Affordable Housing: A Realistic Approach (Gregor Robertson)

Table of Contents
Understanding the Affordable Housing Crisis
The affordable housing crisis is a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. Millions struggle to afford rent or mortgages, while homelessness continues to rise. The gap between rising housing costs and stagnant wages is widening, forcing many into precarious living situations. This isn't just a problem for low-income individuals; it affects families across a wide range of incomes who are finding it increasingly difficult to secure safe and stable housing.
Contributing factors to this crisis are multifaceted and interconnected:
- High housing costs relative to average income: In many areas, housing costs consume a disproportionately large percentage of household income, leaving little left for essential needs.
- Lack of available rental units below market rate: A severe shortage of affordable rental units exacerbates the problem, creating intense competition for limited resources.
- Increased homelessness and housing insecurity: The lack of affordable housing is a leading driver of homelessness, leaving vulnerable populations exposed to the elements and lacking basic necessities.
- Impact on economic growth and social well-being: The affordable housing crisis hampers economic growth by limiting workforce mobility and increasing healthcare costs associated with housing instability. It also negatively impacts social well-being, leading to increased stress and reduced overall quality of life.
Innovative Solutions for Affordable Housing Development
Creating more affordable housing requires a multi-pronged approach, encompassing diverse strategies and innovative solutions. Several models can effectively increase the supply of affordable housing units:
Density and Mixed-Use Development
Increasing housing density through thoughtful urban planning and mixed-use zoning can significantly increase the availability of housing units while reducing land costs. By allowing for a variety of housing types and commercial spaces in the same area, mixed-use developments create vibrant, walkable communities and reduce reliance on cars.
- Example: Converting underutilized commercial spaces into affordable housing units.
- Benefit: Increased housing density, reduced reliance on cars, and more vibrant communities.
Inclusionary Zoning
Inclusionary zoning policies require developers of new housing projects to include a specific percentage of affordable units within their developments. This ensures that affordable housing is integrated into new communities, preventing the segregation of low-income families.
- Example: Requiring 20% of units in a new apartment complex to be designated as affordable housing.
- Benefit: Guarantees affordable housing within new developments, promoting social equity.
Government Subsidies and Incentives
Government funding and tax credits are crucial for supporting the development and preservation of affordable housing. These incentives can make projects financially viable that would otherwise be unfeasible.
- Example: Providing low-interest loans or grants to developers of affordable housing projects.
- Benefit: Makes affordable housing projects financially feasible.
Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborations between government agencies and private developers can leverage the strengths of both sectors, leading to more efficient and impactful affordable housing development.
- Example: A partnership between a city government and a private developer to build a mixed-income housing complex.
- Benefit: Combines public resources with private sector expertise and efficiency.
Community Land Trusts
Community Land Trusts (CLTs) are non-profit organizations that acquire and hold land in perpetuity, ensuring that housing built on that land remains permanently affordable. This innovative model protects residents from market fluctuations and secures long-term affordability.
- Example: A CLT acquiring land and developing affordable homes that are sold or rented to low- and moderate-income families.
- Benefit: Permanently affordable housing, preventing displacement due to rising market prices.
Addressing Barriers to Affordable Housing
Despite the existence of viable solutions, several obstacles hinder the creation and preservation of affordable housing.
NIMBYism (Not In My Backyard)
Community resistance to new housing developments ("NIMBYism") often delays or prevents affordable housing projects. Addressing these concerns through transparent communication, community engagement, and thoughtful urban planning is crucial.
- Solution: Engage with communities early in the planning process, addressing concerns about density, traffic, and other potential impacts.
Regulatory Hurdles
Complex permitting processes and restrictive zoning regulations can significantly slow down and increase the cost of affordable housing projects. Streamlining these processes is essential.
- Solution: Simplify permitting procedures and update zoning regulations to encourage higher density and diverse housing options.
Funding Limitations
A chronic shortage of funding for affordable housing initiatives is a major barrier. Increased public and private investment is needed to address this critical gap.
- Solution: Advocate for increased government funding and explore creative funding mechanisms, such as impact investing.
The Role of Community Engagement in Affordable Housing Initiatives
Engaging residents in the planning and development of affordable housing projects is vital for building consensus and ensuring that projects meet the needs of the community. Effective methods include:
- Public forums: Open discussions to gather feedback and address concerns.
- Surveys: Collecting data to understand community priorities and preferences.
- Participatory design processes: Involving residents in the design and development of projects.
By fostering inclusive and transparent processes, developers can address community concerns and build support for affordable housing initiatives.
Finding Realistic Paths to Affordable Housing
Addressing the affordable housing crisis demands a multifaceted approach that incorporates the diverse strategies discussed above. We must confront the root causes of the problem—rising housing costs, stagnant wages, restrictive zoning, and insufficient funding—while simultaneously implementing innovative solutions. The role of community engagement in fostering collaboration and addressing concerns cannot be overstated.
To create a future where everyone has access to safe, decent, and affordable housing, we must all actively participate. Learn more about affordable housing initiatives in your community, support affordable housing organizations, and advocate for policy changes that prioritize affordable housing solutions. Find affordable housing solutions near you and get involved; the future of our communities depends on it.

