts
Eradicating zebra mussels once established is extremely challenging, making long-term management a necessity.
- Potential Long-Term Ecological Changes: The long-term ecological effects of zebra mussels on Casper's waterways require continuous monitoring and assessment.
- Ongoing Costs of Management: Managing the infestation will require sustained investment in control measures and monitoring.
- Potential for Future Outbreaks: The potential for future outbreaks in other areas needs to be proactively addressed through strict prevention measures.
Conclusion
The discovery of zebra mussels in Casper poses a significant threat to the city's environment and economy. The rapid reproductive rate and destructive nature of these invasive mollusks demand immediate and sustained action. Local, state, and community efforts are underway to manage the infestation, but long-term vigilance and collaborative strategies are crucial. The success of controlling this zebra mussel infestation in Casper depends on continued monitoring, research, and the active participation of the community. Stay informed, participate in prevention efforts, and report any sightings to the Wyoming Game and Fish Department or other relevant authorities to help protect our local waterways from this devastating invasive species. Visit the Wyoming Game and Fish Department website for more information on zebra mussel identification and prevention strategies.

Featured Posts
-
 Core Weave Stock Recent News And Market Trends
May 22, 2025
Core Weave Stock Recent News And Market Trends
May 22, 2025 -
 A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
 Original Sin Season 1 Re Examining Debra Morgans Fate In Light Of The Finale
May 22, 2025
Original Sin Season 1 Re Examining Debra Morgans Fate In Light Of The Finale
May 22, 2025 -
 Air Traffic Control Outages Beyond Newarks Black Screens And Silent Radios
May 22, 2025
Air Traffic Control Outages Beyond Newarks Black Screens And Silent Radios
May 22, 2025 -
 Real Madrid In Yeni Teknik Direktoerue Arda Gueler Icin Olumlu Bir Gelisme Mi
May 22, 2025
Real Madrid In Yeni Teknik Direktoerue Arda Gueler Icin Olumlu Bir Gelisme Mi
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Xay Dung Cau Ma Da Ket Noi Giao Thong Hai Tinh Dong Nai
May 22, 2025
Xay Dung Cau Ma Da Ket Noi Giao Thong Hai Tinh Dong Nai
May 22, 2025 -
 Kien Nghi Xay Dung Tuyen Duong 4 Lan Xe Tu Dong Nai Den Binh Phuoc Qua Rung Ma Da
May 22, 2025
Kien Nghi Xay Dung Tuyen Duong 4 Lan Xe Tu Dong Nai Den Binh Phuoc Qua Rung Ma Da
May 22, 2025 -
 Du An Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Kien Nghi Voi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Du An Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Dong Nai Kien Nghi Voi Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Den Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Den Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 De Xuat Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
De Xuat Xay Dung Duong 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
