2023 Sees Record Global Forest Loss Due To Increased Wildfire Activity
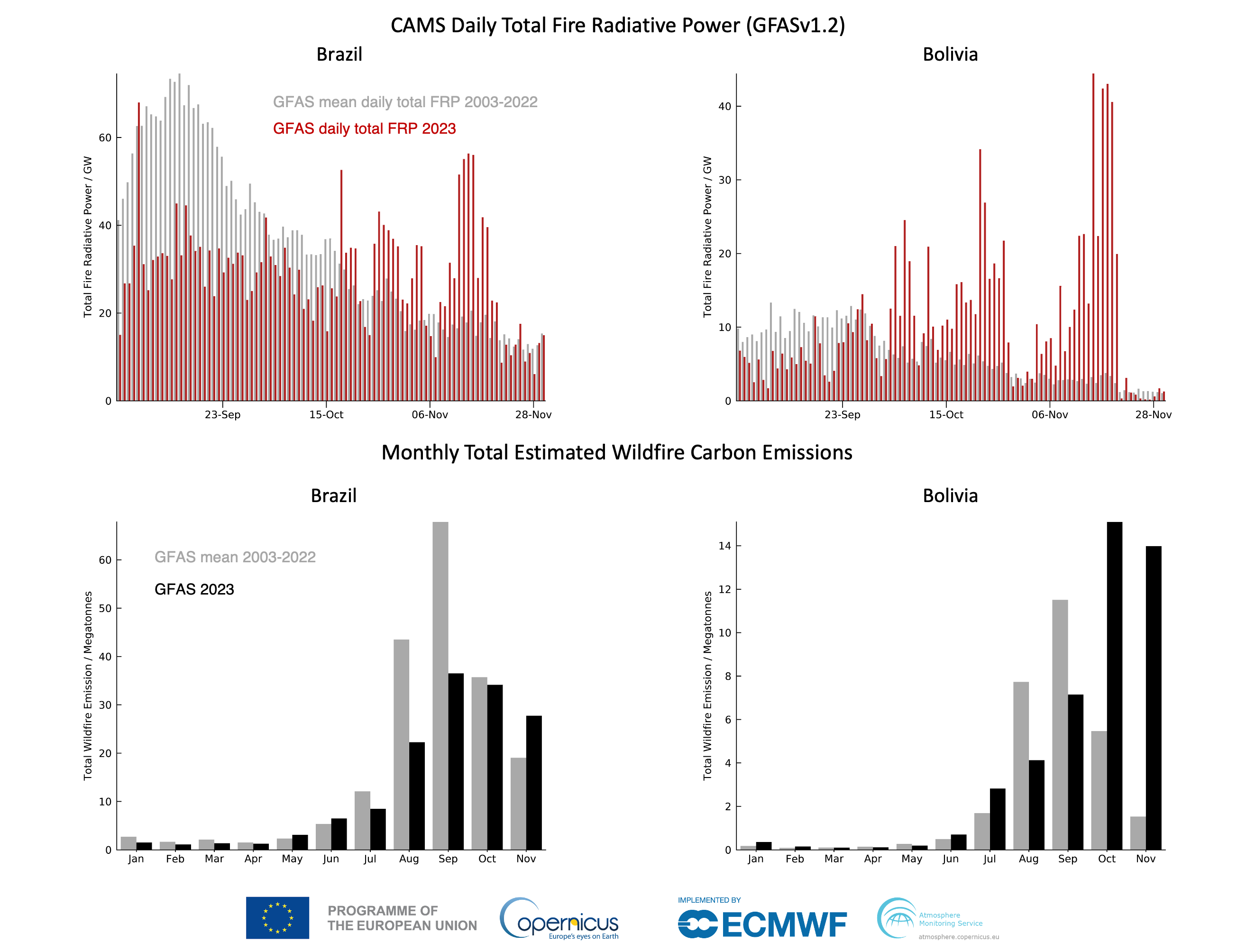
Table of Contents
The Role of Climate Change in Increased Wildfire Activity and Global Forest Loss
Climate change is undeniably a primary driver of increased wildfire activity and subsequent global forest loss. Rising temperatures and increasingly erratic weather patterns create a perfect storm for devastating blazes.