Featured Posts
-
 La Caf Prend Position Sur Le Sahara Occidental Les Details
May 27, 2025
La Caf Prend Position Sur Le Sahara Occidental Les Details
May 27, 2025 -
 Hbcu Spring Breaks Resurgence The Story Of Orange Crush 2025 On Tybee Island
May 27, 2025
Hbcu Spring Breaks Resurgence The Story Of Orange Crush 2025 On Tybee Island
May 27, 2025 -
 Urgent Response Needed Nine Killed In Katsina Attack Policeman Included
May 27, 2025
Urgent Response Needed Nine Killed In Katsina Attack Policeman Included
May 27, 2025 -
 Le Congres Du Ps Bouamrane Pour L Union Faure En Ligne De Mire
May 27, 2025
Le Congres Du Ps Bouamrane Pour L Union Faure En Ligne De Mire
May 27, 2025 -
 Osimhen To Chelsea Malouda Believes Transfer Would Be Excellent
May 27, 2025
Osimhen To Chelsea Malouda Believes Transfer Would Be Excellent
May 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Joint Venture Manitoba And Nunavut Develop Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Infrastructure
May 30, 2025
Joint Venture Manitoba And Nunavut Develop Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Infrastructure
May 30, 2025 -
 High Rates Of Cfs Intervention Among First Nations Parents In Manitoba A 1998 2019 Analysis
May 30, 2025
High Rates Of Cfs Intervention Among First Nations Parents In Manitoba A 1998 2019 Analysis
May 30, 2025 -
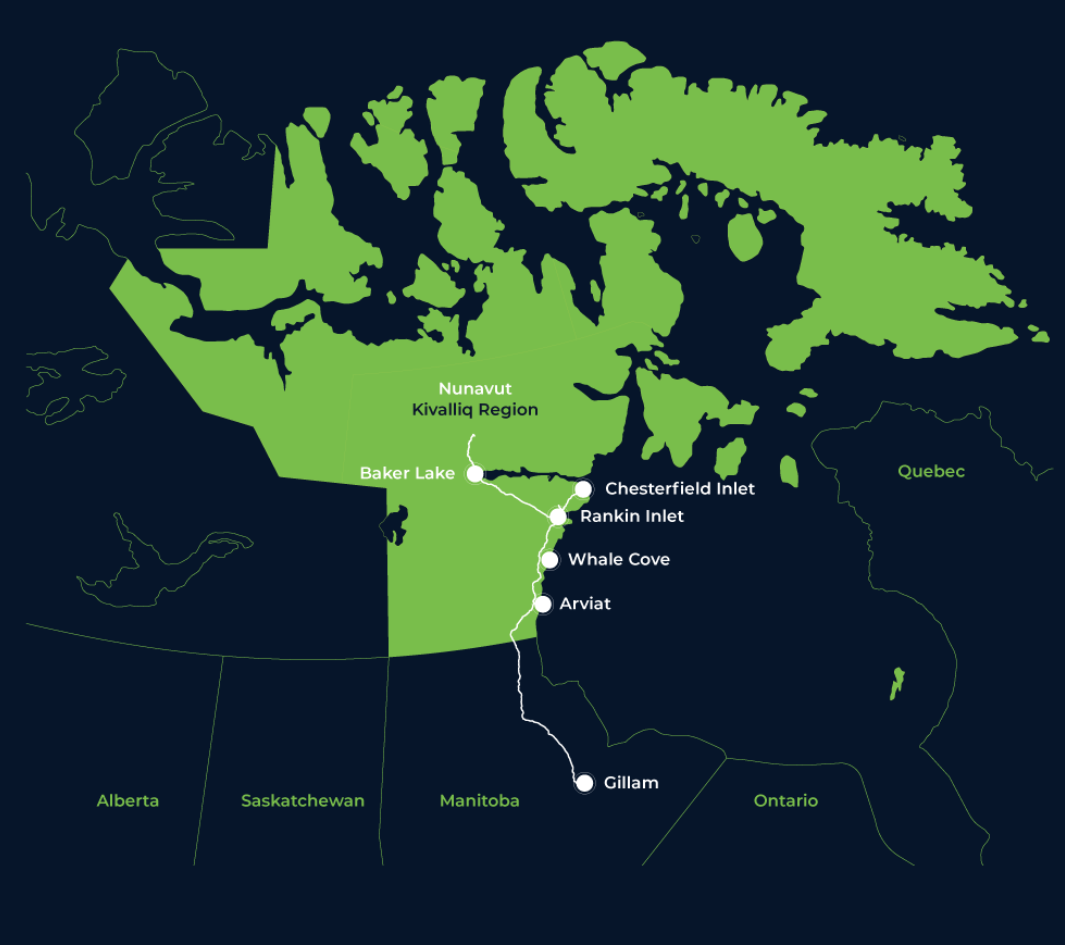 Strategic Energy Corridor Manitoba And Nunavut Collaborate On Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Project
May 30, 2025
Strategic Energy Corridor Manitoba And Nunavut Collaborate On Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Project
May 30, 2025 -
 Manitoba Child And Family Services First Nations Family Intervention Rates 1998 2019
May 30, 2025
Manitoba Child And Family Services First Nations Family Intervention Rates 1998 2019
May 30, 2025 -
 Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Link A Strategic Energy And Economic Corridor For Manitoba And Nunavut
May 30, 2025
Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Link A Strategic Energy And Economic Corridor For Manitoba And Nunavut
May 30, 2025
