Canada's Economy: Addressing The Overvalued Canadian Dollar
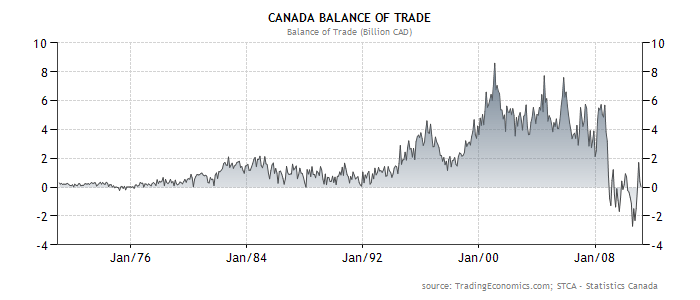
Table of Contents
The strength of the Canadian dollar, the "Loonie," has become a double-edged sword for Canada's economy. While a strong CAD can benefit consumers through lower import costs, it simultaneously presents significant challenges to Canadian exporters and overall economic growth. This article delves into the complexities of an overvalued Canadian dollar and explores potential solutions to navigate this intricate economic landscape. We will examine the factors contributing to the overvaluation, its consequences, and potential strategies for mitigation, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more robust Canadian economy.
<h2>Understanding the Overvaluation of the Canadian Dollar</h2>
<h3>Factors Contributing to an Overvalued CAD:</h3>
Several interconnected factors contribute to the current valuation of the Canadian dollar. A strong CAD isn't always indicative of a healthy economy; understanding the underlying causes is crucial. These include:
- Increased Commodity Prices: Booming prices for Canadian commodities like oil and natural gas significantly increase demand for the CAD, driving up its value. Higher export revenues lead to increased capital inflow, strengthening the currency.
- Higher Interest Rates: The Bank of Canada's (BoC) interest rate decisions directly impact the CAD. Higher interest rates compared to other major economies make Canadian investments more attractive to foreign investors, increasing demand for the CAD and pushing up its value.
- Strong Investor Confidence: Positive economic indicators and a stable political climate boost investor confidence in the Canadian economy, leading to increased foreign investment and a higher CAD exchange rate.
- Geopolitical Factors: During times of global uncertainty, the Canadian dollar is often seen as a safe-haven currency. This increased demand for safety pushes up the CAD's value, even if underlying economic fundamentals don't entirely support it.
The impact of each factor is complex and intertwined. For example, high oil prices boost the CAD, but a sudden drop can significantly weaken it.
<h3>Measuring Overvaluation:</h3>
Determining whether the CAD is truly overvalued requires sophisticated analysis. Economists employ several methods:
- Purchasing Power Parity (PPP): PPP compares the cost of a basket of goods and services in different countries to determine the fair exchange rate. A significant deviation from PPP suggests overvaluation or undervaluation.
- Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER): The REER measures the CAD's value against a basket of currencies, adjusted for inflation. A high REER indicates a potentially overvalued currency.
These methods aren't perfect and offer different perspectives, but they provide valuable insights into the CAD's valuation.
<h3>Consequences of an Overvalued CAD:</h3>
An overvalued Canadian dollar poses several significant challenges:
-
Reduced Export Competitiveness: Canadian goods and services become more expensive for international buyers, impacting export volumes and revenues. This negatively impacts industries relying on exports, leading to decreased profitability and potential job losses.
-
Increased Trade Deficit: Cheaper imports lead to higher import volumes and a wider trade deficit, potentially impacting the country's balance of payments.
-
Slower Economic Growth: Reduced export revenues and a trade deficit contribute to slower economic growth overall. The impact is particularly felt in export-oriented sectors.
-
Impact on Specific Sectors: Industries like manufacturing and agriculture, heavily reliant on exports, are particularly vulnerable to the effects of an overvalued CAD. Reduced competitiveness forces them to cut costs, potentially impacting employment and innovation.
-
Bullet points detailing the negative impacts on various industries and the economy:
- Reduced profits for export-oriented businesses
- Job losses in affected industries
- Decreased investment in export sectors
- Potential for economic stagnation
<h2>Strategies to Address the Overvalued Canadian Dollar</h2>
Addressing the overvalued Canadian dollar requires a multifaceted approach involving government policies, central bank actions, and proactive measures from the private sector.