Rising Temperatures and Drier Conditions
Increased global temperatures lead to prolonged periods of drought, turning forests into tinderboxes.
- Examples of regions particularly affected: The western United States, Australia, the Amazon rainforest, and parts of Siberia experienced record-breaking heat and drought in 2023, significantly increasing wildfire risk.
- Statistics on increased average temperatures: Global average temperatures have risen by approximately 1 degree Celsius since the pre-industrial era, with some regions experiencing far greater increases. This warming trend is directly linked to more frequent and intense heatwaves.
- Links to scientific studies: Numerous peer-reviewed studies demonstrate a clear correlation between rising temperatures, drought severity, and increased wildfire activity.
Changes in Wind Patterns and Increased Lightning Strikes
Altered weather patterns, including changes in wind speed and direction, contribute to the rapid spread of wildfires. Increased lightning strikes, often associated with more intense storm systems, are another significant ignition source.
- Data on changes in wind patterns: Studies show shifts in jet stream patterns, leading to more erratic and unpredictable wind conditions, fueling the spread of wildfires.
- Correlation between lightning strikes and wildfire outbreaks: Data suggests a link between increased lightning activity and the number of wildfires initiated, particularly in dry regions.
- Examples of specific wildfire events linked to these factors: The 2023 wildfires in Canada and parts of the Mediterranean are prime examples of how shifts in wind patterns exacerbated the spread of already established fires.
The Feedback Loop: Forest Loss Exacerbates Climate Change
Deforestation creates a vicious cycle. Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Their loss reduces this capacity, accelerating climate change and increasing the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
- Explanation of carbon sequestration: Trees absorb and store significant amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis.
- Impact of lost trees on carbon dioxide levels: The destruction of forests releases stored carbon back into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
- Contribution of burning forests to greenhouse gas emissions: Wildfires release vast quantities of greenhouse gases, further exacerbating the climate crisis and creating a positive feedback loop.
Deforestation and its Contribution to Global Forest Loss
Beyond wildfires, deforestation itself is a major contributor to global forest loss. Human activities are driving the destruction of forests at an alarming rate.
Illegal Logging and Land Conversion
Illegal logging and the conversion of forests for agriculture (especially for palm oil and soy) and urban development are primary drivers of deforestation.
- Statistics on illegal logging in key regions: The Amazon rainforest, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa experience extensive illegal logging, contributing significantly to forest loss.
- Examples of deforestation driving force: The expansion of cattle ranching in the Amazon is a key example of land conversion driving deforestation.
- Mention of governmental policies and their impact (or lack thereof): Weak enforcement of environmental regulations and inadequate land-use planning contribute to the problem.
Agricultural Practices and their Role
Unsustainable agricultural practices, such as slash-and-burn agriculture, contribute to both deforestation and increased wildfire risk.
- Examples of slash-and-burn agriculture: This destructive practice clears land for farming by burning existing vegetation, often leading to uncontrolled wildfires.
- Impact of monoculture farming: Large-scale monoculture farming can deplete soil nutrients and increase vulnerability to pests and diseases, sometimes necessitating further land clearing.
- Sustainable agriculture practices as a solution: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as agroforestry and crop rotation, can reduce the pressure on forests.
Regional Impact: Examining Areas Most Affected by Global Forest Loss
The impact of global forest loss is not evenly distributed. Certain regions are disproportionately affected.
The Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, often called the "lungs of the planet," is facing an unprecedented crisis. Deforestation and wildfires are devastating its biodiversity and impacting global climate patterns.
- Statistics on Amazon deforestation: Recent years have witnessed alarming rates of deforestation in the Amazon, with significant implications for biodiversity and climate regulation.
