Assessing The Impact: Congo's Cobalt Export Ban And The Upcoming Quota System

Table of Contents
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the world's leading producer of cobalt, a crucial mineral for electric vehicle batteries and other technological advancements. Recent announcements regarding a potential cobalt export ban and the implementation of a quota system have sent shockwaves through the global supply chain. This article assesses the potential impact of Congo's cobalt export ban and the upcoming quota system on global markets, industry players, and the DRC itself. We will explore the implications for electric vehicle manufacturing, battery production, and the broader geopolitical landscape. Understanding the ramifications of Congo's cobalt export ban is critical for navigating this evolving market.
H2: The Current State of Cobalt Mining in the DRC
The DRC's cobalt mining landscape is complex and multifaceted. It's characterized by a blend of large-scale, industrial mining operations and a significant informal sector dominated by artisanal miners. This duality presents both opportunities and challenges.
-
Overview of DRC cobalt production volume and global market share: The DRC accounts for over 70% of global cobalt production, making it a dominant force in the market. This concentration of supply makes the country's policies highly influential on global prices and availability.
-
Discussion of artisanal mining practices and their challenges: Artisanal mining, while providing livelihoods for many, often involves unsafe working conditions, child labor, and significant environmental damage. This sector lacks the regulatory oversight and safety standards of formal mining operations.
-
Analysis of existing export regulations and their effectiveness: Current export regulations in the DRC have been criticized for their lack of transparency and enforcement, leading to concerns about revenue leakage and unsustainable practices. Improving regulatory frameworks is crucial for responsible cobalt production.
-
Examination of the involvement of multinational corporations in cobalt mining: Major multinational companies source cobalt from the DRC, directly or indirectly. Their involvement highlights the interconnectedness of the global supply chain and the responsibility these corporations bear in ensuring ethical and sustainable sourcing.
H2: Analyzing the Proposed Cobalt Export Ban and Quota System
The proposed cobalt export ban and quota system aim to reshape the DRC's cobalt industry. The government's stated goal is to increase domestic processing of cobalt, generating greater value within the country and attracting foreign investment in refining facilities.
-
Details of the proposed ban or quota, including timelines and exemptions: The specifics of the proposed ban or quota system are still evolving. However, it is likely to involve phased implementation, with potential exemptions for certain buyers or types of cobalt products. Clear timelines and transparent criteria are crucial for successful implementation.
-
Government's stated objectives behind the policy change: Besides boosting domestic processing, the government aims to improve revenue collection, enhance environmental protection, and create more high-skilled jobs within the DRC.
-
Analysis of the legal and political feasibility of implementing the ban/quota: The success of the ban or quota hinges on effective implementation, requiring strong legal frameworks, robust enforcement mechanisms, and political stability. Challenges could include resistance from international stakeholders and the informal sector.
-
Potential loopholes and challenges in enforcement: The complexity of the cobalt supply chain, coupled with potential corruption, could lead to loopholes and difficulties in enforcement. Monitoring and transparency are vital to avoid undermining the policy's objectives.
H3: Economic Implications for the DRC
The economic implications for the DRC are complex and potentially far-reaching. While domestic processing holds the promise of increased revenue and job creation, risks also exist.
-
Potential for increased revenue generation through domestic processing: Adding value to cobalt domestically—through refining and processing—can significantly increase the DRC's revenue compared to exporting raw ore.
-
Risks associated with reduced export earnings and market volatility: A complete ban could lead to short-term losses in export revenue, potentially impacting government finances and social programs. Market volatility, driven by changes in global demand, adds another layer of risk.
-
Opportunities for job creation and economic diversification within the DRC: Developing a robust domestic cobalt industry could create numerous jobs in refining, processing, and related sectors, contributing to economic diversification.
-
Impact on government revenue and social programs: Government revenues are significantly linked to cobalt exports; therefore, the policy's success depends on generating equivalent or greater revenue from domestic processing.
H2: Global Market Impacts of Congo's Cobalt Restrictions
Congo's cobalt restrictions will undoubtedly reverberate across the global market, impacting prices, supply chains, and geopolitical relations.
-
Predicted impact on cobalt prices and global supply chains: Reduced supply from the DRC could lead to significant cobalt price increases, disrupting the electric vehicle and battery industries. Supply chains will need to adapt to secure alternative sources.
-
Analysis of potential shifts in sourcing strategies by battery manufacturers and electric vehicle producers: Manufacturers will likely diversify their sourcing strategies, seeking alternative cobalt sources or exploring alternative battery technologies that use less cobalt.
-
Examination of alternative cobalt sources and their viability: Other countries, such as Australia, Canada, and Indonesia, are exploring cobalt mining, but their production volumes are currently far lower than the DRC's.
-
Discussion of the potential for geopolitical tensions due to the restricted supply: The DRC's dominant position in the cobalt market could lead to geopolitical tensions as countries compete for access to the remaining supply.
H2: Ethical and Environmental Considerations
Ethical and environmental concerns are paramount in the DRC's cobalt mining sector. The proposed changes offer an opportunity to address these issues.
-
Concerns about child labor and human rights abuses in artisanal cobalt mining: The informal sector is plagued by human rights abuses, including child labor and unsafe working conditions. The new regulations should prioritize tackling these issues.
-
Environmental impact of cobalt mining, including deforestation and water pollution: Cobalt mining can significantly damage the environment, causing deforestation, water pollution, and soil degradation. Sustainable mining practices are essential.
-
Potential for the new regulations to improve environmental and social standards: The proposed changes present an opportunity to implement stricter environmental and social safeguards, driving improvements across the industry.