<h3>Government Policies:</h3>
Government intervention can play a vital role. Strategies could include:
- Fiscal Policy Adjustments: Targeted tax incentives or subsidies for export-oriented industries could enhance their competitiveness in the global marketplace, offsetting the negative effects of a strong CAD.
- Targeted Support for Export Sectors: Investing in research and development, infrastructure improvements, and skills development programs tailored to export-focused sectors can strengthen their competitiveness.
<h3>Bank of Canada's Role:</h3>
The Bank of Canada (BoC) employs monetary policy tools to influence the CAD exchange rate:
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Lowering interest rates can make Canadian investments less attractive to foreign investors, potentially reducing demand for the CAD and easing its overvaluation. However, this can also fuel inflation.
- Quantitative Easing: While less frequently used, quantitative easing involves injecting liquidity into the financial system, potentially influencing the exchange rate.
<h3>Diversification of the Canadian Economy:</h3>
Reducing reliance on commodity exports is crucial:
- Fostering Growth in Other Sectors: Investing in sectors like technology, services, and renewable energy can create a more diversified and resilient economy, less vulnerable to fluctuations in commodity prices and exchange rates.
- Strategies for Economic Diversification: Government support for innovation, entrepreneurship, and skills development in non-commodity sectors are crucial steps.
<h3>Improving Export Competitiveness:</h3>
Enhance competitiveness through:
- Innovation and Technological Advancements: Investing in research and development, adopting advanced technologies, and promoting innovation within industries can help Canadian businesses create higher-value products and services that command premium prices.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Modernizing infrastructure – including transportation, communication, and energy – enhances efficiency and reduces costs, making Canadian businesses more competitive globally.
<h2>Long-Term Outlook and Predictions for the Canadian Dollar</h2>
Predicting the future trajectory of the Canadian dollar is challenging due to its sensitivity to global economic conditions and domestic factors.
<h3>Economic Forecasts:</h3>
Expert opinions vary, but many forecasts consider various factors including global economic growth, commodity price fluctuations, and interest rate differentials. These forecasts should be viewed cautiously as they are subject to change based on unforeseen events.
<h3>Potential Risks and Uncertainties:</h3>
Several factors could significantly impact the CAD's future value:
- Global Recession: A global economic downturn could negatively impact demand for Canadian exports and weaken the CAD.
- Shifts in Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in oil, natural gas, and other commodity prices will continue to impact the CAD's value significantly.
- Political Instability: Political uncertainty, both domestically and internationally, can negatively impact investor confidence and the CAD's value.
- Unexpected Geopolitical Events: Unforeseen global events can create volatility and unpredictability in currency markets.
<h2>Conclusion</h2>
The overvalued Canadian dollar presents both opportunities and challenges for Canada's economy. Understanding the factors contributing to its valuation and the consequences of this overvaluation is critical for policymakers, businesses, and individuals. The strategies outlined above—including government policies, BoC actions, economic diversification, and improved export competitiveness—offer a path towards mitigating the negative impacts and fostering sustainable economic growth. Staying informed about the Canadian economy and the fluctuations of the Canadian dollar is crucial. Understanding the complexities of an overvalued Canadian dollar is essential for navigating the future and ensuring the long-term health of the Canadian economy. For further information on the Canadian economy and exchange rates, consult the Bank of Canada website and other reputable financial news sources.

Featured Posts
-
 Xrp Rally Analysis Of The Us Presidents Article On Trumps Ripple Connection
May 08, 2025
Xrp Rally Analysis Of The Us Presidents Article On Trumps Ripple Connection
May 08, 2025 -
 Ben Affleck Matt Damons Calculated Success In Hollywood
May 08, 2025
Ben Affleck Matt Damons Calculated Success In Hollywood
May 08, 2025 -
 Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Singer Ella Mai New Commercial Fuels Speculation
May 08, 2025
Nba Star Jayson Tatum Welcomes Son With Singer Ella Mai New Commercial Fuels Speculation
May 08, 2025 -
 Canadas Trade Overture Will Washington Listen
May 08, 2025
Canadas Trade Overture Will Washington Listen
May 08, 2025 -
 The Great Decoupling Impacts On Businesses And Consumers
May 08, 2025
The Great Decoupling Impacts On Businesses And Consumers
May 08, 2025