- Specific examples of recent wildfires: Numerous large-scale wildfires have ravaged parts of the Amazon, releasing massive amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- Consequences for indigenous communities: Indigenous communities who depend on the forest for their livelihoods are severely impacted by deforestation and wildfires.
Other Key Regions
Beyond the Amazon, other regions are experiencing significant forest loss, including:
- Siberia: Vast areas of boreal forests in Siberia are vulnerable to wildfires, exacerbated by climate change.
- Australia: Australia experienced devastating bushfires in recent years, highlighting the vulnerability of its unique ecosystems.
- The Mediterranean: The Mediterranean region is facing increased wildfire risk due to climate change and human activities.
Consequences of Global Forest Loss
The consequences of record global forest loss are far-reaching and devastating.
Biodiversity Loss
Habitat destruction due to deforestation and wildfires leads to a catastrophic loss of biodiversity.
- Examples of endangered species affected: Numerous plant and animal species are driven towards extinction as their habitats are destroyed.
- The role of forests in maintaining biodiversity: Forests are vital for maintaining the complex web of life on Earth, providing habitats for countless species.
Impact on Climate Change
Forest loss accelerates climate change through the release of stored carbon and reduced carbon sequestration capacity.
- Specific data on increased CO2 emissions: Deforestation and wildfires release massive amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing significantly to global warming.
- Impact on global temperature rise: The loss of forests exacerbates the warming trend, creating a positive feedback loop.
Economic and Social Consequences
The economic and social implications of forest loss are significant, impacting livelihoods, food security, and displacing communities.
- Examples of communities reliant on forests: Many communities rely on forests for their livelihoods, including indigenous peoples and those involved in forestry and agriculture.
- Economic losses due to forest fires and deforestation: Forest fires and deforestation cause significant economic losses through damage to infrastructure, lost timber production, and reduced tourism revenue.
Conclusion
The unprecedented levels of global forest loss in 2023 underscore the urgent need for immediate and concerted action. The combined impact of climate change and deforestation is creating a devastating cycle of destruction. We must address the root causes, including mitigating climate change, combating illegal logging, and promoting sustainable land management practices. We must work together to protect existing forests, promote reforestation efforts, and reduce our carbon footprint to prevent further devastating losses and secure a healthier future. Let's fight against global forest loss, together.

Featured Posts
-
 Universals 7 Billion Theme Park A New Era In The Disney Universal Rivalry
May 23, 2025
Universals 7 Billion Theme Park A New Era In The Disney Universal Rivalry
May 23, 2025 -
 Zimbabwe Test England Announces Starting Eleven
May 23, 2025
Zimbabwe Test England Announces Starting Eleven
May 23, 2025 -
 Canadians Cut Corners On Car Security Due To Rising Living Costs
May 23, 2025
Canadians Cut Corners On Car Security Due To Rising Living Costs
May 23, 2025 -
 My Cousin Vinny Reboot Ralph Macchio On Potential Sequel And Joe Pescis Return
May 23, 2025
My Cousin Vinny Reboot Ralph Macchio On Potential Sequel And Joe Pescis Return
May 23, 2025 -
 Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Todo Lo Que Necesitas Saber
May 23, 2025
Horoscopo Semanal 11 17 Marzo 2025 Todo Lo Que Necesitas Saber
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025
Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Hilarious Reaction
May 23, 2025 -
 Joe Jonas Perfect Response To A Couples Fight Over Him
May 23, 2025
Joe Jonas Perfect Response To A Couples Fight Over Him
May 23, 2025 -
 The Jonas Brothers Drama A Couples Fight And Joes Response
May 23, 2025
The Jonas Brothers Drama A Couples Fight And Joes Response
May 23, 2025 -
 Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Reaction Is Golden
May 23, 2025
Couple Fights Over Joe Jonas His Reaction Is Golden
May 23, 2025 -
 Joe Jonas Addresses Couples Dispute His Perfect Reaction
May 23, 2025
Joe Jonas Addresses Couples Dispute His Perfect Reaction
May 23, 2025