-
The role of international organizations and NGOs in monitoring and improving conditions: International collaboration and NGO involvement are critical for monitoring compliance, providing support for community development, and ensuring the ethical sourcing of cobalt.
Conclusion:
Congo's cobalt export ban and the upcoming quota system represent a significant shift in the global cobalt market. While the intention might be to improve domestic processing, increase revenue, and address ethical concerns, the actual impact will depend heavily on the effective implementation of these new regulations. The global community needs to closely monitor the situation and collaborate with the DRC government to ensure a sustainable, ethical, and equitable cobalt supply chain. Further analysis and proactive strategies are necessary to navigate the complexities of Congo's cobalt export ban and the upcoming quota system to mitigate potential disruptions and foster a responsible industry. Understanding the implications of Congo's cobalt export ban is crucial for all stakeholders. Proactive planning and collaboration are key to mitigating the potential negative impacts of Congo’s cobalt export ban and ensuring the long-term stability of the global cobalt market.

Featured Posts
-
 Microsoft Announces Major Job Cuts 6 000 Employees Impacted
May 16, 2025
Microsoft Announces Major Job Cuts 6 000 Employees Impacted
May 16, 2025 -
 Gurriels Pinch Hit Rbi Single Delivers Padres 1 0 Victory Over Braves
May 16, 2025
Gurriels Pinch Hit Rbi Single Delivers Padres 1 0 Victory Over Braves
May 16, 2025 -
 The King Of Davoss Demise Causes And Consequences
May 16, 2025
The King Of Davoss Demise Causes And Consequences
May 16, 2025 -
 Coquimbo Unido Vs Everton Vina Reporte Del Partido 0 0
May 16, 2025
Coquimbo Unido Vs Everton Vina Reporte Del Partido 0 0
May 16, 2025 -
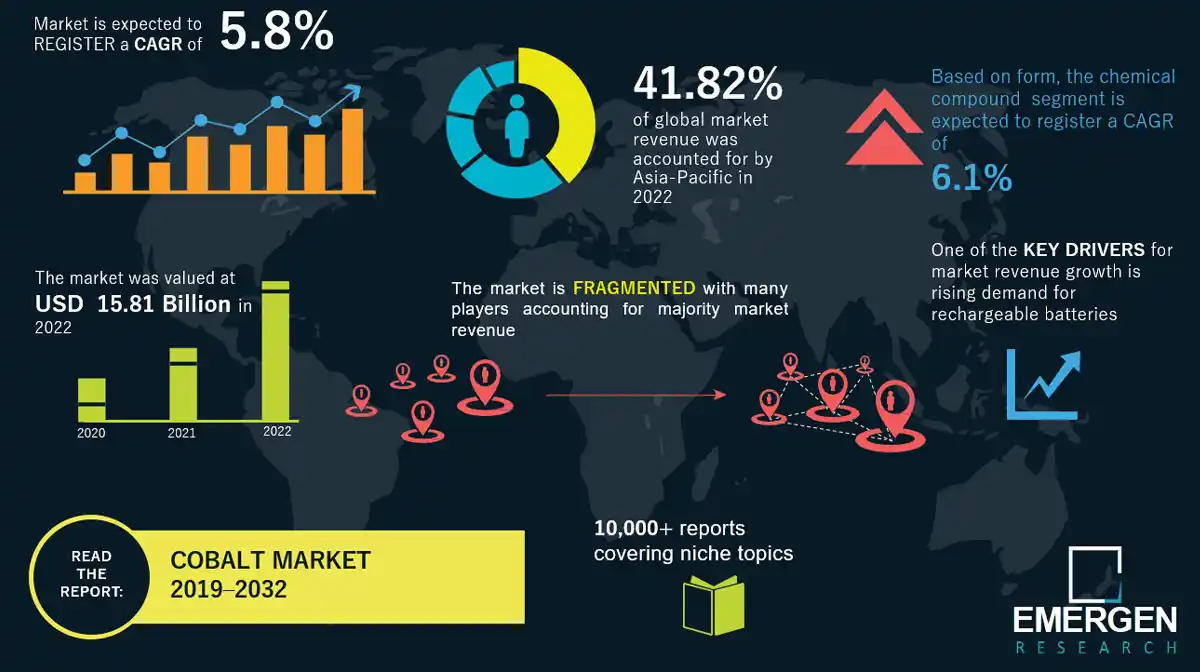 The Cobalt Market After Congos Export Ban Awaiting The Quota Plan
May 16, 2025
The Cobalt Market After Congos Export Ban Awaiting The Quota Plan
May 16, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ohtanis Selfless Act Celebrating Teammates Home Run Above His Own
May 16, 2025
Ohtanis Selfless Act Celebrating Teammates Home Run Above His Own
May 16, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Los Angeles Dodgers Offseason Activity
May 16, 2025
Analyzing The Los Angeles Dodgers Offseason Activity
May 16, 2025 -
 Dodgers Recall Hyeseong Kim Is He Ready For The Majors
May 16, 2025
Dodgers Recall Hyeseong Kim Is He Ready For The Majors
May 16, 2025 -
 Freeman And Kims Home Runs Lead Dodgers To Victory Over Giants
May 16, 2025
Freeman And Kims Home Runs Lead Dodgers To Victory Over Giants
May 16, 2025 -
 Dodgers Offseason Review Examining The Roster Changes
May 16, 2025
Dodgers Offseason Review Examining The Roster Changes
May 16, 2025
